Coccus celatus De Lotto, 1960
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaXa.4460.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:DB841017-698F-4D44-A633-461D350DC984 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5966436 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0974884C-B665-FFC6-FF6C-F954038AFCC3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Coccus celatus De Lotto, 1960 |
| status |
|
Coccus celatus De Lotto, 1960 View in CoL
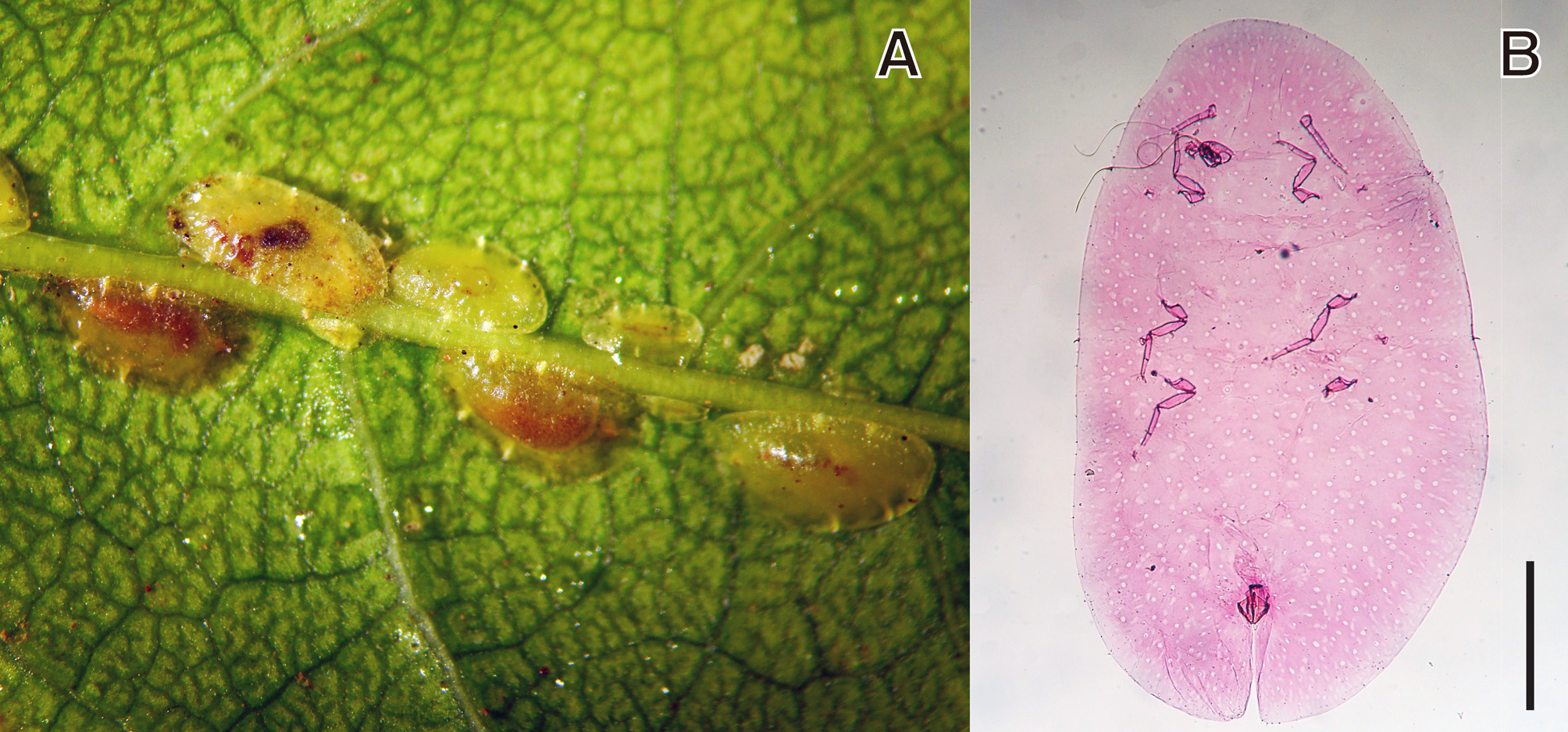
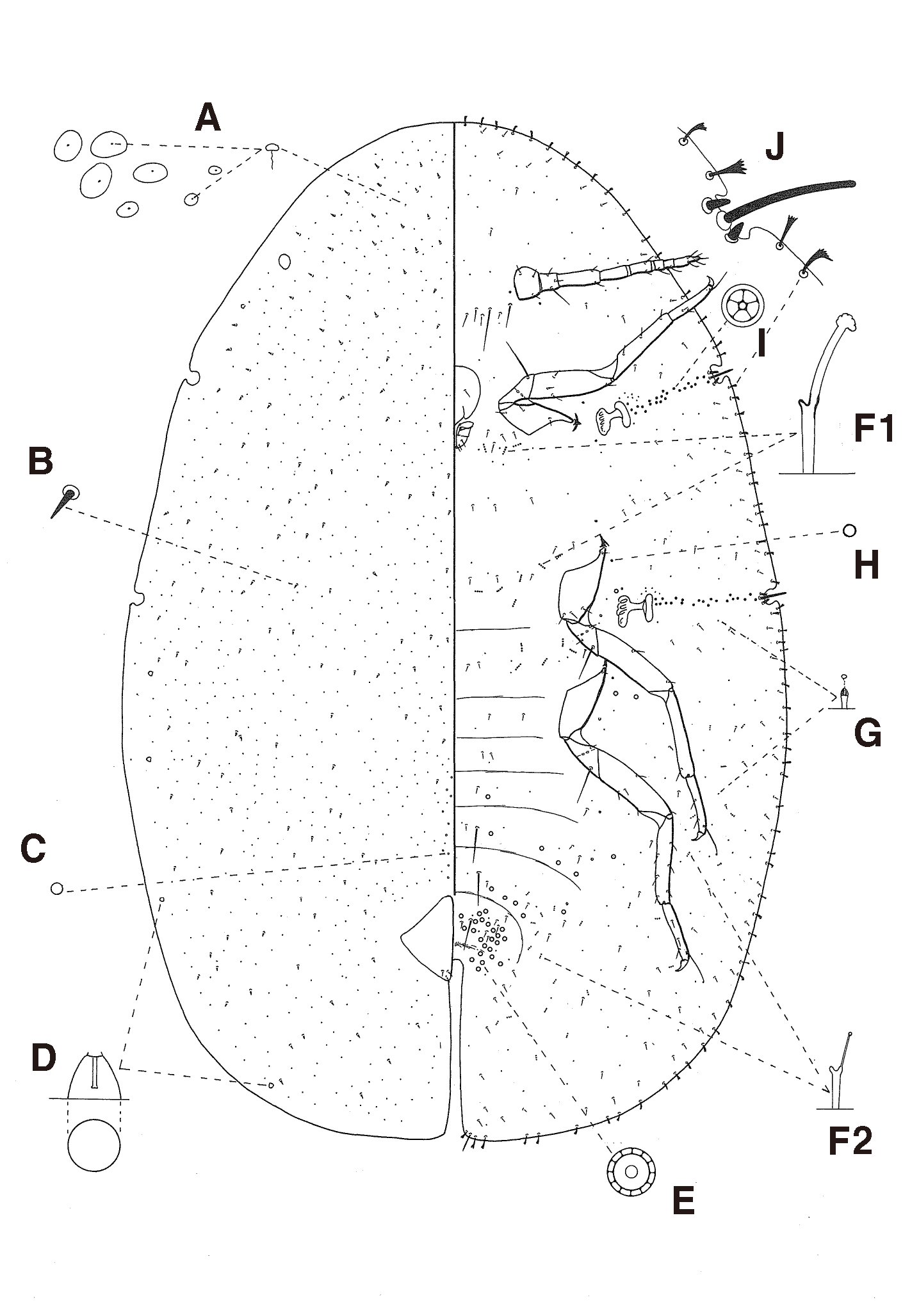
( Figs 18 View FIGURE 18 , 19 View FIGURE 19 )
Coccus celatus De Lotto, 1960: 395 View in CoL .
Diagnosis. Dorsum with setae bluntly spinose ( Fig. 19B View FIGURE 19 ); tubular ducts absent; duct tubercles present ( Fig. 19D View FIGURE 19 ); and preopercular pores present anterior to anal plates ( Fig. 19C View FIGURE 19 ). Marginal setae spinose, with conspicuous fimbriate apices ( Fig. 19J View FIGURE 19 ). Venter with multilocular disc-pores each usually with 10–12 loculi ( Fig. 19E View FIGURE 19 ); tubular ducts of 2 types: type I each with a broad inner ductule, present around meta-, meso-, and procoxa, and type II each with a filamentous inner ductule, usually present in submarginal areas of abdomen, also a few ducts present on submargin of thorax ( Fig. 19F View FIGURE 19 ); pregenital setae numbering 3 pairs; antenna 8 segmented; and legs each with a tibio-tarsal articulatory sclerosis (partially adopted from De Lotto 1960; Williams & Watson 1990).
Material examined. 5 ♀♀, LAOS, Xaythany Dist , Vientiane Capital, 16.i.2017, coll. P.P. Soysouvanh, on Wrightia religiosa (Teijsm. & Binn.) Benth. ( Apocynaceae ).
Hosts. Polyphagous. According to García Morales et al. (2016), C. celatus has been recorded from plants belonging to 17 genera in 10 families.
Distribution. Mainly known from Afrotropical, Neotropical and Oriental Regions ( Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines and Vietnam) ( García Morales et al. 2016); Laos (new country record).
Economic importance. Coccus celatus was listed as a coffee pest together with C. alpinus De Lotto and C. viridis (Green) ( Waller et al. 2007). Infestation of C. celatus on coffee has been reported also from Brazil (Granara de Willink et al. 2010) and Papua New Guinea ( Williams 1982; Murphy 1991).
Remarks. Among coffee soft scale pests in Laos, Coccus celatus is similar to C. viridis (Green) , but is easily separated by having multilocular disc-pores mostly each with 10–12 loculi, and ventral tubular ducts each with a filamentous inner ductule present in submarginal areas of the abdomen. In contrast, C. viridis has multilocular discpores mostly each with 7 loculi, and ventral tubular ducts each with a broad inner ductule mainly distributed in medial areas of the thorax.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.