Capsaloides cristatus Yamaguti, 1968
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.172308 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C21EA9A2-6A92-452C-849D-DC11B657E4C4 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6255187 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FC8787-E168-FFC2-FED3-F92F9B0EFBE9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Capsaloides cristatus Yamaguti, 1968 |
| status |
|
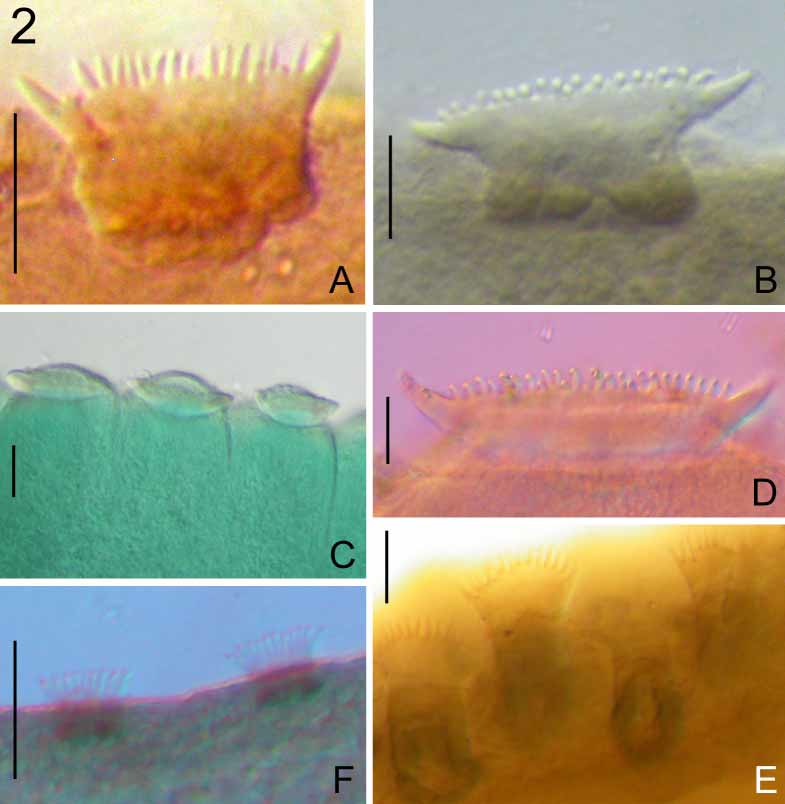
Capsaloides cristatus Yamaguti, 1968 View in CoL ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 B, 2B)
Typehost: Makaira sp. ( Istiophoridae ).
Typelocality: Hawaii, USA [Pacific Ocean].
Additional records: Tetrapterus angustirostris Tanaka, 1915 (Istiophoridae) , Hawaii, USA [Pacific Ocean] (see Yamaguti 1968); Makaira indica (Cuvier, 1832) (Istiophoridae) , Cape Moreton, off Brisbane, Queensland, Australia [Pacific Ocean] (see Speare 1994, 1999).
Site: Gills.
Specimens examined: Holotype (USNPC 63597); 1 voucher (QM G212782).
Remarks
Yamaguti (1968) distinguished C. cristatus from the closely related C. sinuatus Goto, 1894 only by the depth of the posterior notch of the body. Unfortunately we could not locate type specimens of C. sinuatus or the 5 specimens Yamaguti (1968) collected and used for his redescription. Our illustration of the haptoral accessory sclerite of the holotype of C. cristatus ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B) is different from that illustrated by Yamaguti (1968; fig. 20B). It is unclear why this is the case since Yamaguti (1968) apparently also based his drawing on the holotype. The dorsomarginal body sclerites ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 B) of C. cristatus have 20–30 cusps. The left anterior isolated group of dorsomarginal body sclerites comprises 10 sclerites each with 12–15 cusps. The right anterior isolated group of dorsomarginal body sclerites comprises 7 sclerites each with 5–7 cusps. According to previously published illustrations, the dorsomarginal body sclerites of C. sinuatus have 15 (see Goto 1894) or 12 (see Yamaguti 1968) cusps and therefore they are smaller than those of C. cristatus . However, we have found that the dorsomarginal body sclerites can differ morphologically depending where on the body they are located (see C. perugiai ). While we suspect that C. cristatus and C. sinuatus are synonymous, we are hesitant to make this decision without additional material of both species.
Speare (1994, 1999) noted the presence (with a mean intensity of 7) of C. cristatus on M. indica off Cape Moreton, Queensland, Australia. A single unmounted specimen was deposited in the QM which we mounted and examined to verify this identification. The voucher specimen was unflattened and in poor condition, but appears to correspond to the description of C. cristatus . This voucher specimen also very closely resembles the unflattened paratype of C. hoffmannae . Like the unflattened specimen of C. hoffmannae (see Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 C), the body margin of the voucher of C. cristatus appears annulated because the sinuations are very close together. This supports our suggestion that C. hoffmannae may not be a valid taxon (see the Remarks section for C. hoffmannae ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |