Xenococcus, Silvestri 1924
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3291.1.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5251998 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3421E53E-FC46-D733-2997-21E8FD51F85F |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Xenococcus |
| status |
|
XENOCOCCUS Silvestri 1924 View in CoL View at ENA
Xenococcus Silvestri, 1924: 312 View in CoL .
Type species: Xenococcus annandalei Silvestri , by monotypy.
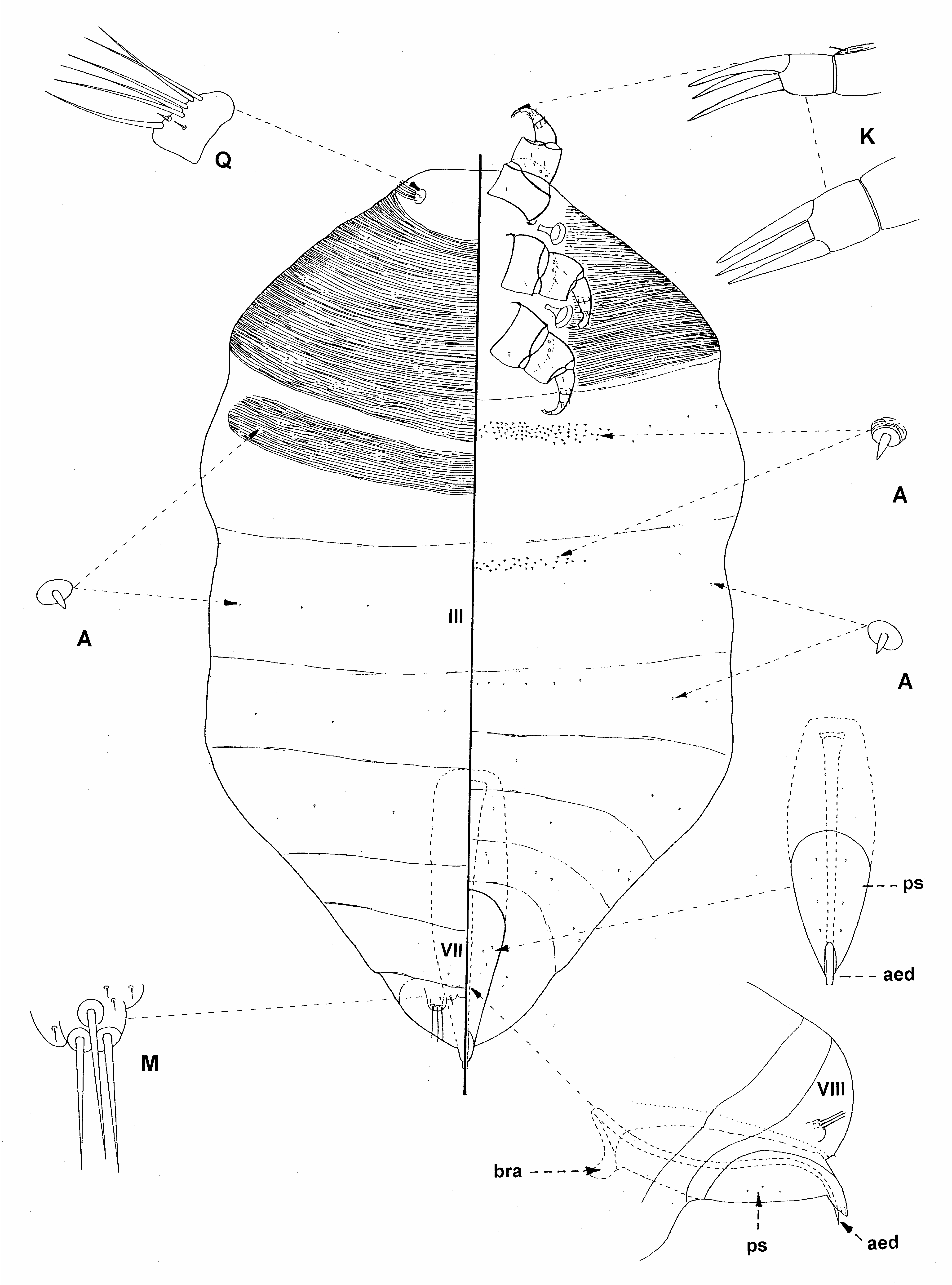
Introduction. At present, five species of Xenococcus are known ( Schneider & LaPolla, 2011), but only the male of X. acropygae Williams has been described ( Williams, 1998) ( Fig. 22 View FIGURE 22 ). If this is typical of the males of this genus, it appears to be significantly different from other rhizoecine males and is easily separated from the other species in Xenococcini by the presence of: (i) spine-like claw digitules; (ii) very short 1-segmented antennae; (iii) presence of a lobe (caudal extension?) on abdominal segment VIII with 3 spine-like setae, and (iv) sclerotised thoracic segments. This suggests that the Xenococcinae might be divisable into two tribes, one to include Eumyrmococcus and Neochavesia and the other for just Xenococcus . However, because the male of only one species is currently known, no action is being taken here.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Xenococcus
| Hodgson, Chris 2012 |
Xenococcus
| Silvestri, F. 1924: 312 |