Chlamydodon bourlandi Qu et al., 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4664.2.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:AD304BBB-FFED-4AFD-940C-F0DAA8C156BE |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5612494 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0E0F87F9-9B77-FFCA-2F95-1DA8B878FAF9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Chlamydodon bourlandi Qu et al., 2018 |
| status |
|
Chlamydodon bourlandi Qu et al., 2018
( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ; Table 1 View TABLE 1 )
Morphological description. Size 130–230 × 65–150 μm in vivo, and 150–200 × 60–85 μm after protargol staining. Body elongated ellipsoid to reverted triangle in outline; posterior end slightly pointed ( Fig. 4A, G View FIGURE 4 ). Cross-strained band complete, 3–4 µm wide ( Fig. 4B, C View FIGURE 4 ). Two orange to reddish pigment spots composed of countless, small pigment particles, located in anterior-left and posterior-right of cell, respectively ( Fig. 4A, D, F View FIGURE 4 ), Cytoplasm transparent, with many irregular-shaped violet-pigmented vacuoles (2–7 μm across), which renders cell reddish to violet. Orange to red cortical particles, about 0.5 μm across, densely distributed between ciliary rows on ventral side ( Fig. 4E View FIGURE 4 ), but irregularly distributed on dorsal side ( Fig. 4D View FIGURE 4 ). Cytostome located at about anterior 25% of cell; cyrtos composed of 14–17 nematodesmal rods ( Fig. 4B View FIGURE 4 ). 22–47 contractile vacuoles (4–5 μm across, counted from 15 protargol-stained specimens) irregularly distributed, with a contraction interval of 5–10 seconds. Spherical macronucleus heteromerous, in mid-body, about 45 × 35 μm in vivo ( Fig. 4C View FIGURE 4 ) and after fluorescent staining ( Fig. 4H View FIGURE 4 ), and about 35 × 28 μm after protargol staining ( Fig. 4I View FIGURE 4 ). Micronucleus not detected. Movement by crawling on the substrate, sometimes swimming in water around the longitudinal axis of body.
Cilia 6–8 μm long in vivo. In total 70–86 somatic kineties including 36–48 right, 27–34 left, and three to five (mostly four) postoral kineties. Five to 15 terminal fragments, each containing three to 20 basal bodies ( Fig. 4L View FIGURE 4 ). Equatorial fragment not detected.
Two (four out of 25 individuals observed have three) circumoral kineties parallel to each other; preoral kinety positioned in anterior-left of circumoral kineties ( Fig. 4J, K View FIGURE 4 ).
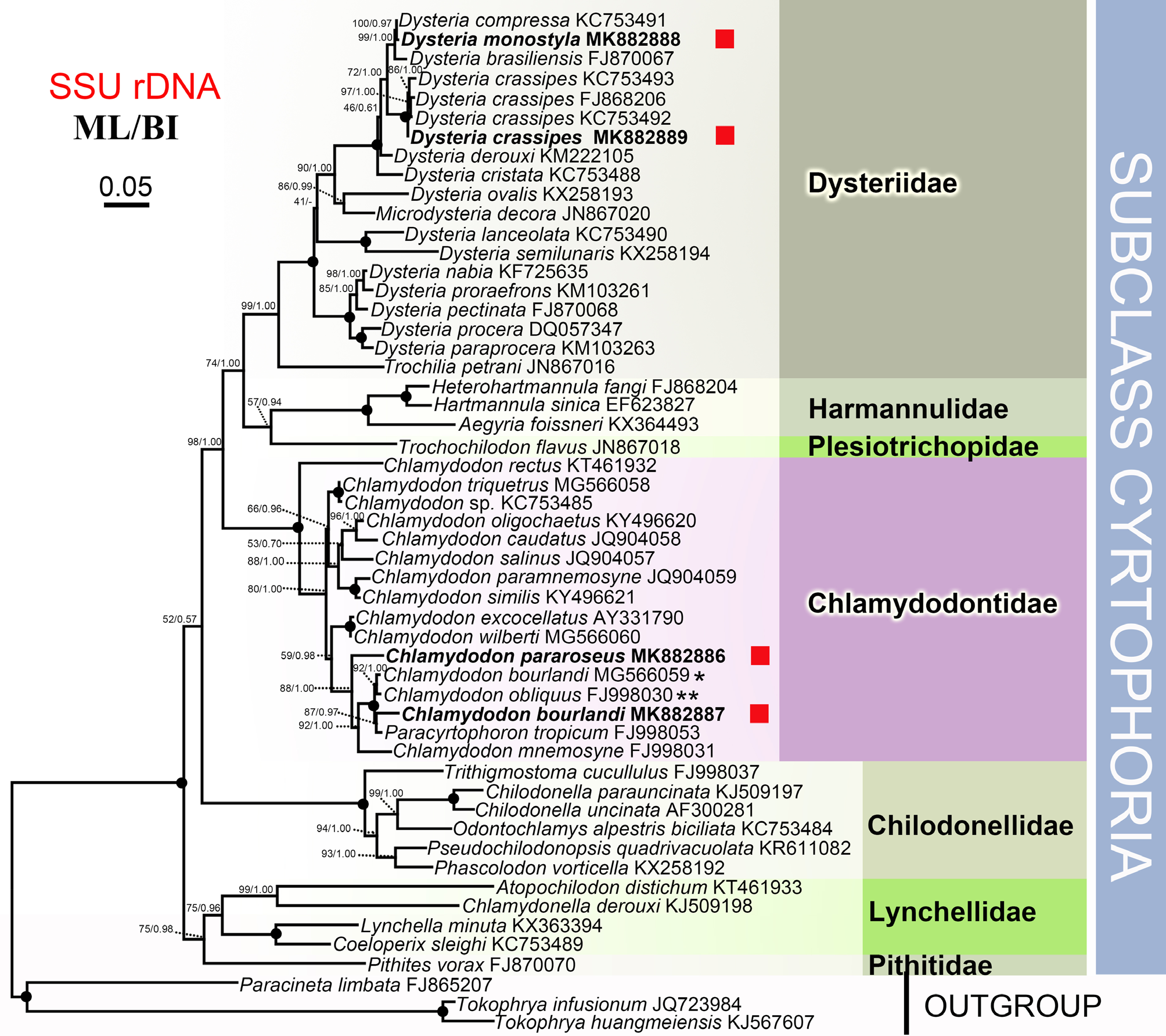
SSU rRNA gene sequence and phylogenetic position. The SSU rRNA gene sequence of the present population of Chlamydodon bourlandi has GenBank accession number, length, and G + C content of MK 882887 View Materials , 1639 bp, and 44.91%, respectively. The closest related Chlamydodon species is C. bourlandi ( MG 566059 View Materials ) with a 99.0% sequence similarity. The sequence similarity of Chlamydodon bourlandi to Paracyrtophoron tropicum ( FJ 998053) is 98.4%. In phylogenetic trees ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 ), our new isolate of C. bourlandi forms a clade with Paracyrtophoron tropicum FJ998053 with moderate bootstrap values ( ML /BI, 87%/0.97), then this clade clusters with the branch formed by C. bourlandi MG 566059 View Materials and C. obliquus FJ998030 View Materials (= C. bourlandi ) with full support ( ML /BI, 100%/1.00).
Abbreviations: CV—coefficient of variation (%); Min—minimum; Max—maximum; M—median; Mean—arithmetic mean; SD—standard deviation; n —number of individuals examined.
| SSU |
Saratov State University |
| MK |
National Museum of Kenya |
| MG |
Museum of Zoology |
| ML |
Musee de Lectoure |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |