Telostholus kubani Loktionov, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4966.2.9 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:FC9B56B9-4346-4046-8E72-47A11BF838AB |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4783919 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FF87B9-FF85-9B27-2FA0-FD30B53EFAC2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Telostholus kubani Loktionov |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Telostholus kubani Loktionov , sp. nov.
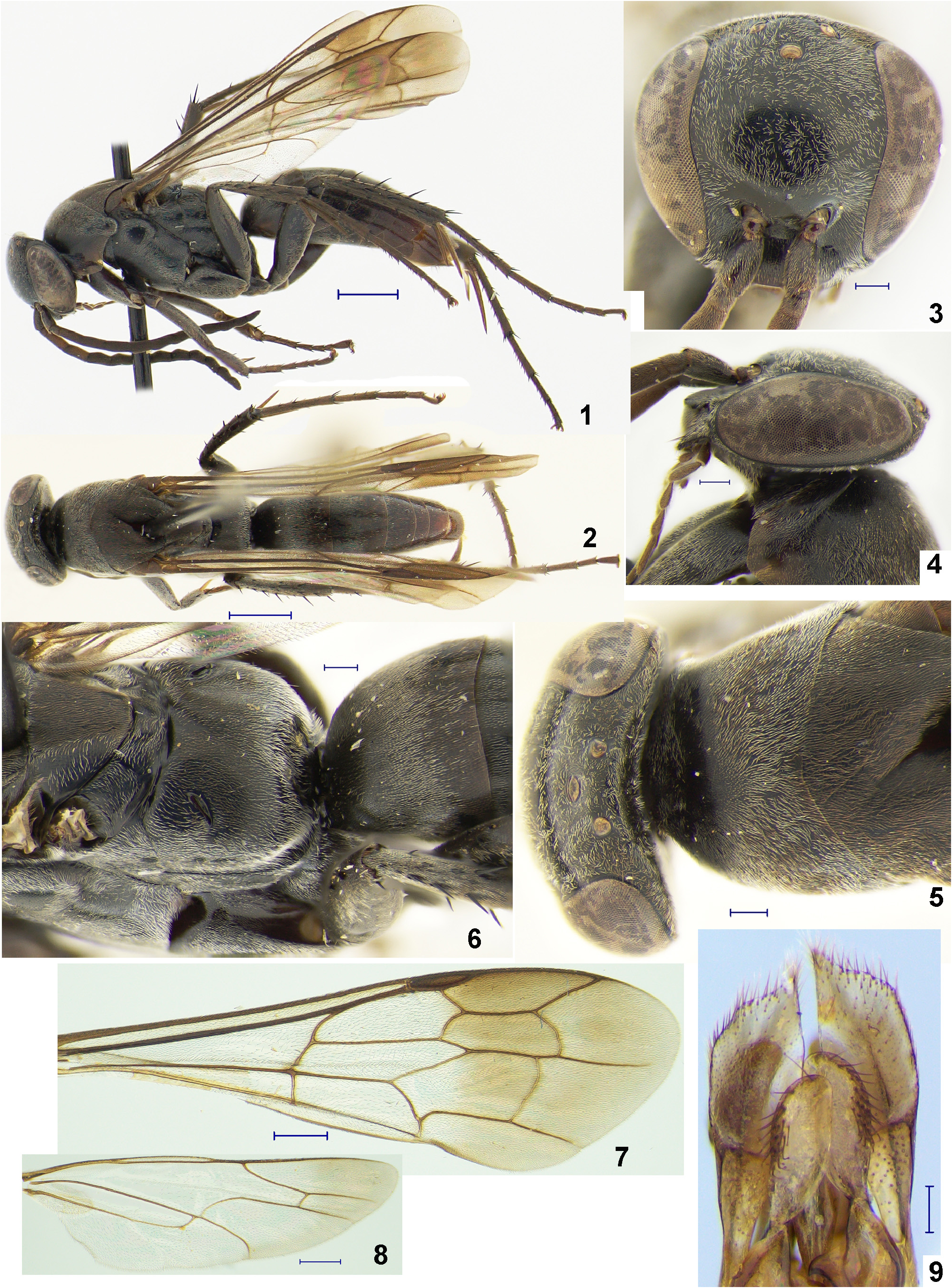
( Figs 1–9 View FIGURES 1–9 , 26–28 View FIGURES 26–34 )
Material examined. Holotype, ♂ “Lao-N, Phongsaly pr., Phongsaly, ~ 1500 m, 21°41’-2’ N, 102°06’-8’ E, Kubáň leg., V-VI.2003” [ Laos: Phongsaly Prov.] [OLL] . Paratypes: 3 ♂ with same label as holotype; 3 ♂ “Lao-N, Phong- saly prov., 21°41-2’ N, 102°06-8’ E, 28.v.-20.vi.2003, Phongsaly env., ~ 1500 m, Vít Kubáň leg.” [ Laos: Phongsaly Prov.] [OLL] .
Diagnosis. Male. The male of this new species can be distinguished from those of other congeners by the following combination of characters: (1) the fore wing with brown apical portion ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 1–9 ); (2) POD: OOD = 1.6–2.0; (3) the paramere broad, paddle-shaped ( Figs 9 View FIGURES 1–9 , 26 View FIGURES 26–34 ); (4) the volsella somewhat narrowed, elongated, its ventral face along outer and apical margin with bristles ( Figs 9 View FIGURES 1–9 , 26 View FIGURES 26–34 ); (5) the hypopygium in ventral view slightly narrowing toward apex, all its ventral face with erect setae, its lateral margin in basal portion without setae ( Fig. 28 View FIGURES 26–34 ). Female. Unknown.
Description. MALE. Length: body 5.7–7.5 mm; forewing 5.2–7.1 mm. Head width 1.1–1.13 times its height; MID 0.6–0.65 times head width in frontal view ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1–9 ). Ocelli large, hardly raised; ocellar triangle right- or slightly obtuse-angled; POD: OOD = 1.6–2.0 ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1–9 ). Head in frontal view with vertex slightly roundly produced above dorsal eye margin ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1–9 ). Posterior margin of vertex in dorsal view slightly concave ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1–9 ). Head in lateral view with frons convex ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–9 ). Temple in dorsal view slightly developed ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1–9 ). Gena in profile very narrow ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–9 ). Malar space short ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1–9 ). Clypeus barely convex, its width 2.2–2.4 times its height, and 0.75–0.85 times LID; anterior margin straight; anterolateral corner rounded. Mandible slender, with small subapical tooth. Labrum well exposed, its anterior margin broadly rounded. Maxillary palps 2–5 about same length, palp 6 slightly longer than others. Flagellum somewhat stout; scape normal shaped; F3–F10 crenulated ventrally ( Fig. 1 View FIGURES 1–9 ); ratio of scape, pedi- cel and F1–11 length (on ventral side; in holotype) 17: 6: 17: 17: 17: 16: 15: 13: 13: 13: 12: 10: 12; scape length 0.39–0.45 times UID; F1 length 2.2–2.4 times its maximum width (in dorsal view), and 0.35–0.45 times UID; apical flagellomere pointed apically.
Mesosoma. Pronotum length in dorsal view 0.47–0.5 times its maximum width; anterior face not differentiated from dorsum; posterior margin rounded and sometimes hardly subangulate medially ( Fig. 5 View FIGURES 1–9 ). Dorsum of mesos- cutum hardly convex. Dorsum of mesoscutellum and metanotum noticeably convex. Metapostnotum depressed, barely emarginated postero-medially, its length 0.1–0.16 times metanotum length medially. Propodeum length in dorsal view 0.55–0.65 times its maximum width; dorsum in lateral view weakly convex; posterior face somewhat differentiated from dorsum ( Fig. 6 View FIGURES 1–9 ).
Legs. Profemur without spines. Protibia: short spines on inner lateral face, 1–2 long spines ventrally, and few different-length spines apically. Protarsomere 1 with three longitudinal rows of short spines ventrally. Protarsomeres 2 and 3 with few very short spines ventrally. Protarsomeres 4 and 5 without spines ventrally. Protarsomere 1 length 0.95–1.0 times length of protarsomere 2–4 combined. Protarsomere 5 in dorsal view symmetrical, its length 2.0–2.17 times its maximum width. Meso- and metafemur with few short spines dorso-apically. Meso- and metatibia with scattered long and shorter spines. Metatibia longer spur length 0.82–0.9 times metatarsomere 1 length. Meso- and metatarsomere 1 with scattered spines which twice shorter than longest one on mesotibia. Meso- and metatarsomeres 2–4 with short spines ventrally. Meso- and metatarsomere 5 without spines ventrally. Tarsal claws of all legs symmetrical and bifid, inner tooth long, broad, and obliquely truncated apically.
Wings. Fore wing ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 1–9 ) translucent, with brownish apical portion. Pterostigma brown, its length 5.2–6.5 times its height (on inner distance), and 1.75–1.9 times Rs 2. Second submarginal cell length 2.8–3.2 times its maximum height, narrowed on vein Rs by 0.55–0.6 times its own length on vein M, receiving crossvein 1m-cu at basal 0.25– 0.32 and receiving crossvein 2m-cu at basal 0.82–0.85. Crossvein 3rs-m arched. Crossvein cu-a straight, originating at or just beyond separation of vein M+CuA. Vein M not touching wing margin. Hind wing ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 1–9 ) translucent, with slightly brownish apical portion; crossvein cu-a evenly arched and hardly anterofurcal.
Metasoma in dorsal view lanceolate, slightly narrower than mesosoma. Genitalia ( Figs 9 View FIGURES 1–9 , 26, 27 View FIGURES 26–34 ); paramere long, paddle-shaped, broadened in apical half, its apex in inner corner more or less pointed (sometimes rounded), its outer margin in apical portion with short bristles; apical part of volsella somewhat narrowed, elongated, its ventral face along outer and apical margin with long erect slightly curved bristles ending at top with small ball; parapenial lobe in upper half somewhat crescent-shaped, with narrowing apex. Hypopygium ( Fig. 28 View FIGURES 26–34 ) in ventral view slightly narrowing toward apex, its apex with straight apical margin or sometimes rounded; all ventral face with thin erect setae; lateral margin in basal portion without setae. S6 deeply roundly emarginate medially; emargination gradually narrowing toward its base.
Sculpture. Head, meso- and metasoma matte, except frons somewhat polished, mandible apically polished. Body with inconspicuous microsculpture. Frons finely and densely punctate, median line slightly depressed. Metapostnotum with indistinct transverse striae laterally. Dorsum of propodeum gently densely punctate. Antenna matte. Legs matte, except metafemur inner surface polished.
Colour and pubescence. Body black ( Figs 1, 2 View FIGURES 1–9 ). Antenna black, sometimes F1 and F2 brownish ventrally. Apical half of mandible dark brown. Claws dark brown. Body without setae except following: vertex with few different length erect pale setae; propodeum postero-laterally sometimes with few short gray erect setae; mandible with few thick brown setae; S2–S5 with scattered pale erect setae. Body with sparse gray pubescence, most intensive on propodeum postero-laterally.
FEMALE. Unknown.
Distribution. Laos (Phongsaly Prov.).
Etymology. The new species is named in honor Vítězslav Kubáň (National Museum, Prague, Czech Republic), who, among other things, is an excellent collector of insects including spider wasps.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |