Rhodopsalta microdora (Hudson, 1936)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1093/zoolinnean/zlab065 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6992889 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FD87FD-FFE0-FFE2-8590-CFFC94BCB8CE |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Rhodopsalta microdora |
| status |
|
Rhodopsalta microdora View in CoL
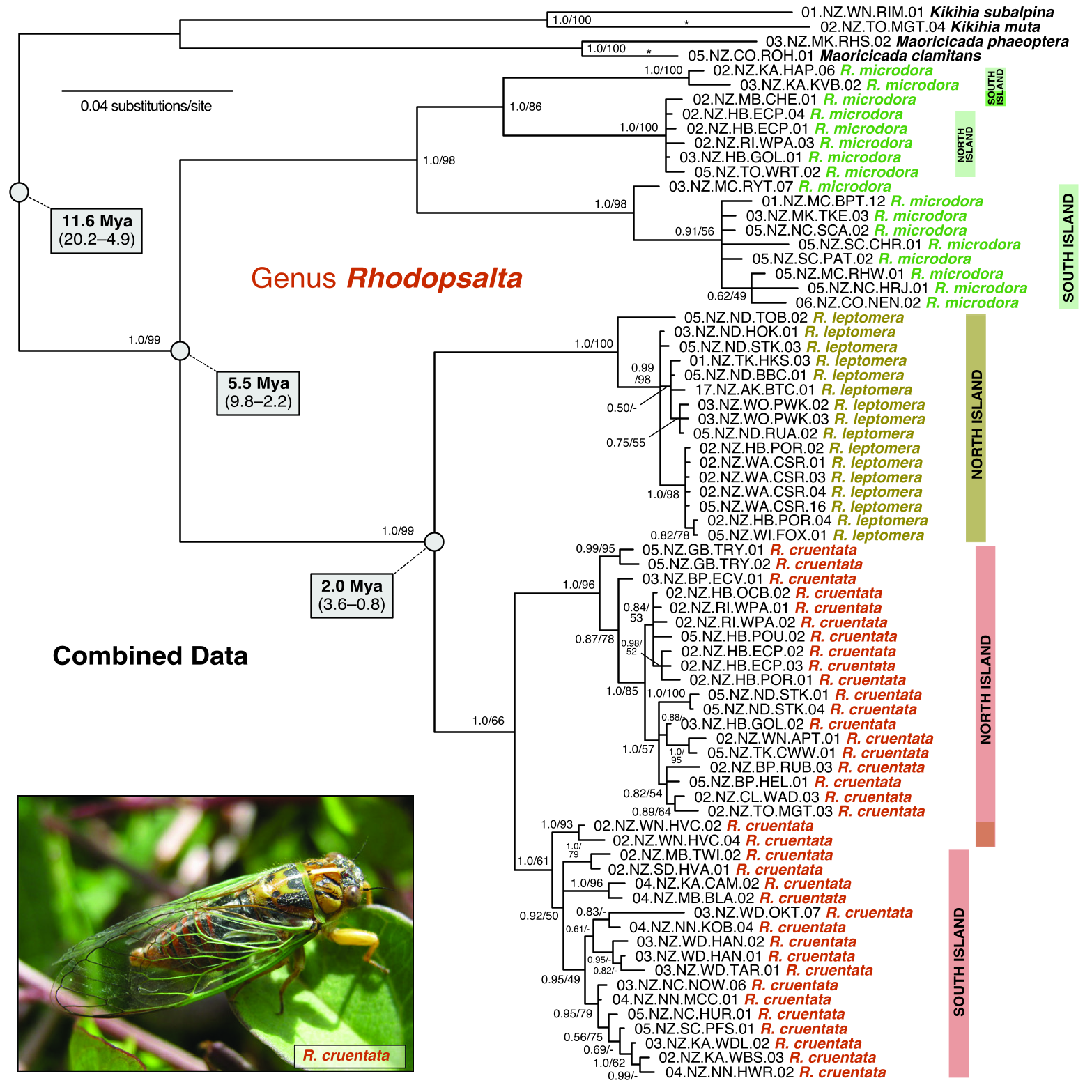
This species comprises three main clades. The southern SI clade is composed of specimens from North Canterbury (NC), Mid Canterbury (MC), South Canterbury (SC), Mackenzie region (MK) and Central Otago (CO). It is sister to an eastern clade made up of a Kaikoura group (SI) + mixed SI/NI clade composed of specimens from Marlborough (MB) (SI) and Rangitikei, Taupo and Hawkes Bay (NI) districts ( Figs 4 View Figure 4 , 5A View Figure 5 ).
GENETIC DISTANCES
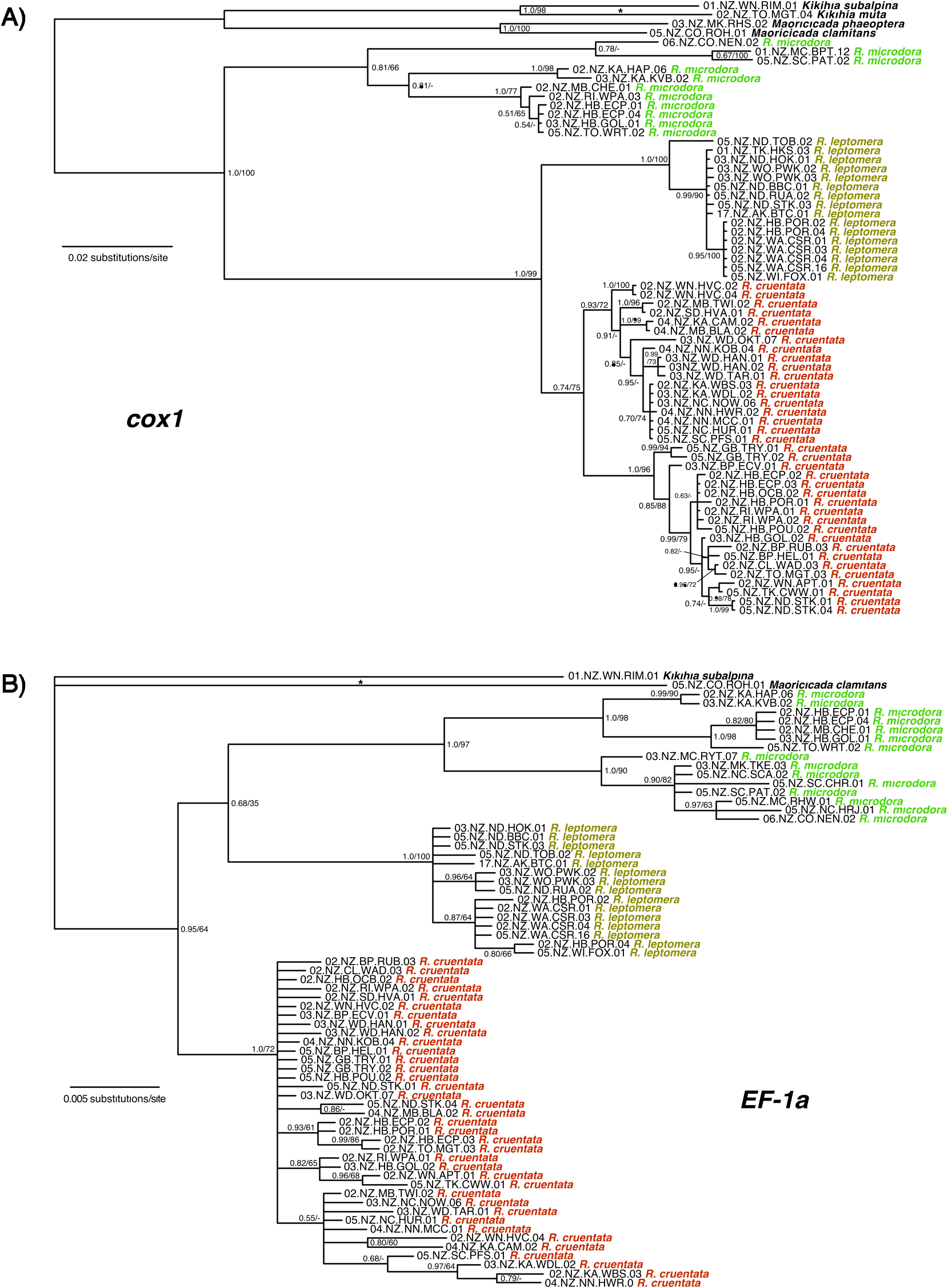
Corrected (patristic) and uncorrected genetic distances from the cox1 locus are presented in the Supporting Information (Table S4). Average uncorrected distances between the three species groups are as follows: Rhodopsalta cruentata – R. leptomera , 0.031; R. cruentata – R. microdora , 0.047; and R. microdora – R. leptomera , 0.047. Average uncorrected intraspecific distances were near zero among populations of eastern NI R. leptomera and largest among populations of SI R. microdora (≤ 0.040). As a whole, R. microdora had the greatest intraspecific average distance (0.019) and R. leptomera the least (0.003) (Supporting Information, Table S5).
MOLECULAR CLOCK DATING
The *BEAST multispecies coalescent analysis estimated that Rhodopsalta diverged from its sister genera, Maoricicada and Kikihia , between ~5 and 20 Mya (mean 11.6 Mya; see interspecific divergence dates plotted in Fig. 4 View Figure 4 ). The wide confidence interval reflects the uncertainty encoded in the cox1 molecular clock prior. The earliest split in the Rhodopsalta clade is the split between R. microdora and the ancestor of R. cruentata and R. leptomera , with a mean estimate of 5.5 Mya ( Fig. 4 View Figure 4 ). Rhodopsalta leptomera diverged from R. cruentata between 0.8 and 3.6 Mya (mean 2.0 Mya).
Although *BEAST cannot be used to estimate dates within assumed populations (species), we present the dated mtDNA gene tree from this analysis ( Fig.7 View Figure 7 ), which can be used to obtain approximate divergence times for geographically coherent intraspecific clades that might correspond to diverging, isolated populations (keeping in mind that this violates the *BEAST model assumptions, as discussed later in this paper). Note that mtDNA clade divergence dates necessarily overestimate any corresponding population splits to an unknown degree, which adds to the uncertainty ( Edwards & Beerli, 2000). The three deepest cox1 subclades within R. microdora diverged during the Pliocene to early Pleistocene ( Fig. 7 View Figure 7 ). The mean estimated divergence date for the split of the central-eastern SI clade from the ancestor of the Kaikoura and Hawkes Bay clades is 2.8 Mya, and the mean estimated date for the Kaikoura/ Hawkes Bay split is 2 Mya, about the time R. leptomera split from R. cruentata . North Island R. cruentata split from SI R. cruentata between 0.5 and 2.5 Mya (mean 0.9 Mya). These date estimates involve additional uncertainty, which is not reflected in the wide confidence intervals, owing to choice of priors and potential violations of model assumptions (see Discussion).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |