Patollini, Szwedo & Stroiński, 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3647.2.8 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:0B7A07C2-ADC1-4531-8DF4-53ABD16D3E0C |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/344587FD-FFE7-FFAD-6891-FB6DE8E8FEF3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Patollini |
| status |
trib. nov. |
Tribe Patollini trib. n.
Type genus: Patollo gen. n., here designated.
Diagnosis. The new tribe differs from other Tropiduchidae by the combination of characters as follows. Head with vertex wider than long in midline. Brachypterous, with costal area present, not reaching apex of clavus; nodal line absent, common portion of M and CuA present. Hind tibiae with three lateral spines. Male genital styles fused at base.
Description. Head with compound eyes wider than pronotum. Vertex distinctly wider than long in midline; with margins strongly carinate; vertex anteriorly widely angulate. Frons and clypeus smooth, lacking pustules or setae. Frons with median carina, lateral margins of frons carinate. Antennal pedicel longer than wide; plate organs, microsetae and macrosetae present only in distal half. Postclypeus without carinae. Apical segment of rostrum distinctly longer than broad. Pronotum short, with two distinct anterolateral carinae fused medially. Mesonotum widely rhomboid, lateral angles at about half of mesonotum length, close to the posterior margin of pronotum; mesonotum tricarinate, lateral carinae not connected anteriorly; scutellum separated from mesonotum by transverse groove.
Tegmen ovoid, with full venation developed, brachypterous; anterior margin strongly convex, anteroapical angle widely angulate, apex rounded, posteroapical angle widely rounded, clavus with apex reaching to about ⅔ of tegmen length. Costal area about as wide as costal cell, subequal throughout, with apex not exceeding apex of clavus, with transverse veinlets. Costal cell with transverse veinlets. Basal cell elongate, stems Sc+R and M leaving basal cell with a common stalk, separately from CuA stem. Forking pattern of stems Sc+R, M and CuA not regular, variable on left and right tegmina, but with common portion of branches M and CuA present. Nodal line absent, transverse veinlets not forming regular pattern or cells. Clavus with transverse veinlets.
Hind tibiae with three lateral spines in distal half and apical row of teeth. Basitarsomere longer than second tarsomere, with apical row of teeth and subapical setae. Second tarsomere with median portion arcuate, covered with setae. Basitarsomere about as long as combined length of second and third tarsomeres.
Abdominal segments III-VIII subequal in length. Pygofer narrow, about 3 times as high as long in the middle at ventral margin. Genital styles lobate, wide, with subapical processes, near the margin of pygofer, fused at base. Anal tube not exceeding length of genital styles, with anus in the middle.
Composition. Patollo gen. n.
Genus Patollo Szwedo et Stroi ń ski gen. n.
Type species: Patollo natangorum Szwedo et Stroi ṅski sp. n., here designated.
Composition. Two species. Patollo natangorum sp. n., P. aestiorum sp. n.
Age and occurrence. Eocene, Baltic amber.
Etymology. The generic name is derived from the name of the Old Prussian (Baltic Prussian) god of war, the underworld, and the dead – Patollo . Gender: masculine.
Diagnosis. Head with vertex wider than long in mid line. Metatibio-tarsal formula 8: 2+(7): 2 (0); Anal tube narrow, about 5 times as long as wide. Male genital style in lateral aspect, about as long as high, with small spine on dorsal margin at level of pygofer apex.
Description. Vertex with margins strongly carinate, anterior aspect of vertex broadly angulate, lateral margins subparallel, elevated, posterior margin broadly concave. Disc of vertex concave, smooth, with incomplete carinae (median or lateral ones). Frons and clypeus smooth, lacking pustules or setae; frons with median carina reaching frontoclypeal suture, lateral margins of frons carinate. Compound eye bulging, about as broad as long, posteroventrally delimited by narrow callus. Antennal fovea placed below the compound eye, elevated at posterior margin; pedicel club-like, longer than wide, arista long, placed centrally on pedicel. Postclypeus without carinae. Rostrum with apex slightly exceeding mesocoxae, apical segment of rostrum distinctly longer than wide.
Mesonotum in apical portion delicately wrinkled. Stem of M forked apicad of fork of stem of Sc+R.
Pro- and mesofemora not flattened, subequal in length; pro- and mesotibiae subtrapezoid in cross section, subequal in length. Profemora and protibiae and mesofemora and mesotibiae subequal in length, respectively. Metafemora slightly flattened, distinctly shorter than metatibiae. Metacoxae very well developed, enlarged, with meracantha distinct, subtriangular with acute apex. Metatibiae dilated apically, flattened to concave in apical portion.
Male. Pygofer in lateral view wider in apical portion with posterodorsal angle widely rounded, without processes. Anal tube narrow, without processes, apical portion, apicad of anus, in lateral view narrower than basal one. Genital styles with rounded apex, lower margin with small tooth-like expansion near base.
Female unknown.
Patollo natangorum Szwedo et Stroi ń ski, sp. n.
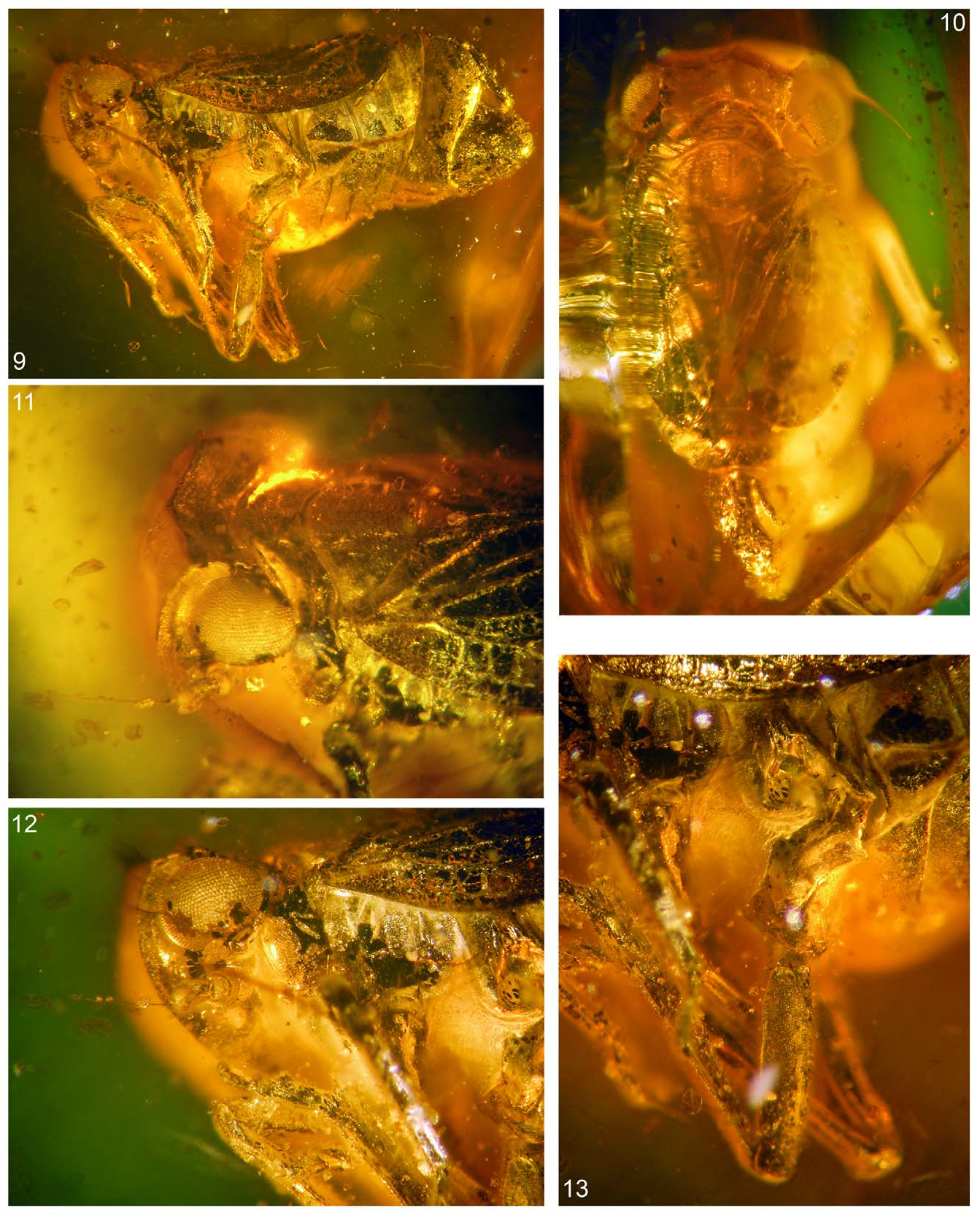
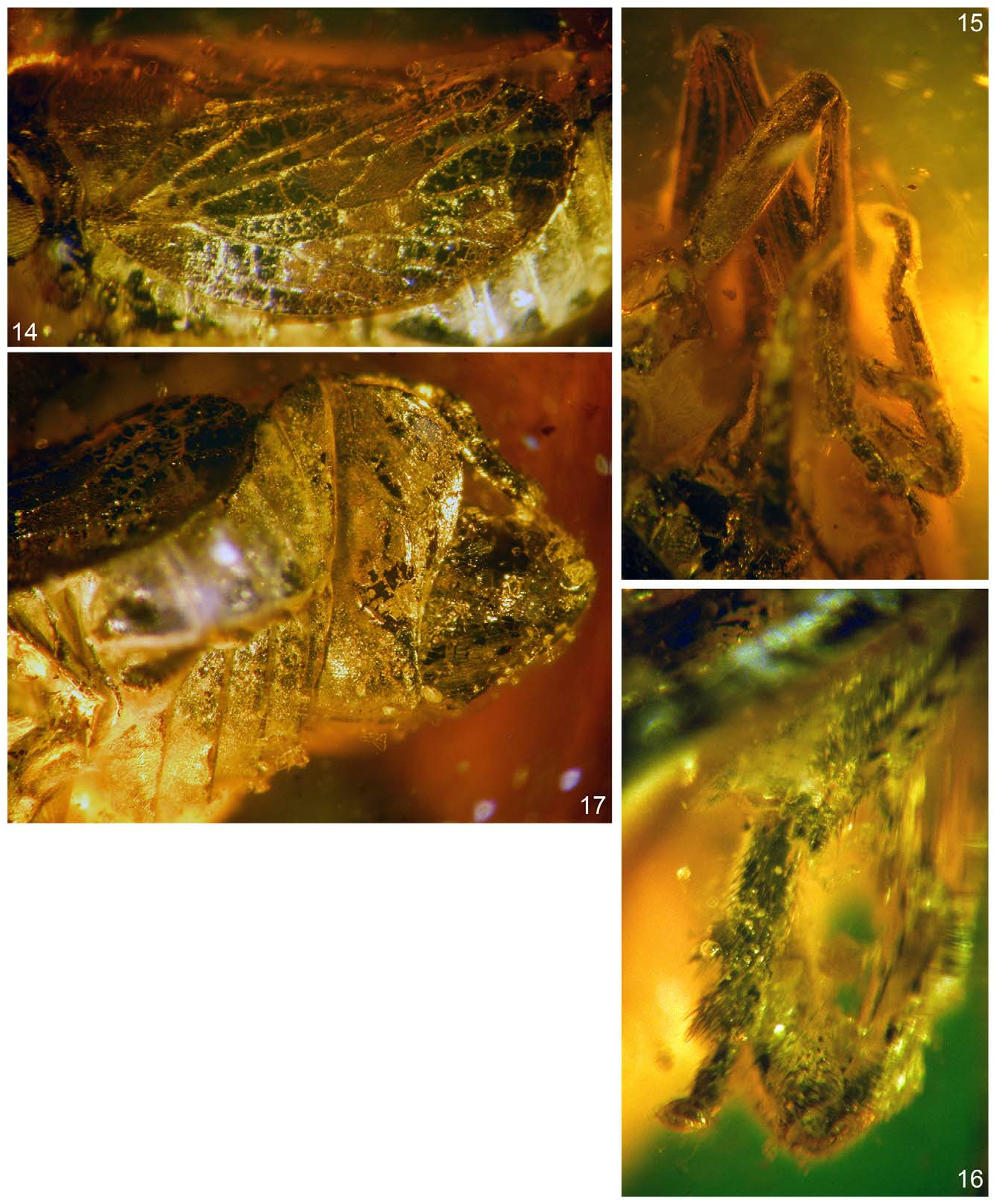
( Figs 1–17 View FIGURES 1–8 View FIGURES 9–13 View FIGURES 14–17 )
Diagnosis. Disc of vertex without median carina; two incomplete and weak lateral carinae from anterior margin of disc of vertex directed posteriorly, these are not reaching half of vertex length measured in the middle.
Description. Total length 4.9 mm, head with compound eyes about 2.16 mm wide, length of vertex in mid line 0.34 mm, 0.4 mm at lateral margin, width of vertex 1.1 mm; length of frons in mid line 1.28 mm, 1.2 mm at lateral margin; apical segment of rostrum 0.33 mm long; antennal scape 0.11 mm long, pedicel 0.23 mm long, arista 0.86 mm long.
Length of pronotum 0.32 mm, width of disc of pronotum 1.52 mm, length of mesonotum+scutellum 0.84 mm, width of mesonotum at base 1.28 mm.
Pronotum slightly shifted from mesonotum, hence the arcuate anterior of mesonotal ridge is visible. Anterior mesonotal ridge strongly arcuate, reaching posterior margin of mesonotum.
Length of tegmen about 2.37 mm, width of tegmen about 1.06 mm; length of clavus 1.52 mm.
Profemur about 1 mm long, protibia 1.04 mm, protarsus with claws 0.43 mm, first tarsomere 0.16 mm, mid tarsomere 0.16 mm, apical tarsomere 0.21 mm, tarsal claws 0.07 mm. Mesotibia 1.18 mm, mesotarsus with