Saigona robusta, Liang, Ai-Ping & Song, Zhi-Shun, 2006
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.174257 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:085A9FE9-6F0C-4E8B-A141-5416DF5B2C06 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6256180 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FE879E-C906-1665-FE88-FCE0FE3CB079 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Saigona robusta |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Saigona robusta View in CoL sp. nov.
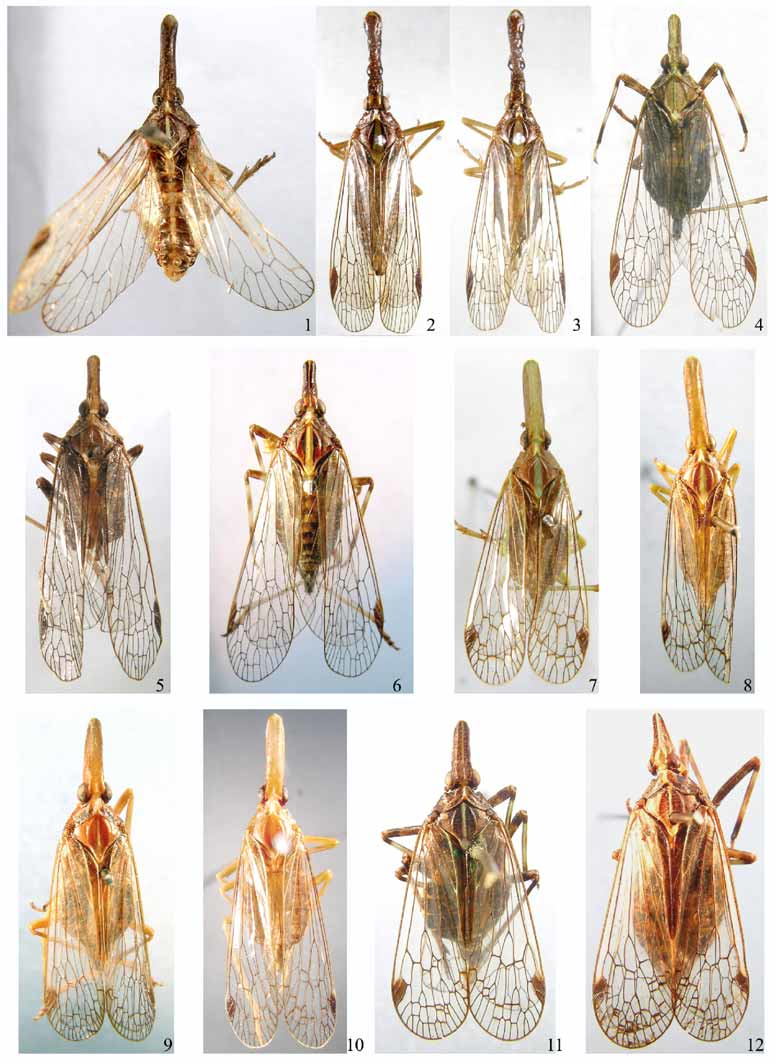
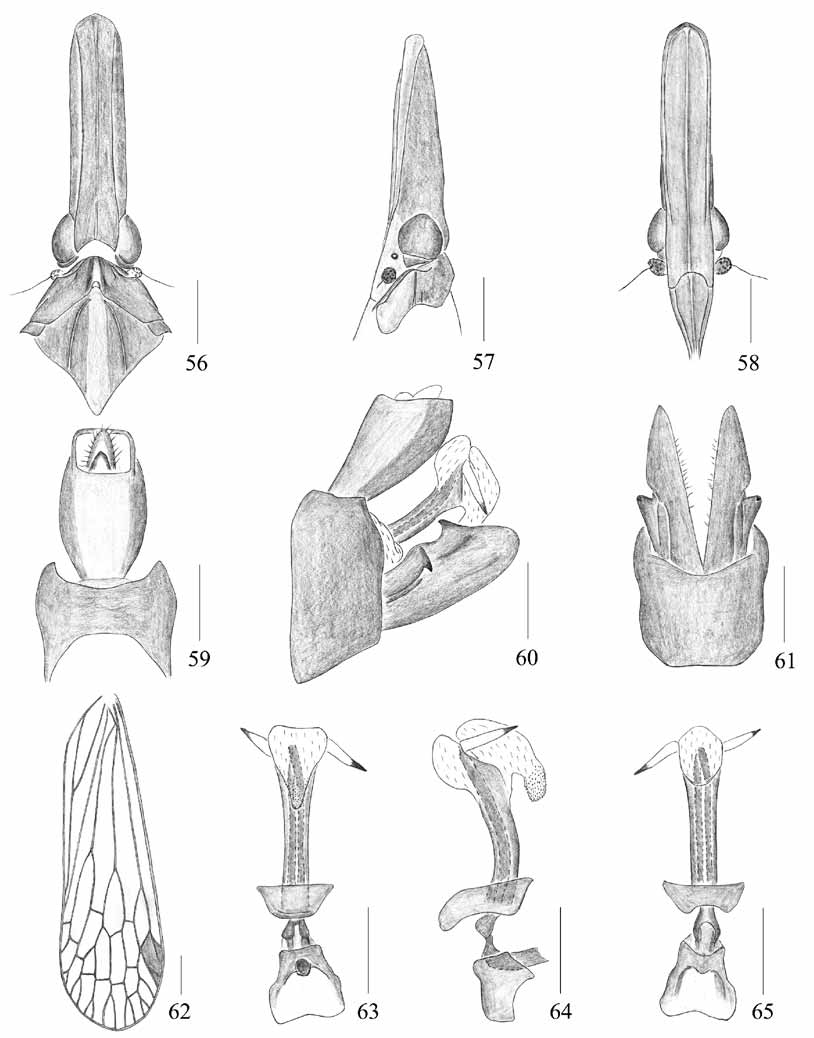
( Figs. 7, 8 View FIGURES 1 – 12 , 56–65 View FIGURES 56 – 65 )
Description
ɗ, BL: 14.7 mm; HL: 4.0 mm; HW: 1.4 mm; FWL: 9.2 mm. Ψ, BL: 14.8 mm; HL: 4.3 mm; HW: 1.5 mm; FWL: 10.0 mm.
General color brown, marked with fuscous and ochraceous. Vertex and most part of genae brown, the areas surrounding ocellus and antenna beneath eye yellowish or yellowish green. Frons, postclypeus, anteclypeus, and rostrum yellowish or yellowish green. Pronotum ochraceous, suffused with fuscous; median carina pale green; lateral, ventrally curved areas yellowish. Mesonotum ochraceous, with broad, pale green stripe along median longitudinal carina. Thorax and abdomen ventrally yellowish or yellowish green; abdomen dorsally dark brown, with yellowish brown spots; pygofer and parameres fuscous, suffused with pale brown; anal tube yellowish dorsally. Legs yellowish brown, marked with ochraceous.
Head ( Figs. 7, 8 View FIGURES 1 – 12 , 56–58 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ) long, much longer than pronotum and mesonotum combined. Vertex ( Figs. 7, 8 View FIGURES 1 – 12 , 56 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ) with cephalic process long, distinctly robust; median carina very faint, only conspicuous at apex and base; lateral carinate margins nearly parallel. Frons ( Fig. 58 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ) with lateral carinae reaching to eyes, not to frontoclypeal suture.
Mesonotum ( Figs. 7, 8 View FIGURES 1 – 12 , 56 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ) with lateral carinae distinct, median carina very faint. Fore wing venation as in Fig. 62 View FIGURES 56 – 65 .
