Uroptychus psilus, Baba, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.3760976 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3805062 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/2A1C87B5-FE3B-4CDF-FF1B-DF9FFA88791D |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Uroptychus psilus |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Uroptychus psilus View in CoL n. sp.
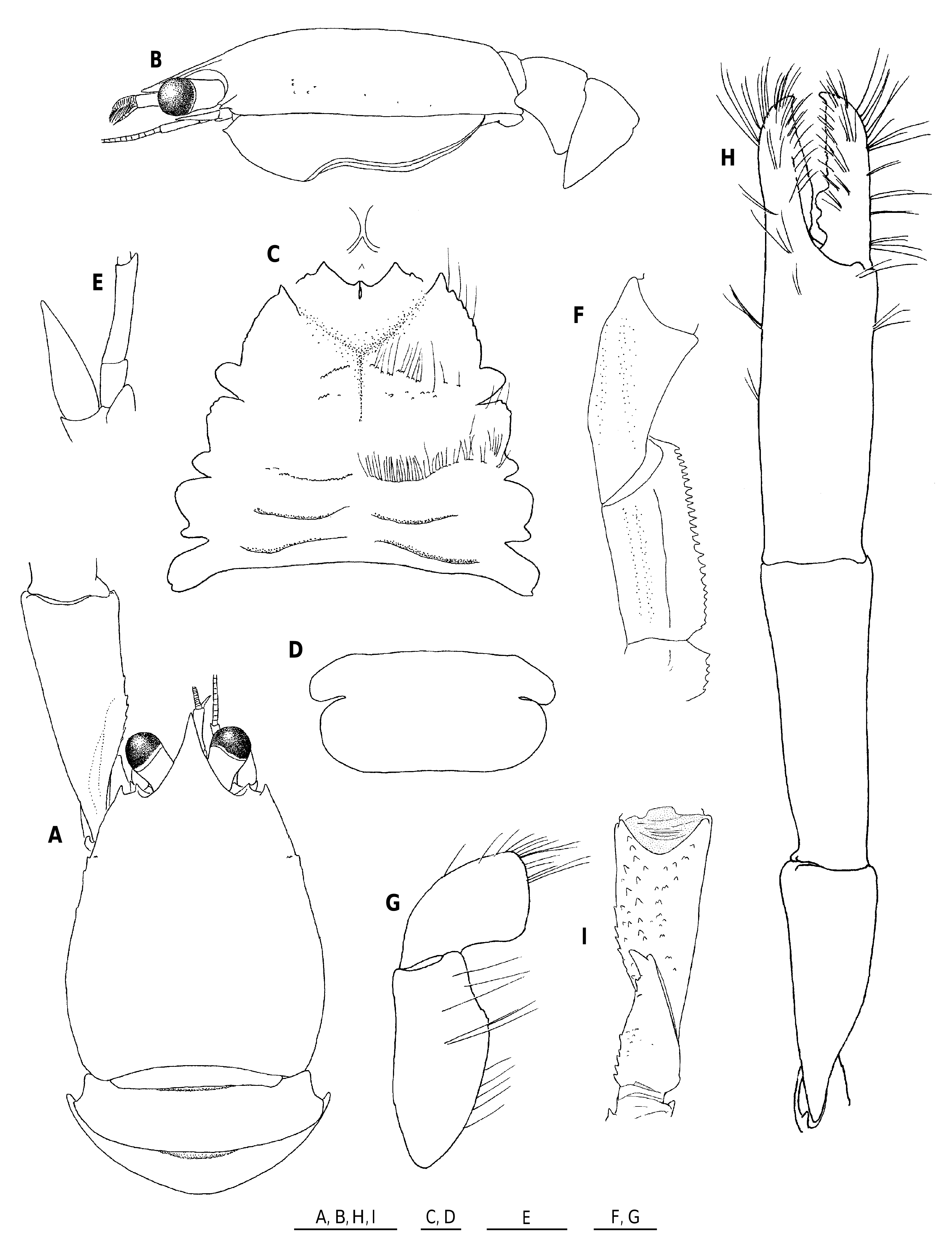
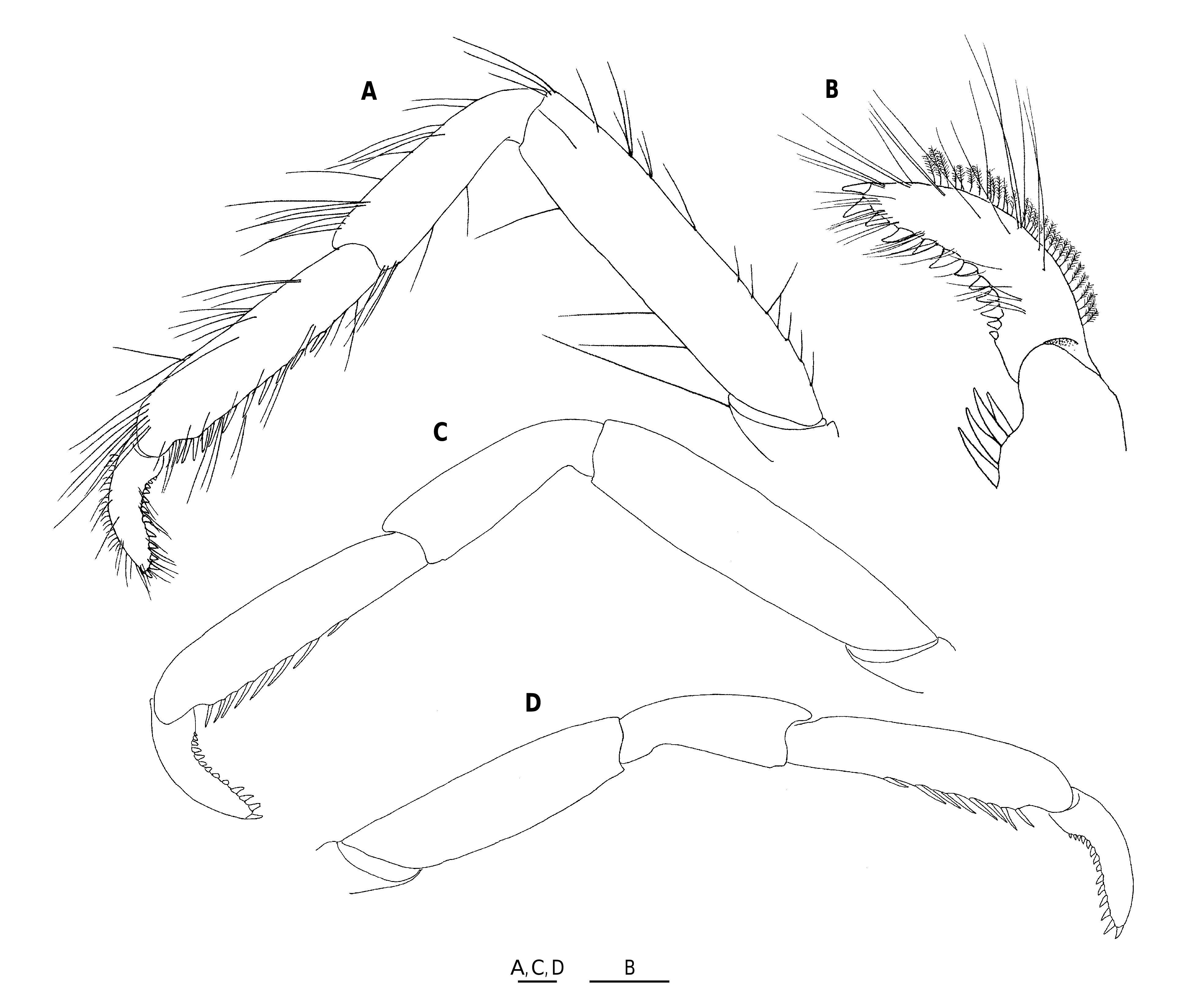
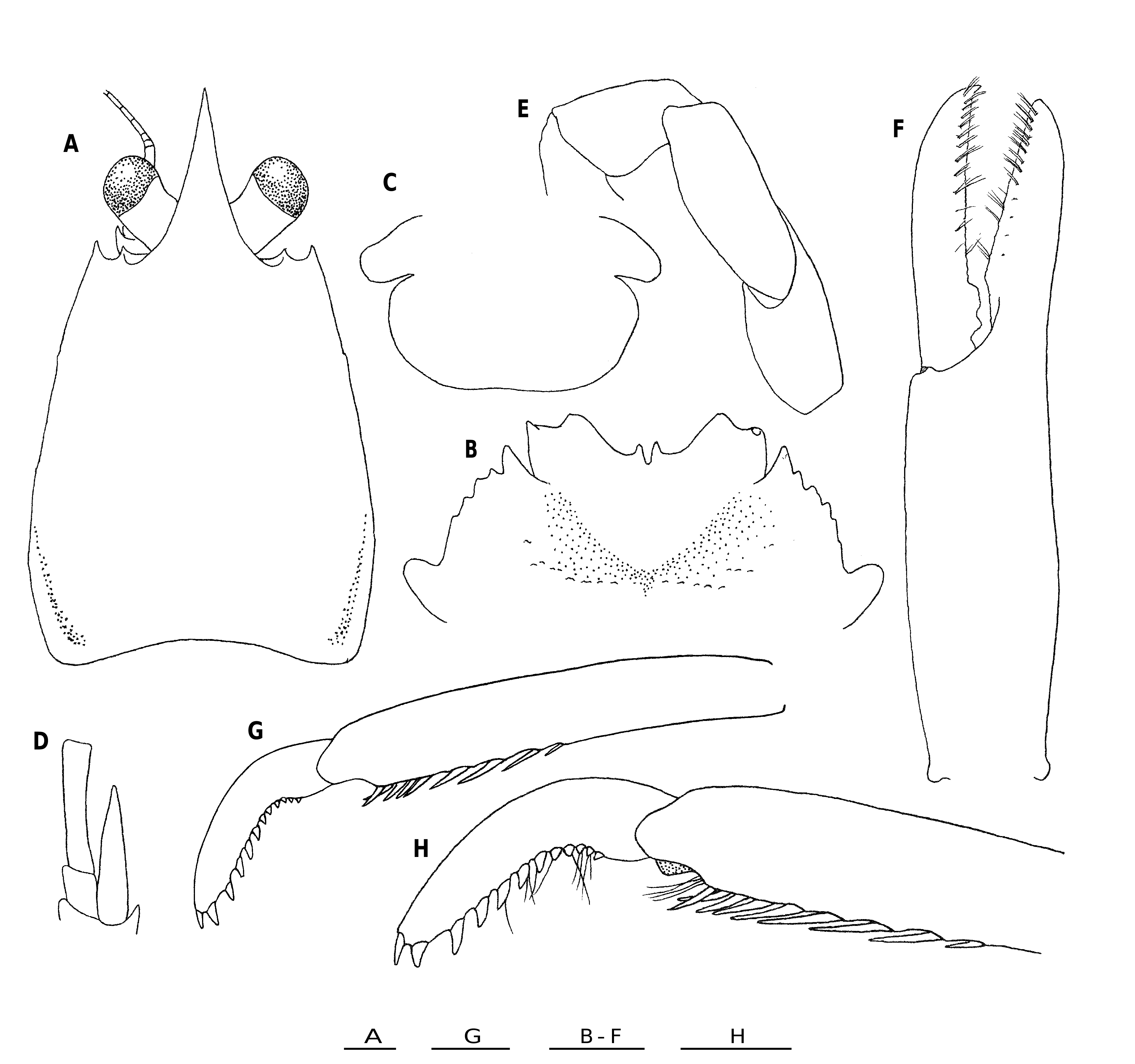
Figures 215 View FIGURE 215 , 216 View FIGURE 216 , 308A
TYPE MATERIAL — Holotype: New Caledonia, Norfolk Ridge. SMIB 4 Stn DW63, 22°58.7’S, 167°21.1’E, 520 m, 10.III.1989, ov. ♀ 13.0 mm ( MNHN-IU-2014-16884 ) GoogleMaps . Paratypes: New Caledonia, Norfolk Ridge. SMIB 2 Stn DW10, 22°50’S, 167°16’E, 490-495 m, 18.IX.1986, 2 ♂ 8.0, 8.1 mm, 1 ov. ♀ 10.0 mm (MNHN-IU-2014-16885) . – Stn DW13, 22°52’S, 167°13’E, 427- 454 m, 18.IX.1986, 1 ♂ (carapace missing), 1 ov. ♀ 12.3 mm (MNHN-IU-2014-16886) . – Stn DC26, 22°59’S, 167°23’E, 500-535 m, 21.IX.1986, 1 ♂ 8.3 mm, 1 ov. ♀ 10.6 mm (MNHN-IU-2014-16887) . SMIB 4 Stn DW64, 22°55’S, 167°15’E, 455-460 m, 10.III.1989, 1 ♂ 9.1 mm (MNHN-IU-2014-16888) . NORFOLK 2 Stn CP2146, 22°50.17’S, 167°17.35’E, 518- 518 m, 4.XI.2003, 1 ♂ 8.4 mm (MNHN-IU-2014-16889) . MUSORSTOM 4 Stn CP214, 22°53.8’S, 167°13.9’E, 425-440 m, 28.IX.1985, 1 ov. ♀ 8.2 mm (MNHN-IU-2014-16890) . – Stn CP215, 22°55.7’S, 167°17.0’E, 485-520 m, 28.IX.1985, 1 ♂ 4.6 mm, 1 ov. ♀ 10.3 mm (MNHN-IU-2014-16891) . – Stn CP216, 22°59.5’S, 167°22.0’E, 490-515 m, with coral Chrysogorgiidae (Calcaxonia) , 29.IX.1985, 9 ♂ 8.0-12.9 mm, 4 ov. ♀ 10.8-12.2 mm, 2 ♀ 8.1, 11.5 mm (MNHN-IU-2014-16892) , 1 ♂ 5.9 mm (MNHN-IU-2014-16893) . HALIPRO 2 Stn BT94, 23°33’S, 167°42’E, 448-880 m, 24.XI.1996, 1 ♂ 13.0 mm (MNHN-IU-2014-16894) . SMIB 8 Stn DW200, 22°59.21’S, 168°20.23’E, 514-525 m, 2.II.1993, 1 ov. ♀ 10.1 mm (MNHN- IU-2014-16895) . New Caledonia, Loyalty Ridge. BERYX 2 Stn CH 16, 23°35.60’S, 169°36.52’E, 660-675 m, 29.X.1991, 1 ov. ♀ 13.7 mm (MNHN-IU-2014-16896) . Tonga. BORDAU 2 Stn CH 1621, 24°19’S, 176°23’W, 570-573 m, 18.VI.2000, 1 ♀ 6.0 mm (MNHN-IU-2014-16897) .
ETYMOLOGY„ From the Greek psilos (bare, smooth), alluding to the smooth carapace surface of the species.
DISTRIBUTION„ Norfolk Ridge, Loyalty Ridge and Tonga; 425- 880 m.
SIZE„ Males, 4.6-13.0 mm; females, 6.0- 13.7 mm; ovigerous females from 8.2 mm.
DESCRIPTION„ Large species. Carapace: As long as broad; greatest breadth 1.6-1.7 × distance between anterolateral spines. Dorsal surface smooth and barely setose, well convex from anterior to posterior, usually with no depression, occasionally with faint depression between gastric and cardiac regions. Lateral margins convex posteriorly, with somewhat elevated small ridge at anterior quarter, followed by a few minute tubercles or granules; anterolateral spine small, reaching but not overreaching tip of lateral orbital spine. Rostrum broad triangular, as long as broad, with interior angle of 35-37°, length 0.3-0.4 that of remaining carapace, breadth half carapace breadth at posterior carapace margin; dorsal surface moderately concave; lateral margins slightly concave. Lateral orbital spine somewhat smaller than anterolateral spine, slightly anterior to level of, and moderately remote from lateral orbital spine. Pterygostomian flap smooth on surface, anterior margin somewhat roundish, ending in small spine.
Sternum: Excavated sternum anteriorly triangular, ending in acute spine, surface somewhat ridged in midline, with small spine in center. Sternal plastron gradually broadened posteriorly, slightly shorter than broad. Sternite 3 strongly depressed, anterior margin relatively narrow and excavated in broad V-shape with narrow median notch flanked by small spine; anterolateral angle sharply produced. Sternite 4 long relative to breadth; anterolateral margin convex, moderately divergent posteriorly, anteriorly produced to distinct spine, followed by posteriorly diminishing serrations; posterolateral margin slightly less than half as long as anterolateral margin. Sternite 5 more than half length of sternite 4, anterolateral margin strongly convex anteriorly, 1.7 × longer than posterolateral margin of sternite 4.
Abdomen: Smooth and glabrous. Somite 1 gently convex from anterior to posterior. Somite 2 tergite 2.4-2.8 × broader than long; pleuron posterolaterally blunt angular, lateral margins concave, moderately divergent posteriorly. Pleuron of somite 3 with bluntly or more or less sharply angular lateral tip. Telson 0.4-0.5 × as long as broad; posterior plate slightly or distinctly concave on posterior margin, length 1.3-1.7 × that of anterior plate.
Eye: More or less elongate (1.5-1.7 × longer than broad), overreaching distal third of rostrum, falling short of rostral tip; mesial and lateral margins concave. Cornea somewhat dilated, length more than half that of remaining eyestalk.
Antennule and antenna: Ultimate article of antennule 2.3-2.7 × longer than high. Antennal peduncle terminating in distal end of cornea. Article 2 with small lateral spine. Antennal scale twice broader than article 5, varying from slightly overreaching midlength of to almost reaching distal end of antennal article 5. Article 4 unarmed. Article 5 with small or obsolescent distomesial spine, length 2.0-2.3 × that of article 4; breadth 0.5 × height of antennular ultimate article. Flagellum of 30-34 segments distinctly overreaching distal end of P1 merus (right flagellum in holotype with 24 segments, barely reaching distal end of P1 merus, presumably regenerated).
Mxp: Mxp1 with bases nearly contiguous to each other. Mxp3 barely setose on lateral surface. Basis with 4-5 denticles on mesial ridge. Ischium with 18-24 denticles on crista dentata, flexor margin distally not rounded. Merus 1.5 × longer than ischium, moderately thick, flexor margin with sharp ridge bearing 0-3 obsolescent denticles at distal third; mesial face setose. Carpus unarmed.
P1: Massive, 4.0-4.9 × longer than carapace. Ischium dorsally with dorsoventrally depressed, short triangular spine, ventrally with relatively short subterminal spine followed proximally by row of tubercle-like spines. Merus dorsally smooth, ventrally with small spines or tubercle-like spines; length subequal to that of carapace. Carpus 1.1-1.2 × longer than merus, smooth and barely setose dorsally, with distinct or tubercle-like spines on ventral surface. Palm 1.9-2.0 × (males), 2.3-2.6 × (females) longer than broad, length varying from slightly shorter to slightly longer than carpus, distally sparsely setose. Fingers nearly straight in lateral view, setose, relatively broad, ending in incurved small spine, crossing when closed; movable finger 0.6-0.8 × as long as palm in both sexes; opposable margin with 2 blunt proximal processes arising from broad base, distal one stronger in males, subequal to proximal process in females, proximal process in females fitting to opposite groove of fixed finger when closed; fixed finger somewhat sinuous on opposable margin.
P2-4: With sparse long setae, slender, unarmed except for distal 2 articles. Meri well compressed mesio-laterally; P3 merus subequal to P2 merus or slightly shorter (0.91-1.00 × length of P2 merus), P4 merus 0.71-0.78 × length of P3 merus; breadths successively slightly smaller posteriorly or slightly larger on P3 than on P2, P4 merus 0.8-0.9 × as broad as P3 merus; length-breadth ratio, 4.1-5.2 on P2, 3.9-4.7 on P3, 3.5-4.0 on P4; P2 merus 0.8-0.9 × length of carapace, 1.4 × length of P2 propodus; P3 merus 1.2 × length of P3 propodus; P4 merus 0.9-1.0 × length of P4 propodus, 0.9 × as broad as P3 merus. Carpi successively shorter posteriorly or P2-3 carpi subequal (P3 carpus 0.9-1.0 × length of P2 carpus, P4 carpus 0.8-0.9 × length of P3 carpus), carpus-propodus length ratio, 0.7 on P2, 0.6-0.7 on P3, 0.5-0.6 on P4. Propodus shorter on P2 than on P3 and P4, or subequal on P2-4; length-breadth ratio, 4.4-5.1 on P2, 4.8-5.2 on P3, 4.8-5.2 on 4; flexor margin straight or feebly concave, ending in pair of spines preceded by 7-11 slender movable spines on distal fourfifths of length on P2, 8-10 spines on distal three-quarters on P3, 5-9 spines in distal two-thirds on P4. Dactyli shorter than carpi (dactylus-carpus length ratio, 0.5-0.6 on P2, 0.6-0.7 on P3, 0.7-0.8 on P4), less than half as long as propodi (dactyluspropodus length ratio, 0.4 on P2 and P3, 0.3-0.4 on P4), curving at proximal third; flexor margin with 10-13 triangular, somewhat obliquely directed, proximally diminishing spines, arranged as illustrated; ultimate spine very slightly smaller than or subequal to penultimate, subequal to antepenultimate; extensor margin with row of plumose setae.
Eggs. Eggs carried, 6-40 in number; eggs ready to hatch, 1.5-1.8 mm; those presumably shortly after spawning, 0.94 mm × 0.97 mm - 1.00 mm × 1.05 mm.
Color. Male 9.1 mm from Norfolk Ridge (MNHN-IU-2014-16888): Pale pink-orange all over the surface, abdomen more or less translucent.
REMARKS — The combination of the following characters links the new species to U. brucei Baba, 1986a , U. maori Borradaile, 1916 and U. granulipes n. sp.: the carapace lateral margin with an anterolateral spine only, sternite 3 with a pair of submedian spines, the P1 ischium with a well-developed subterminal spine on the ventromesial margin, the P2-4 propodi with a pair of terminal spines proximally preceded by a row of single slender spines, and the dactyli with the penultimate spine subequal to or smaller than the ultimate and subequal to the antepenultimate. However, U. psilus is readily distinguished from these congeners by the anterolateral spine rather small, not overreaching instead of distinctly overreaching the lateral orbital spine, by the P1 merus covered with small, distinct spines instead of being granulose on the ventral surface, and by the antennal article 4 spineless instead of bearing a distomesial spine.
Uroptychus psilus also resembles U. septimus n. sp. in the carapace shape, especially in having the anterolateral spine small, not overreaching the lateral orbital spine. Characters distinguishing U. psilus from U. septimus are discussed under the remarks of the latter species (see below).
The species account of U. indicus Alcock, 1901 ( Alcock 1901: 284) suggests that this new species may be close to that species. However, the original description is not detailed enough to warrant its systematic status, as also not are subsequent descriptions ( Van Dam 1933, 1937; Tirmizi 1964). In fact, four lots of the SIBOGA material of U. australis var. indicus (see Van Dam, 1933) are referable to U. vandamae (see below). Examination of the John Murray material of U. australis var. indicus (see Tirmizi 1964) discloses that the specimens from Stations 108 and 122 in Zanzibar area are identical with the Madagascar material reported under U. gracilimanus by Baba (1990) (= undescribed species, see Baba 2005; and under the remarks of U. gracilimanus ). In addition, the material reported under U. nitidus from off Durban ( Kensley 1977) will in all probability be referred to this species. A female specimen collected by the R/V Meiring Naude at Station 121 south of Durban, 900- 625 m and identified by B. Kensley but not included in his 1977 paper, now in the collection of the Smithsonian Institution (USNM 1101919), is also identical with this undescribed species.
Fortunately, one of the syntypes (ovigerous female) of U. indicus was examined on loan through the courtesy of K. K. Tiwari, then the director of the Zoological Survey of India, in 1974. The morphological features of U. indicus ( Figure 217 View FIGURE 217 ) obtained by the examination of the syntype are not well detailed, but U. psilus n. sp. can be distinguished from that species by the following: the carapace is as long as instead of longer than broad, bearing no ridge along the posterior part of the branchial lateral margin; the antennal article 2 bears a small instead of pronounced distolateral spine; the P2 propodus bears flexor marginal spines along the entire length instead of restricted to the distal half. The flexor marginal spines of the P2 dactylus are closer to each other in the distal portion (the antepenultimate spine is equidistant between the penultimate and the distal quarter spines in U. psilus , much more remote from the penultimate than from the distal quarter in U. indicus ), with the ultimate spine subequal to instead of distinctly more slender than the penultimate.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Chirostyloidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |