Homogryllacris parcibrevipenna, Liu & Lu & Bian, 2021
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4985.4.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:AE0C59C6-5C59-4D77-9B60-008FDF6027D0 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5648080 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/081E87EA-876C-FFE8-FF7E-FE78A782F9FC |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Homogryllacris parcibrevipenna |
| status |
sp. nov. |
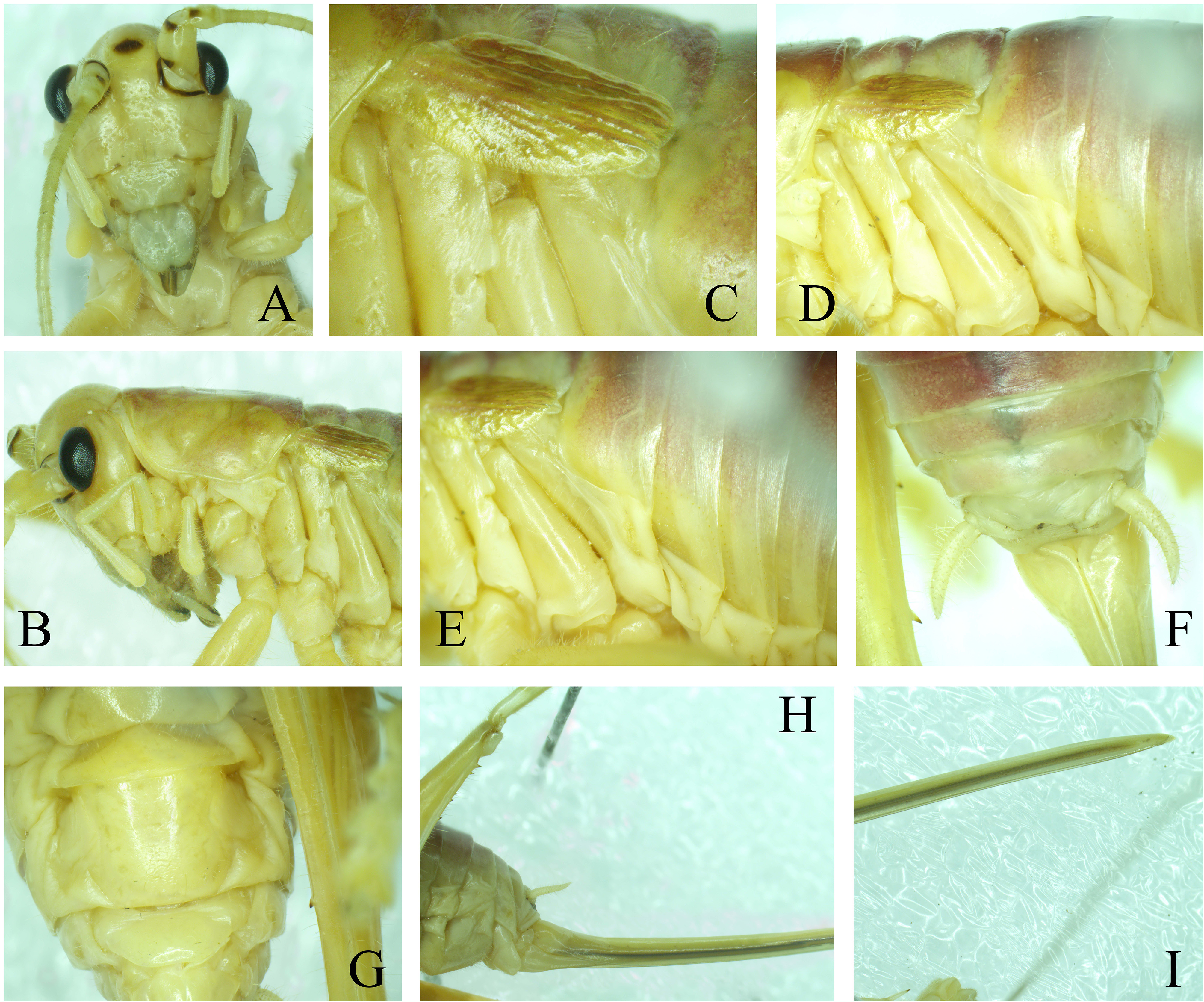
Homogryllacris parcibrevipenna sp. nov. Chinese name: 异短Oi同ḋü ( Figures 1–3 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 )
Diagnosis. The species is distinctive in the macropterous tegmina of the male and the absence of styli on the male subgenital plate.
Description. Small, micropterous. Face narrow ovoid; occiput nearly smooth with scattered impressed dots ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 ). Fastigium verticis wider than scape. Eyes ovoid; ocelli indistinct. Scape slightly longer than eyes, pedicel about two thirds the length of scape ( Fig. 1A View FIGURE 1 ). Apical segment of maxillary palpi slightly longer than subapical one, apices slightly inflated. Anterior margin of pronotum projected in the middle, posterior margin truncate ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ), lateral lobes longer than high, ventral margin undulating, humeral sinus absent ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ).
Fore coxae with 1 small spine; fore and middle femora unarmed on ventral surface, tibiae with 4 pairs of ventral spines which the apical one spine obviously smaller than others, apices with 1 pair of spurs on ventral margins. Middle tibiae with 1 dorsal spine on internal margin. Hind femora with 1–3 internal and 3–6 external spines on ventral margins; tibiae with 6 internal and 5–6 external spines on dorsal margins, apices with 3 pairs of apical spurs, the dorsal internal spurs much larger than the external ones.
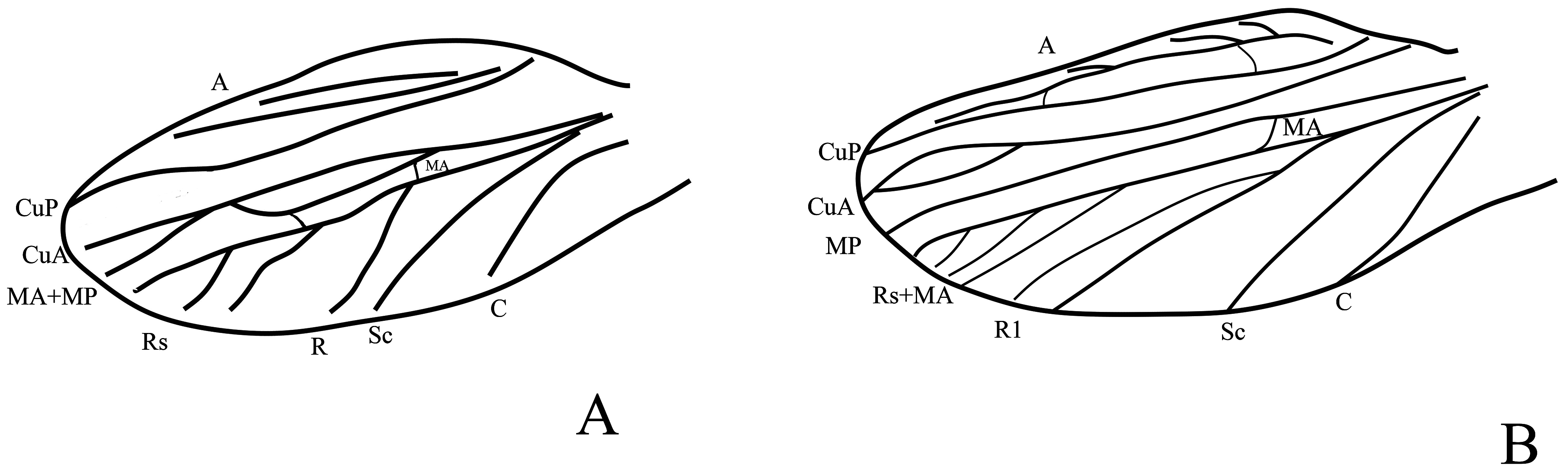
Tegmina reaching the posterior margin of metasternum ( Fig. 1D View FIGURE 1 ). Left tegmen ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ): radius with two branches, RS forked near tip. M+CuA veins fused before the basal third length, in third area M and CuA divided, then media anterior fused with RS. After the middle length of Rs+M, media anterior again forked from RS, and fused with MP. Cubitus posterior forked near tip; with 2 anal veins. Hind wings slightly longer than tegmina ( Fig. 1D View FIGURE 1 ).
Abdominal tergites second and third each with a pair of rows of stridulatory pegs, the most cephalad of which contains 5–6 pegs ( Fig. 1E View FIGURE 1 ). Eighth abdominal tergite prolonged. Ninth abdominal tergite semi-globular: prolonged and down-curved ( Fig. 1G View FIGURE 1 ). Tenth abdominal tergite with 1 pair of long spines, basal area crossed each other, apical half curved ventrad and slightly forward, apical part sclerotized and sickle-shaped ( Fig. 1F View FIGURE 1 ). Cerci slender. Subgenital plate longer than wide, anterior margin straight; posterior margin arched, with U-shaped medial excision, the lateral lobes triangular ( Fig. 1H View FIGURE 1 ). Styli absent.
Female. Left tegmen ( Fig. 3B View FIGURE 3 ): Radius releases RS before mid-length of tegmen, both forked again; media forked, the anterior fused in about basal third with RS, the posterior vein undivided, singled branched. Cubitus anterior forks before third two veins, then again fused. With 1 anal veins.
Seventh abdominal tergite longer than other sterna, basal area semi-oval with 1 pair of copulatory depressions ( Fig. 2G View FIGURE 2 ). Subgenital plate with straight anterior margin and narrowly rounded posterior margin ( Fig. 2G View FIGURE 2 ). Ovipositor longer than body, not strongly curved dorsad, margins slightly and gradually narrowing towards tip ( Fig. 2H View FIGURE 2 ); tip subacute ( Fig. 2I View FIGURE 2 ).
Coloration. General color yellowish (discolored due to storage in alcohol). Frons with black spot. Margins of antennal sockets, internal margins of scape and pedicel with black spots. Eyes black. Tegmina yellowish brown. Apical area of processes in male tenth abdominal tergite black.
Measurements (mm). BL: ♂ 23.5–25.0, ♀ 24.0–28.2; PL: ♂ 5.2–5.4, ♀ 5.8–6.0; HFL: ♂ 14.2–14.4, ♀ 14.8–15.2; TL: ♂ 3.1–3.7, ♀ 3.0–3.2; OvL: 32.0–34.0.
Material examined. Holotype: male, Banggang, Mensong, Menhai , Yunnan, 16 July , 2019, coll. by Mingying Guo . Paratypes: 10 males and 6 females, Banggang, Mensong, Menhai, Yunnan, 16 July, 2019, coll. by Mingying Guo, Haiqing Huang, Lei Pang & Xun Bian .
Distribution. China ( Yunnan).
Etymology. The name of the new species is derived from brevipenna adding the prefix parci, referring to the superficial similarity Homogryllacris brevipenna .
Discussion. The new species appears most closely related to Homogryllacris brevipenna Du, Bian & Shi, 2016 (Chinese name: 短Oi同ḋü) based on length of tegmina, but differs by the processes of tenth abdominal tergite slender and longer, and the male subgenital plate without styli. The new species differs from Homogryllacris anelytra Shi, Guo & Bian, 2012 (Chinese name: ṚOi同ḋü) by the micropterous, male subgenital plate with 1 large U-shaped concavity on posterior margin and absent styli, and posterior margin of female subgenital plate narrowly rounded.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Tribe |
Gryllacridini |
|
Genus |