tarsal claws 0.33 mm, basitarsomere 0.17 mm, mid tarsomere 0.17 mm, apical tarsomere with tarsal claws 0.33 mm. Metafemur 1.15 mm long, metatibia 1.82 mm long, 0.26 wide at apex, metatarsus with tarsal claws 0.66 mm long, basitarsomere 0.37 mm long, about 0.15 mm wide at apex, midtarsomere 0.21 mm long, 0.13 mm wide at apex, apical tarsomere 0.21 mm long.
Abdomen with genital segment 2.5 mm long. Anal tube 1.07 mm long, 0.2 mm wide. Pygofer 1.61 mm high, 0.63 mm long at upper margin 0.43 mm long in the narrowest point, 0.5 mm near ventral margin. Genital style 0.91 mm long, 1 mm wide.
Left tegmen. Stem Sc+R forked in basal half of tegmen, basad of stem M forking; apicad of claval veins Pcu and A 1 junction. Branch ScRA 1 forked basad of stem M forking, RA forked basad of fork of RP; stem RP forked slightly basad of fork of branch M 1+2. Stem M forked at about half of tegmen length; branch M 3+4 fused with branch CuA 1, which extends to the margin. Stem CuA forked slightly apicad of stem M forking, slightly basad of costal area apex. Claval veins Pcu and A 1 connected slightly basad of half of clavus length.
Right tegmen. Stem Sc+R forked slightly apicad of stem CuA forking, well basad of stem M forking. Branch RA probably with three terminals, stem RP forked apically at level of claval apex. Stem M forked basad of claval apex; branch M 1+2 forked apically, branch M 3+4 fused with CuA 1 for a long distance, then terminal M 3 separated near apex. Stem CuA forked well basad, at basal ⅓ of tegmen length, basad of claval veins junction. Claval veins Pcu and A 1 connected at half of tegmen length. The details are difficult to discern because of a milky veil obstructing the specimen.
Etymology. The specific epithet is derived from the Natangi—the Old Prussian tribe inhabiting the area between the rivers Pregel (now Pregolya) and Alle (now Łyna) during the Middle Ages.
Age and occurrence: Baltic amber, Middle Eocene. This fossil resin is aged within the range of 38–47 Ma ( Ritzkowski 1997; Perkovsky et al. 2007). Absolute dating analyses of glauconites from Sambia Peninsula showed that the “blue earth” formation (amber bearing Prussian Formation) is allocated to the Middle Eocene (Lutetian: 44.1 ± 1.1 Ma) and is thus significantly older than previously assumed ( Wappler 2003, 2005). Limnic sediments of Eckfeld Maar, aged 44.3 ± 0.4 Ma, correlate with K-Ar radiometric data from the Sambia Peninsula and contain insect genera known only from Baltic amber ( Wappler 2005). However, assumptions on the Middle Eocene age of Baltic amber was discussed by Perkovsky et al. (2007), and the Upper Eocene (Bartonian/Priabonian: 37.7 ± 3 Ma) age of the Prussian Formation is preferred by these authors. Weitschat & Wichard (2010) mentioned that two additional amber-bearing horizons in the underlying beds of “blue earth” indicate that amber had already been transported to secondary deposits about 50 million years ago.
Material examined. Holotype, male. Specimen No. MIBUG 5419 (AUF 084JS), Coll. Jacek Serafin, Piaseczno , deposited in the Museum of Amber Inclusions , University of Gda ṅsk, Poland. Right side of the inclusion covered with a milky veil. Syninclusions: fragment of unidentified plant, a few bubbles of gas.
Patollo aestiorum Szwedo et Stroi ń ski, sp. n.
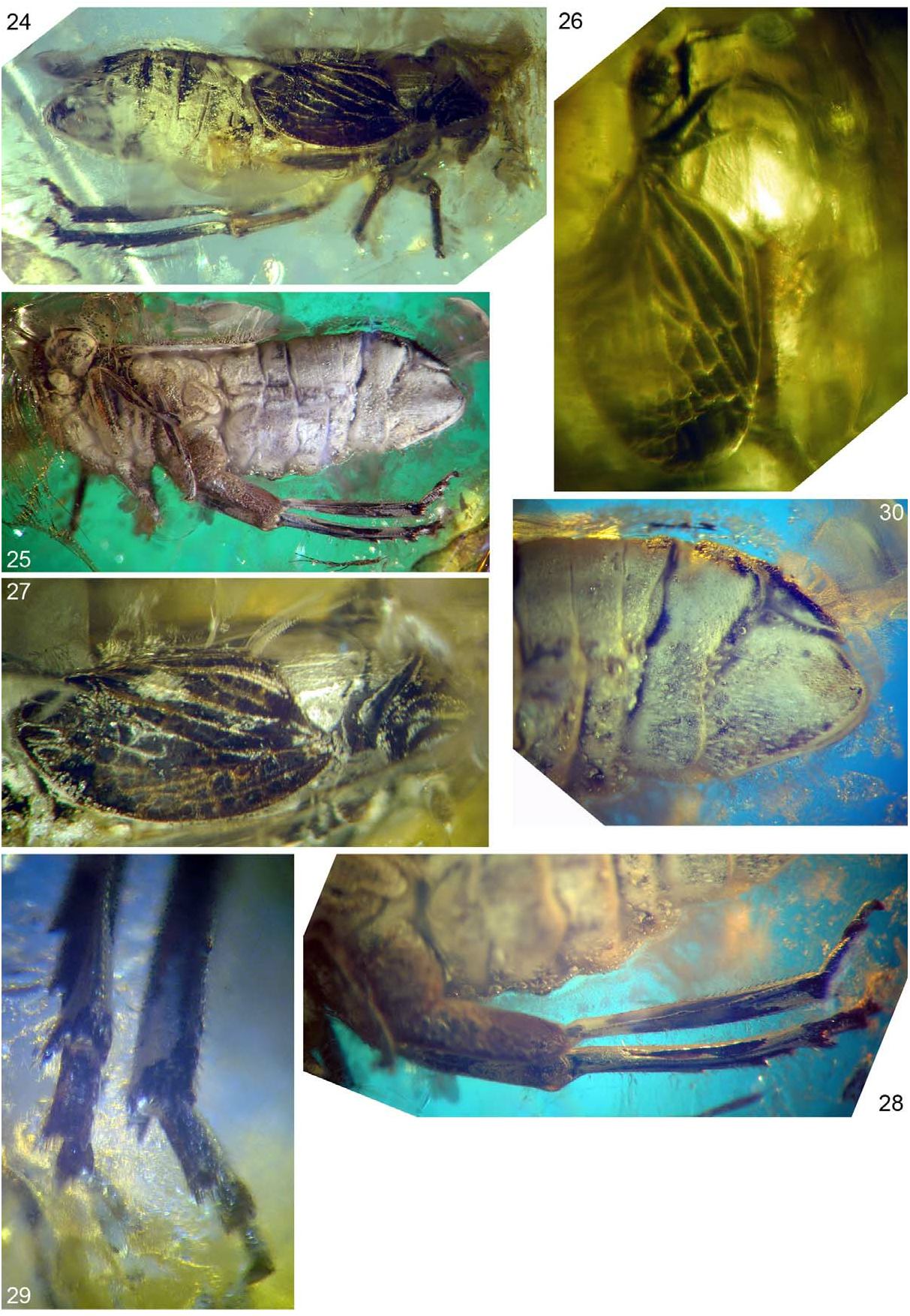
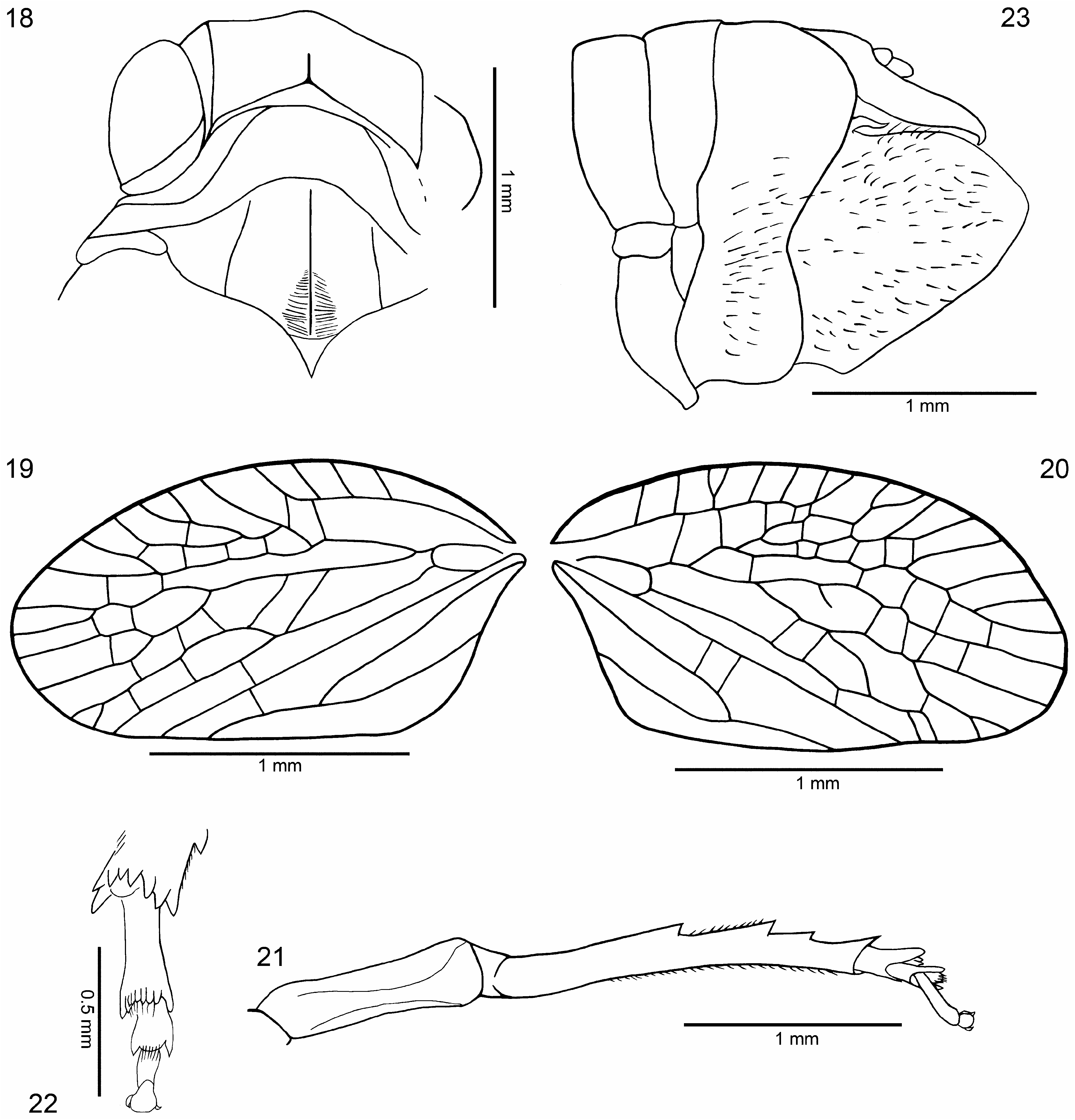
( Figs 18–30 View FIGURES 18–23 View FIGURES 24–30 )
Diagnosis. Disc of vertex with incomplete and weak median carina posteriorly, not reaching half of vertex length.
Description. Total length 5.33 mm, head with compound eyes 1.57 mm wide, length of vertex in mid line 0.28 mm, 0.35 mm at lateral margin, width of vertex 0.86 mm; length of frons in mid line 1 mm, 1.14 mm at lateral margin, length of postclypeus in mid line 0.67 mm, length of anteclypeus in mid line 0.5 mm, length of clypellus 0.14 mm, length of rostrum 0.93 mm, subapical segment 0.41 mm, apical segment 0.4 mm; length of second antennal joint 0.29 mm, length of antenna 0.78 mm.
Length of pronotum 0.28 mm, width of disc of pronotum 0.86 mm between anterolateral carinae at posterior margin, about 1.37 mm, length of mesonotum+scutellum 0.71 mm, width of mesonotum at base 1.2 mm.
Length of tegmen 2.05 mm, width of tegmen 1.05 mm; length of clavus 1.5 mm.
Profemur 1 mm long, fore tibia 0.86 mm, protarsus with claws 0.43 mm, first tarsomere 0.17 mm, mid tarsomere 0.17 mm, apical tarsomere 0.24 mm, tarsal claws 0.07 mm. Mesofemur 1 mm, mid tibia 1.14 mm, mesotarsus with tarsal claws 0.5 mm, basitarsomere 0.2 mm, mid tarsomere 0.2 mm, apical tarsomere 0.29 mm. Metacoxa 0.22 mm long, metatrochanter 0.22 mm long, metafemur 1 mm long, metatibia 1.8 mm long, 0.25 wide at apex, metatarsus with tarsal claws 0.64 mm long, basitarsomere 0.36 mm long, 0.16 mm wide at apex, midtarsomere 0.23 mm long, 0.13 mm wide at apex, apical tarsomere 0.23 mm long.
Abdomen with genital segment 3.33 mm long. Anal tube 1.07 mm long, 0.2 mm wide. Pygofer 1.43 mm high, 0.64 mm long at upper margin 0.4 mm long in the narrowest point, 0.47 mm near ventral margin, 0.36 mm in mid line at ventral margin. Genital style 1.07 mm long, 1.14 mm wide.
Tegmen length: width ratio 1: 1.95, claval apex reaching 0.73 of tegmen length. Clavus with veinlet between stem CuA and CuP, apicad of claval veins junction, free portion of vein Pcu measured from anterior claval angle to claval veins junction 1.8 times longer than common claval vein Pcu+A 1. Metatibio-tarsal formula 8: 2+(7): 2 (0); basitarsomere longer dorsally than wide between tips of outermost teeth (2.45: 1); mid tarsomere longer dorsally than wide between tips of outermost teeth (1.6: 1). Anal tube narrow, about 5 times as long as wide, with lateral margins subparallel, apical margin straight. Male genital style in lateral aspect, about as long as high, with small appendix on dorsal margin at level of pygofer apex, with indistinct lateral keel; apical margins thickened; covered with short, thick setae.
Terminal system of branches RA, RP and M forking disorganized, vary on left and right tegmen; veinlets on corium and membrane between longitudinal branches not regular, vary on left and right tegmen. Variability in tegminal venation and veinlets system of left and right tegmina as in figures.
Left tegmen. Stem Sc+R forked slightly anteriad of stem M forking and anteriad of stem CuA forking, branch ScRA 1 forked at level of stem M forking; branch RA forked twice reaching margin with three terminals; branch RP forked slightly basad of level of claval apex. Stem M forked at level of claval veins junction, branch M 1+2 forked at level of contact of fused claval veins with claval margin, branch M 1 reaching apex with two terminals, branch M 2 reaching margin with two terminals; branch M 3+4 fused for a long distance with branch CuA 1, basad of claval apex, then common branch forked slightly before apex. Stem CuA forked slightly apicad of claval veins junction, branch CuA 1 fused with M 3+4 then with M 4, branch CuA 2 not forked before apex. Claval vein Pcu and A 1 fused apicad of half of length of clavus.
Right tegmen. Stem Sc+R forked slightly apicad of claval veins junction, branch ScRA 1 forked at level of stem M forking; ScRA 1 forked before reaching the margin; branch RA forked before reaching the margin; branch RP forked twice before the margin, reaching it with three terminals. Stem M forked slightly apicad of claval veins junction, branch M 1+2 reaching the margin with as single terminal (but see discussion); branch M 3+4 forked at level of apex of costal area, branch M 3 forked just after the apex of clavus; branch M 4 fused with CuA 1 for a distance, reaching margin together with CuA 1. Stem CuA forked just before margin, slightly apical of claval apex. Claval veins Pcu and A 1 fused at about half of length of clavus.
Remarks. The venation of the right wing of P. aestiorum can be interpreted as described above or, alternatively, the stem M 1+2 is forked distinctly basad of the claval apex, with blind branch M 2. Another equally probable interpretation is that branch M 2 is “broken” and the distal portion of the branch M 2 is fused with M 3 for a distance with branch M 3 re-emerging at the level of claval apex.
Age and occurrence. Eocene, Baltic amber, for details see comments in the section on P. natangorum .
Etymology. The specific epithet is derived from the name of the people inhabiting the eastern Baltic Coast during the Antiquity – Aestii.
Material examined. Holotype, male, Nr. 373 B; collection of Mr. Carsten Gröhn, Glinde, Germany, to be deposited in the Geologisch-Paläontologisches Institut, Hamburg Universität, Germany. Left side covered with milky veil, abdominal segment exposed, very probably due to the activity of decaying gases. Syninclusions: a bunch of stellate hairs, very tiny apterous aphid.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |