Peucedanum praeruptorum, Dunn, Dunn
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.11.006 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10565504 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2812FE14-FA2A-AC2F-FCDB-FB69FC7AF9BC |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Peucedanum praeruptorum |
| status |
|
2.1. Identification of the cDNA encoding PAL in P. praeruptorum View in CoL
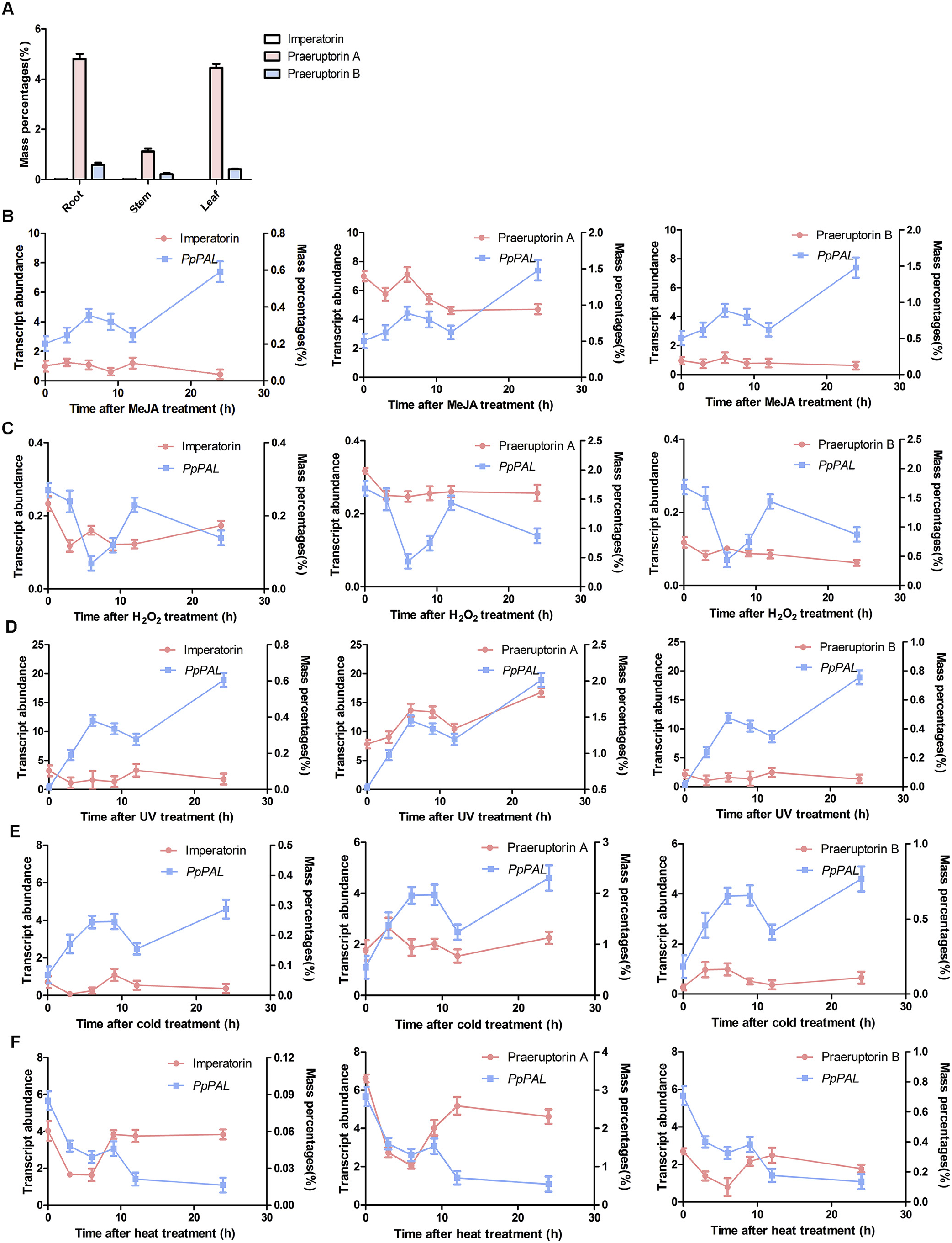
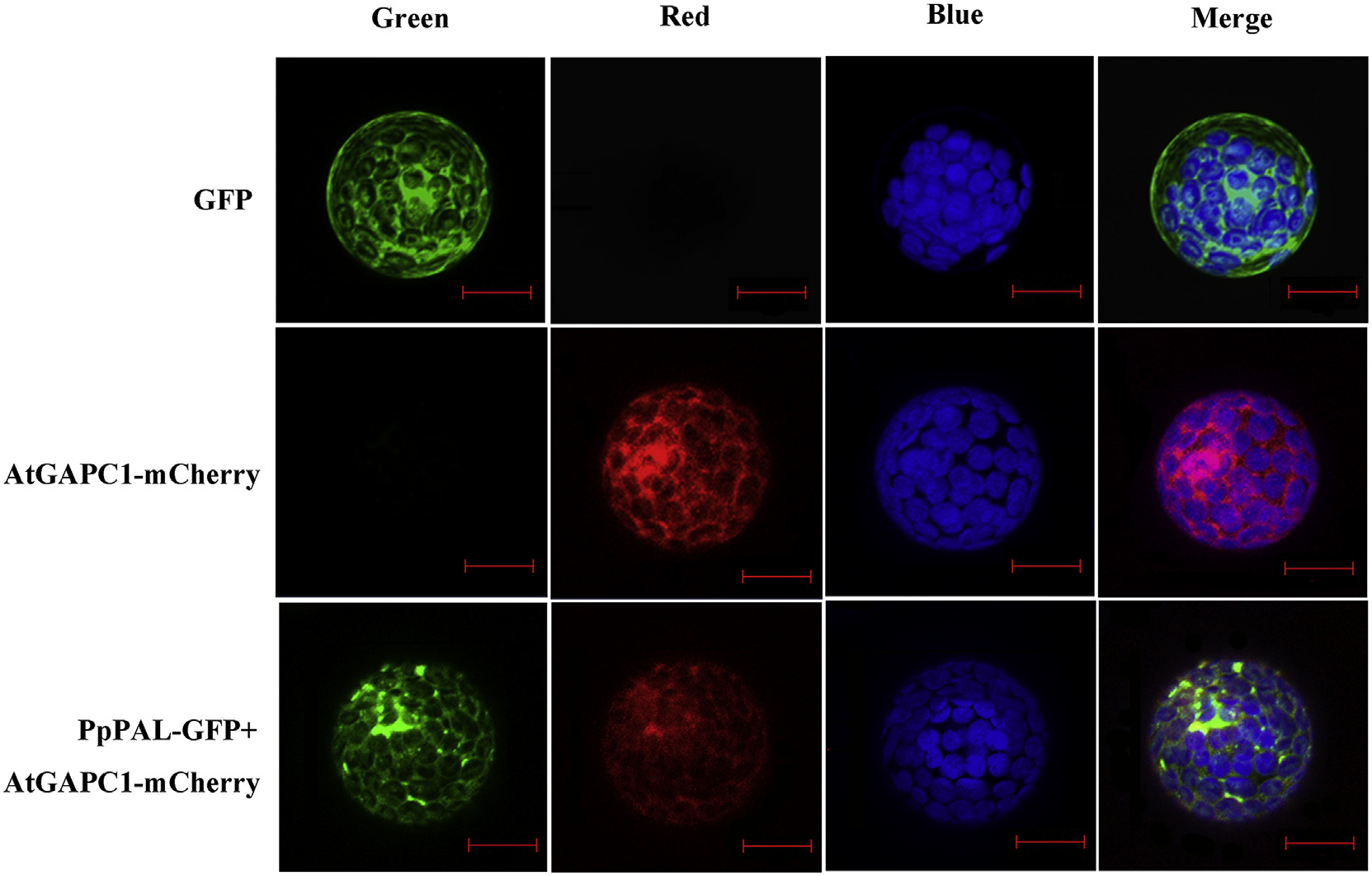
Using PAL sequences reported previously and our transcriptome database of P. praeruptorum (accession no. SRX997427) ( Zhao et al., 2015), a BLAST search was conducted. According to the E -value of alignments, only one PAL was identified and cloned. This cDNA, which encodes a 719 amino acid residue protein (Table S1), was designated PpPAL. According to bioinformatics, PpPAL is most closely related to PAL of Angelica sinensis (AsPAL) , which also belongs to Apiaceae ( Fig. S2 View Fig ). The amino acid sequences of PpPAL also contain a highly conserved MIO group, which is formed by Ala-Ser-Gly residues ( Fig. S3 View Fig ). The high sequence similarity revealed that they might display the same enzymatic functions such as substrate specificity, optimal pH and catalytic mechanism.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |