Speonemadus, Jeannel, 1922
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4543.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:31ABFA6E-6126-4603-B84F-4BEC7632D1E8 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5927160 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FB8C32-F803-FFAF-FF60-FB84FF4D48D1 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Speonemadus |
| status |
|
Biogeography of Speonemadus View in CoL
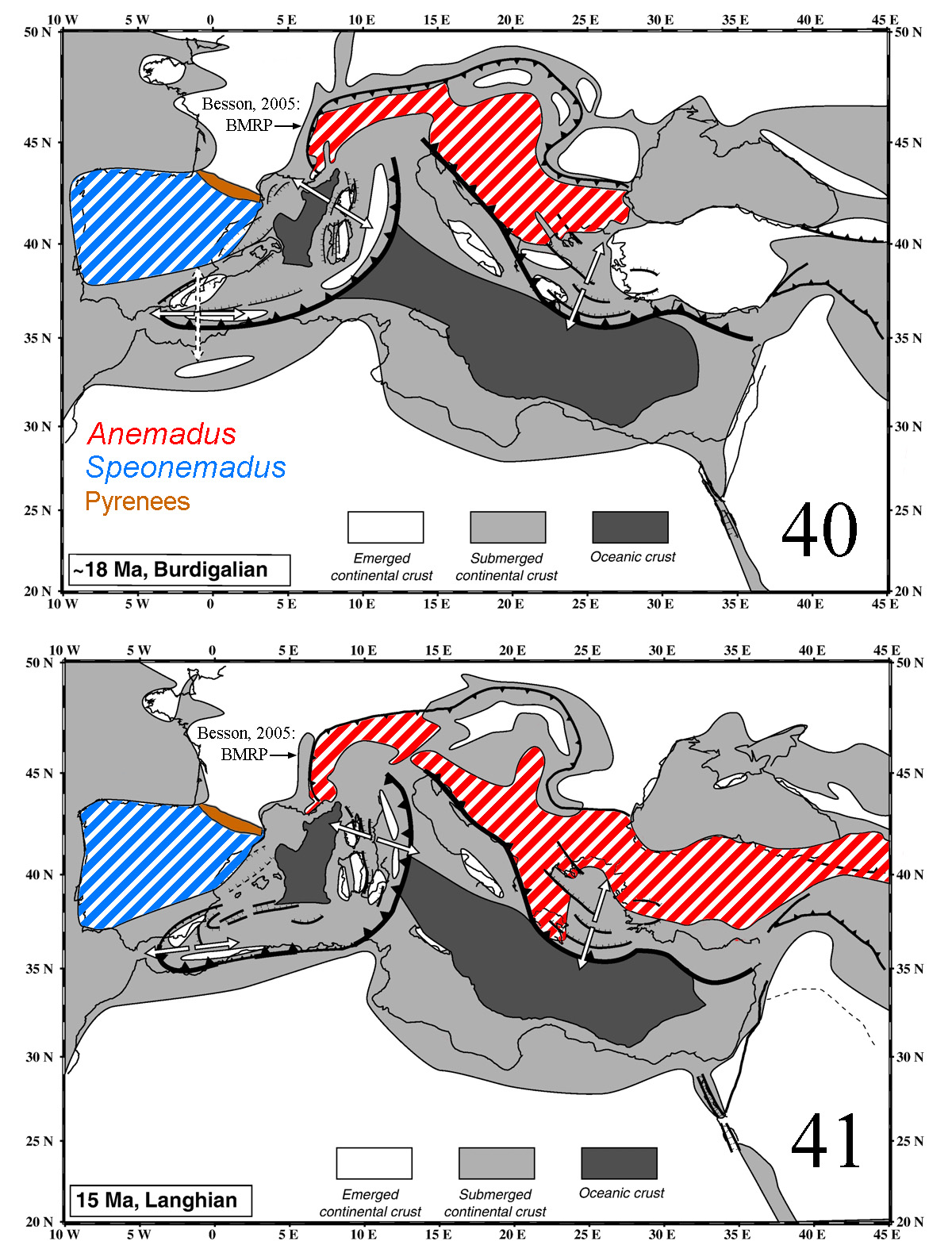
The estimated phylogeny of Speonemadus and the current distribution of the species are in agreement with the palaeogeography of the Betic-Rifean area during the Miocene ( Figs 40–43 View FIGURES 40–41 View FIGURES 42–43 ), as happens with other subterranean groups in the area (e.g. the ground beetle Trechus fulvus -group, Faille et al. 2014). The geographic origin of the genus Speonemadus cannot be unambiguously reconstructed, but considering the distribution of the presumed sister genus Anemadus (Palaearctic, mostly from Italy to the eastern Mediterranean and with species until Japan; see Perreau 2000), the origin is likely the western Palaearctic. Most Mediterranean islands are populated by species of Anemadus ( Corsica, Sardinia, Cyprus and some Greek Islands), which may have a late Messinian origin although there is no available phylogenetic data for the species.
We estimated a crown age of Speonemadus of ca. 10–11 Ma, with a split from the sampled Anemadus at ca. 15 Ma ( Figs 40–41 View FIGURES 40–41 ). This excludes the possibility of a colonisation of North Africa from Europe through the tectonic rafting of the Kabylian plates, which started to drift from the Iberian Peninsula at ca. 33 Ma, keeping some contact with the plates of the Balearic and Alboran islands until 26 Ma ( Rosenbaum et al. 2002; Schettino & Turco 2006). Assuming a northern Mediterranean (i.e. European) origin of the genus, the separation between the ancestor of Speonemadus and Anemadus could have been mediated by the isolating effect of the Pyrenean chain (which was already formed by the late Oligocene, at ca. 23 Ma, ISC 2017) or, more likely, by the opening of the Rhone- Provençal basin (the "Basin miocène rhodano-provençal", BMRP, of Besson 2005). The BMRP bordered the north side of the Alps from Marseille to Vienna ( Meulenkamp & Sissingh 2003; Besson 2005), with the stronger fluvial erosion dating from the Burdigalian ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 40–41 ), and a marine transgression inundating the region from the Langhian ( Fig. 41 View FIGURES 40–41 ). This is in agreement with the hypotheseis of Giachino & Vailati (1993) of a separation between Anemadus and Speonemadus during the late Miocene at both sides of the BMRP.
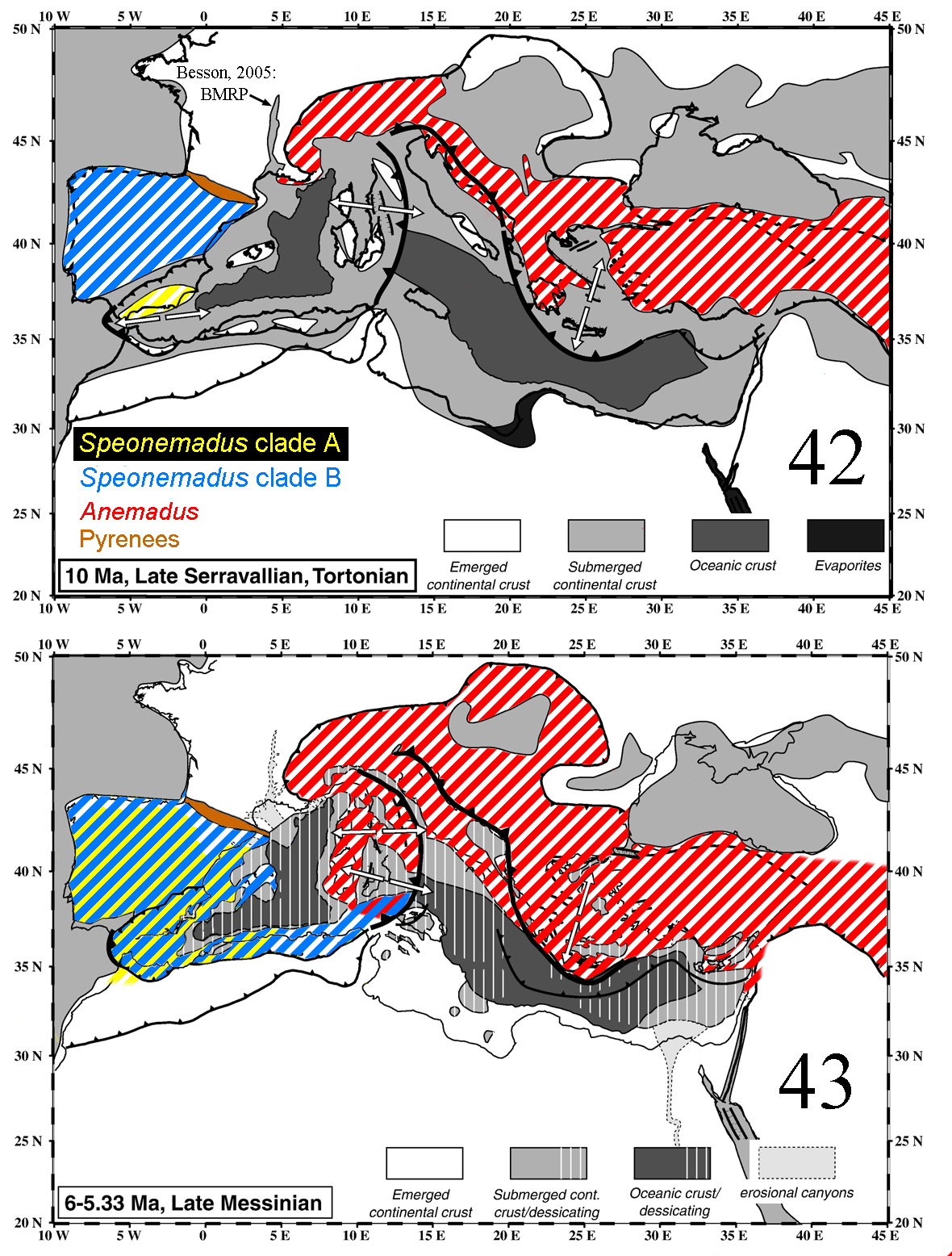
The first cladogenesis separating the two basal clades of Speonemadus (A and B) was estimated to have occurred in the Tortonian (ca. 10.5 Ma) ( Fig. 42 View FIGURES 42–43 ). Subsequently, in the early Messinian (ca. 6.5 Ma), a further split separated clades B1 and B2 ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES 42–43 ). Each of these three clades has species both on the Iberian Peninsula and in North Africa. During the Tortonian and early Messinian the isolation of the highly dynamic Betic microplates has been hypothesised to have promoted the diversification of some groups (e.g. Hydrochidae water beetles, Hidalgo- Galiana & Ribera 2011, or Mesocarabus and Trechus ground beetles, Andújar et al. 2012 and Faille et al. 2014, respectively); this could also have been the case in Speonemadus , with the isolation of three lineages (A, B1 and B2) either in Iberia, North Africa or some of the Betic-Rifean plates. During the salinity crisis of the late Messinian all these areas became united, likely allowing the expansion of the species through the Strait of Gibraltar. The reopening of the Gibraltar strait at the end of the Messinian salinity crisis 5.33 Ma ( García-Castellanos et al. 2009) isolated the Iberian from the North African populations of these three widespread ancestral Speonemadus , resulting in an almost simultaneous split into three clades: (1) clade A, the Iberian S. clathratus and the species of the S. escalerai -group vs. the North African S. brusteli sp. n. and S. maroccanus (plus most likely S. orchesioides and S. subcostatus ); (2) clade B1, the Iberian S. gracilis vs. the North African S. tenuipes ; (3) clade B2, the Iberian S. vandalitiae vs. the North African S. pulchellus .
This scenario would require the colonisation of south Iberia by S. maroccanus during the Pleistocene, and of Sicily—and possible continental Italy—during the Plio-Pleistocene. There is no information on the timing of these colonisations, they may have been related to the climatic fluctuations during the Pliocene, with first a temperature and precipitation higher than at present ( Dowsett et al. 1999; Haywood et al. 2000) and then the establishment of the Mediterranean climate at ca. 3.2 Ma ( Suc 1984), or they may have been facilitated by the descent of the sea level during the Pleistocene glaciations.
Within the Iberian Peninsula, in the late Pliocene S. clathratus may have been isolated from the ancestor of the S. escalerai -group by the Gualdalquivir valley, either due to the onset of the Mediterranean climate or by the marine transgressions and inland seas that inundated most of the valley until the Middle Pleistocene ( Torres et al. 2003). The increased seasonality and aridification, as well as the Pleistocene glaciations and the associated climatic changes, may have limited the surface movement of some species of Speonemadus , promoting the isolation of peripheral populations in the subterranean medium and giving origin to the current species of the S. escalerai - group.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Cholevinae |
|
Tribe |
Anemadini |