Male genitalia with pygofer ( Figs. 59–61 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ) large and broad in lateral view ( Fig. 60 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ), posterior margin nearly straight, abruptly curved anteriorly near 1/6 apex to accommodate anal tube, length ratio of upper margin to lower margin about 1: 2.2. Anal tube ( Figs. 59, 60 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ) large, nearly triangular in lateral view ( Fig. 60 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ), large, long, oval in dorsal view ( Fig. 59 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ), ratio of length to width at middle about 1.7: 1. Anal style ( Figs. 59, 60 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ) short, broad. Parameres ( Figs. 60, 61 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ) relatively large, broad in lateral aspect ( Fig. 60 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ), apex sharply rounded, protruded posteriorly. Aedeagus ( Figs. 63–65 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ) with phallobasal conjunctival processes produced dorsally and ventrally, respectively; phallobase narrow and long, curved dorsally; apical, dorsal, membranous lobe small, semi-globose in lateral view ( Fig. 64 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ), without spines; apical, ventral, membranous lobe converging towards apex and triangular in ventral view ( Fig. 63 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ), directed anteroventrally in lateral view ( Fig. 60 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ), covered with numerous fine spines at apex.
Material examined
Holotype ɗ, China, Hubei, Fang County, Qiaoshang, 16.vi.1977, Q. Mu (NU). Paratype, China, Hubei: 1Ψ, Mt. Shennongjia, Yangri, 500–600 m, 2.vi.1981, Y. H. Han ( IZCAS).
Remarks
This species can be distinguished from other known species in Saigona by its distinctly elongate and robust cephalic process ( Figs. 7, 8 View FIGURES 1 – 12 , 56–58 View FIGURES 56 – 65 ).
Distribution
China (Hubei).
| IZCAS |
Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Fulgoroidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |