Lygephila procax
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.184735 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6229096 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/03FF87F8-FFAB-2D38-338F-2A84CD621E15 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Lygephila procax |
| status |
|
Lygephila procax (Hubner, [1813])
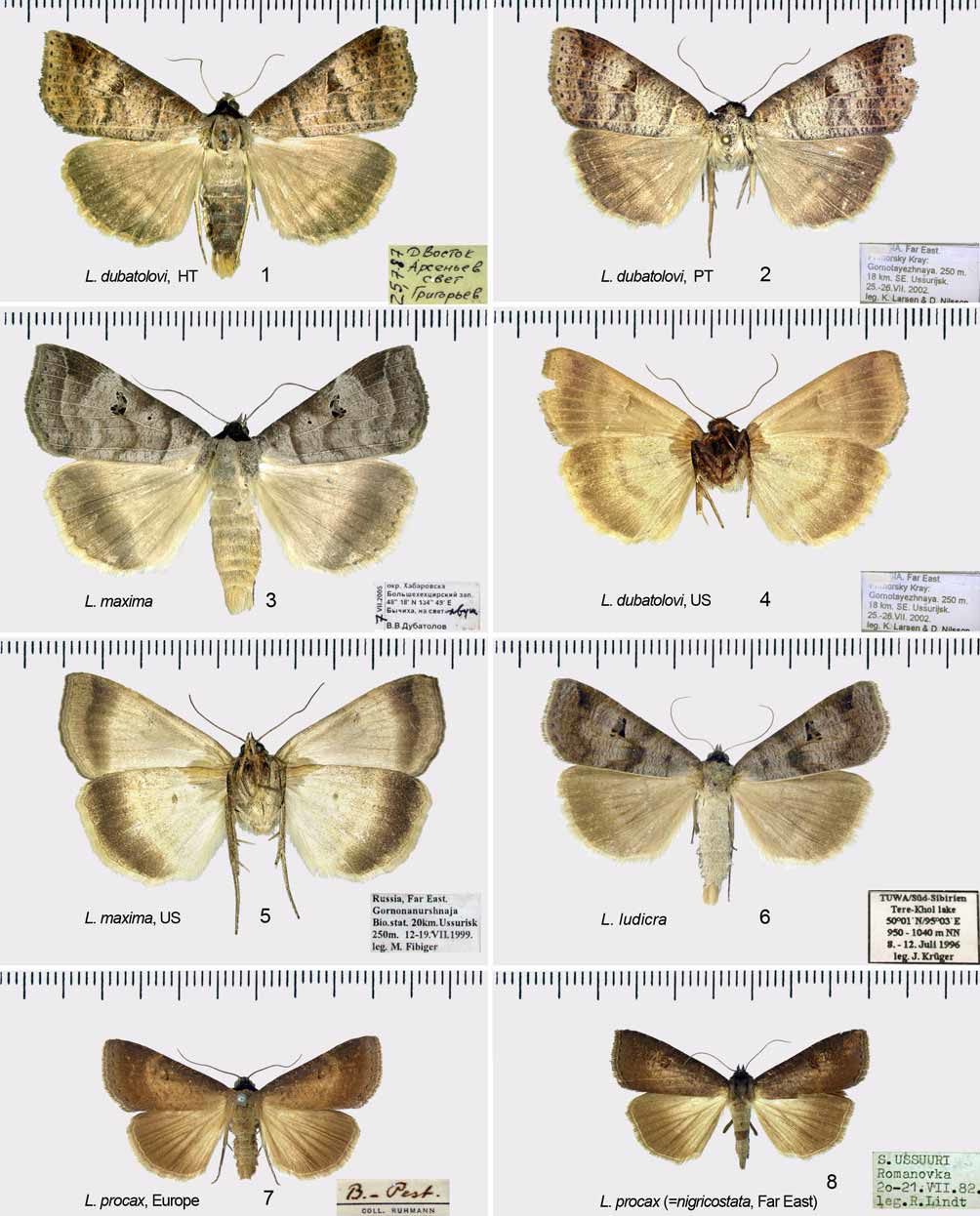
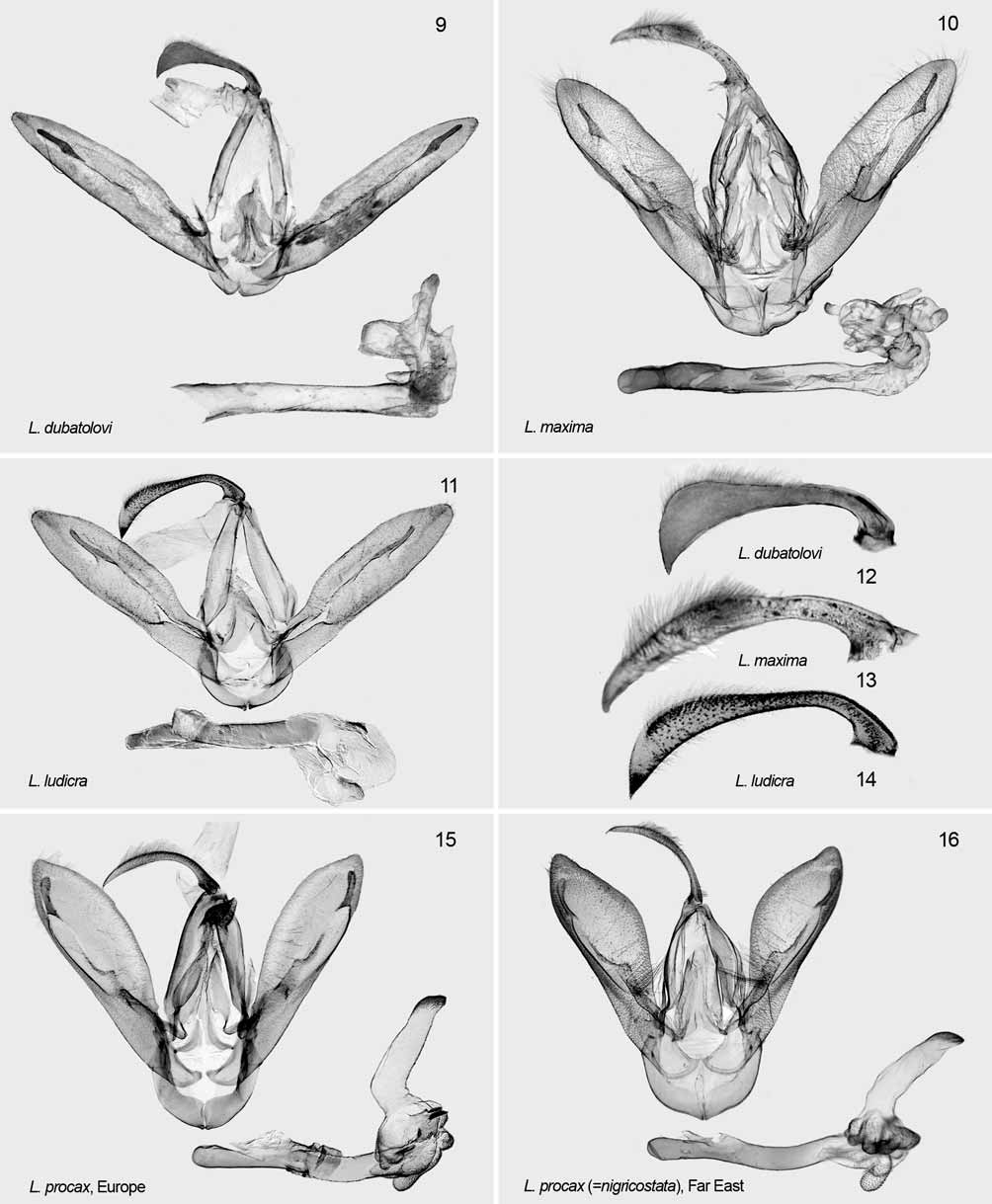
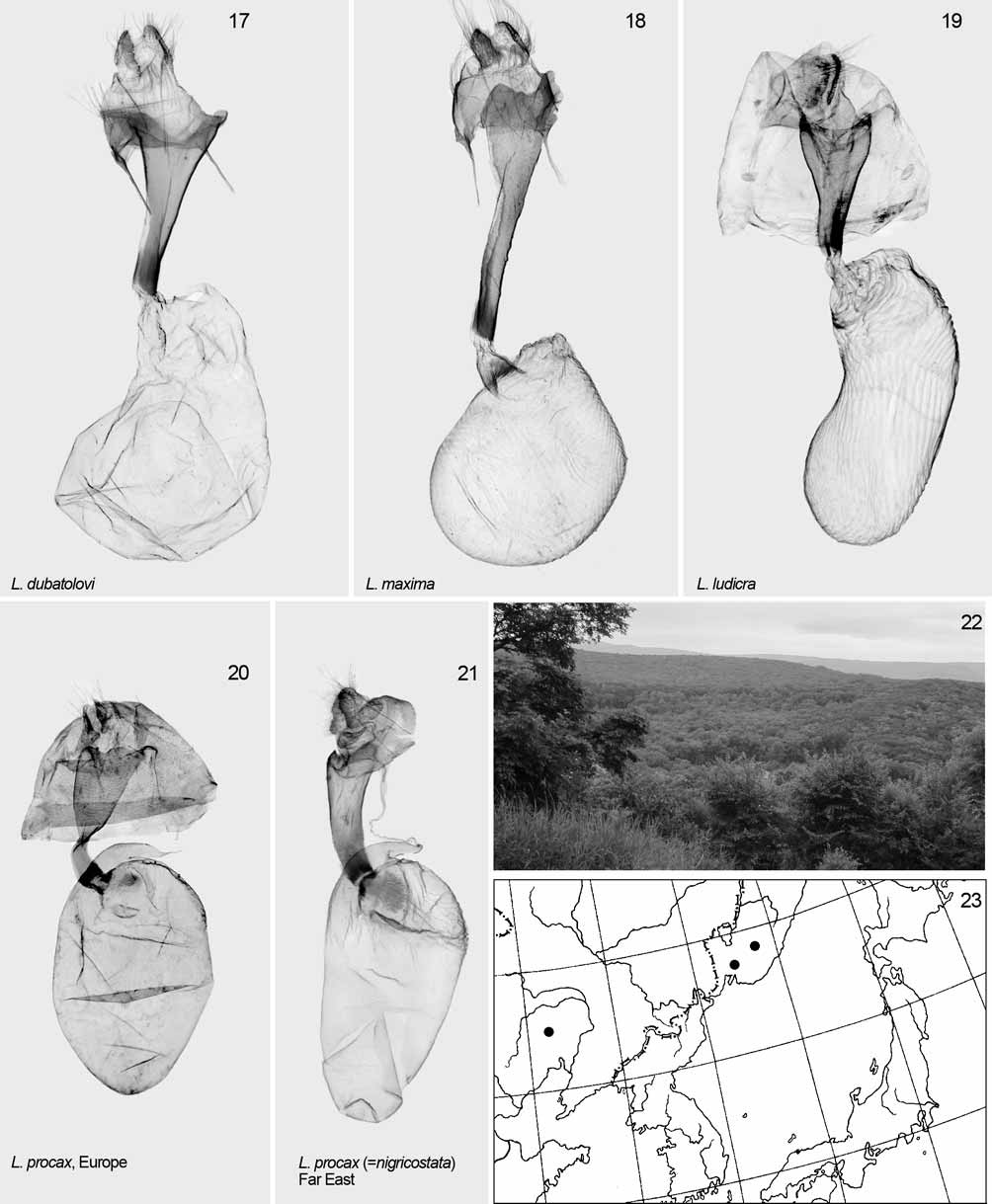
( Figs. 7, 8 View FIGURES 1 – 8 , 15, 16 View FIGURES 9 – 16 , 20, 21 View FIGURES 17 – 23 )
Noctua procax Hübner , [ 1809–1813], Sammlung Europäischer Schmetterlinge 4: Pl. 109: 510. Type locality: Europe. Asticta proclivis Hübner , [1823]), Verzeichniss bekannter Schmettelinge: 266. Type locality: Europe. Ophiusa limosa Treitschke, 1826 , Die Schmeterlinge von Europa 5(3): 298. Type locality: Hungary, vicinity of Budapest,
coll. HNHM, Budapest.
Toxocampa limosa var. nigricostata Graeser, 1890 , new synonymy. Berliner Entomologische Zeitschrift 35: 80. Type locality: Russia: Ussuri [Primorye territory]), Sidemi [Bezverkhovo], coll. MNHU, Berlin.
Taxonomy. The taxon described as Toxocampa limosa var. nigricostata Graeser (1890) has been treated by authors as a full species, Lygephila nigricostata (Staudinger & Rebel 1902; Warren 1914; Draudt 1950; Sygi & Inoue 1958; Sugi 1982; 1989; Chen, 1982; Chen et al. 1991; Poole 1989; Hacker 1990; Kononenko 1990, 2005; Kononenko et al. 1998; Sviridov 2003; Goater et al. 2003; Kononenko & Han 2007). We examined male and female genitalic preparations from topotypical material of L. nigricostata and compared these to the European Lygephila procax (see Figs. 15, 16 View FIGURES 9 – 16 , 20, 21 View FIGURES 17 – 23 ). The two Lygephila are similar both in wing pattern as well as genitalia, and we find no consistent differences, and therefore relegate nigricostata herein to the synonymy of procax . 4
Biology. The species ccurs in steppe and meadows, scattered deciduous forests, bushes, forest meadows, hillsides. Bivoltine in the southern part of it range, in south Europe three broods, in the Far East two broods. The moth in flight in end IV–VI, and again in VII–VIII to early IX. Larvae feed on Fabaceae : Vicia , Coronilla , Colutea , Lathyrus . Overwinters as pupa.
Distribution. The geographic range of Lygephila procax is trans-Paleractic: Central and southern Europe, Turkey, Transcaucasia, Kazakhstan, Central Asia (Turkmenia, Uzbekistan), Iran, North India, China, southern Siberia (Transbaikalia), south of Russian Far East (Amur region, Khabarovsk and Primorye territory, south Sakhalin, South Kuriles), Korean peninsula and Japan.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Lygephila procax
| Fibiger, Michael, Kononenko, Vladimir S. & Nilsson, Danny 2008 |
var. nigricostata
| Graeser 1890 |