Glomerida
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5164069 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/350B6716-0D2D-FFD2-FF71-F9F7FC7CF8BF |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Glomerida |
| status |
|
Order Glomerida View in CoL ( Fig. 9 View Figure 7-9 -12)
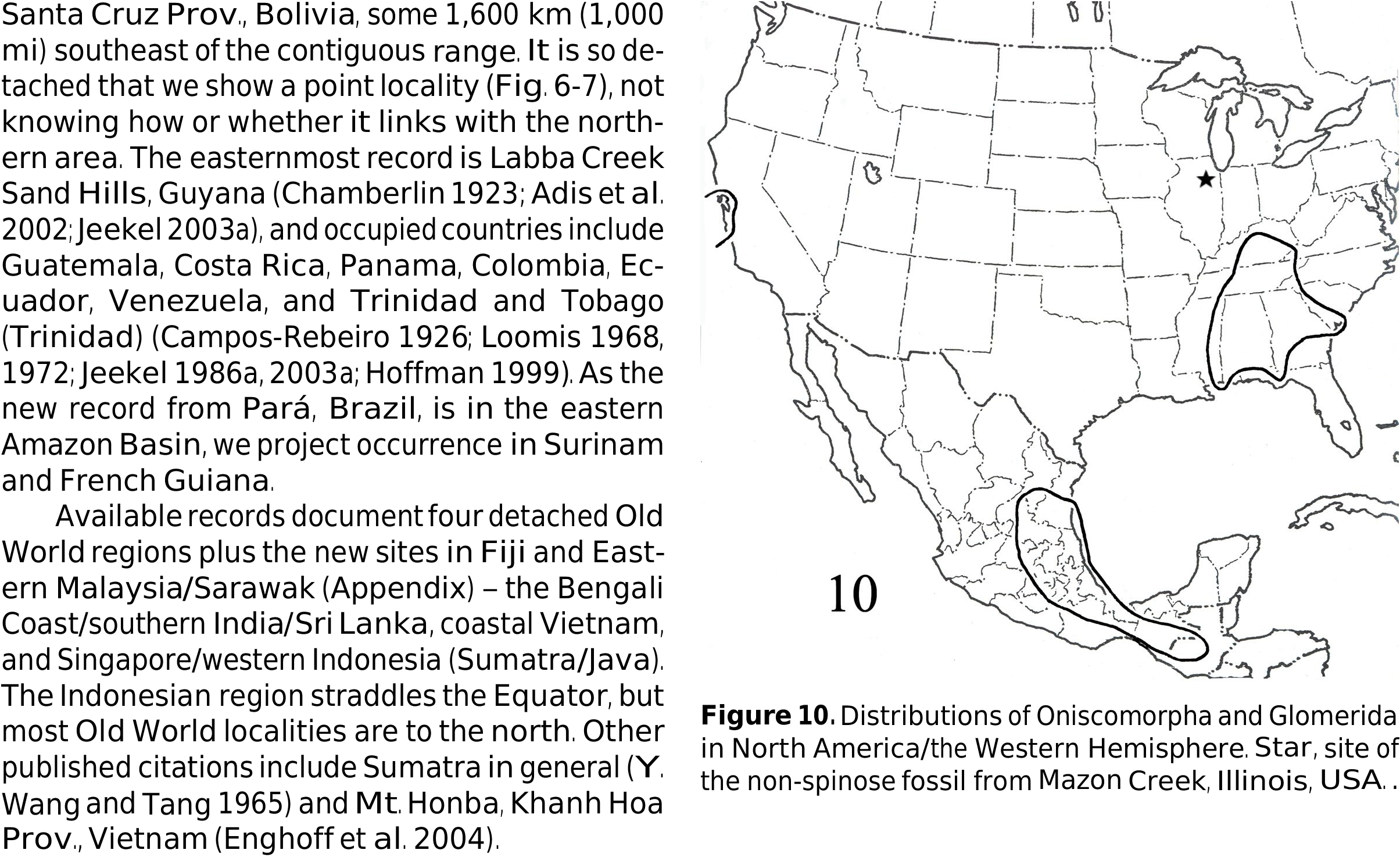
Glomerida are north temperate and tropical oniscomorphs that occupy six areas ( Fig. 9 View Figure 7-9 ), three each in the New and Old Worlds. Those in the former are widely segregated with the two in the US wholly north of the Tropic of Cancer and the other spanning this meridian over a swath of Mexico and Guatemala ( Fig. 10 View Figure 10 ). The Old World areas in Europe/North Africa and east/southeastern Asia are large and irregular, and the third is ovoid in Central Asia, primarily Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. The European region, eastwardly lobate, expands through Ukraine, indents slightly westward then spreads eastward again to the Caspian Sea and northwestern Iran; it also expands southward to Israel and, on the west, the Canary Islands. The southeast Asian region spans both the Tropic of Cancer and the Equator, extending roughly
from 40 oN in North Korea to 6 oS in Indonesia; over-
all, the northern limit is 60 oN in Norway. The
Central Asian area is equidistant from the others,
each of which points generally to it with a
subdactyliform extension. It therefore appears to
be a remnant of a prior connection of the Euro-
pean and southeast Asian faunas that ran along
the southern Laurasian/Eurasian border through
what is now the Himalayan region of northern
India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, and perhaps
lower mountain areas in Uzbekistan and north-
eastern Iran.
The US regions, separated by ~ 2,880 km (1,800
Figure 11. Distributions of Oniscomorpha and Glomerida mi), include an irregularly shaped one in the south-
in Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa.
east and a small one around San Francisco and
Monterey Bays, California. The former comprises
two unrevised genera – Onomeris Cook, 1896 , with two species, and the monotypic Trichomeris Loomis, 1943 – but the actual number of genera and species is unknown and surely substantially larger. A taxonomic study of southeastern glomerids is a major need in Nearctic diplopodology that can largely be accomplished with VMNH material, where the great majority of samples are housed. The area extends ~ 816 km ( 510 mi) in both dimensions, ranging, north-south, from the Ohio River in central Kentucky to the Florida panhandle and Gulf Coast of Alabama / Mississippi and, east-west, from the Atlantic Coast of Georgia / South Carolina to eastern Mississippi. It covers parts of nine states and essentially all of Alabama ( Fig. 10 View Figure 10 ), and we provide records in the Appendix. The unknown but non-spinose, glomeridan-like, onicsomorph fossil from Illinois is compatible with the present area, lying just to the north. It may therefore represent an ancestral form from the radiation that occurred when Laurentia collided with Baltica+Siluria in the early Silurian.
The Californian and Mexican regions harbor 17 species of Glomeroides ( Chamberlin 1922b) , but only G. primus ( Silvestri, 1929) occupies the former, a narrow coastal strip ~ 240 km ( 150 mi), north/south, and 56 km ( 35 mi), east/west. We add new records
(Appendix) to the three published localities – Mill
Valley and S.P. Taylor State Park, Marin Co.,
and Pfeiffer Big Sur State Park, Monterey Co.
( Silvestri 1929, Shear 1986, Hoffman 1999).
The Mexican area, primarily south of the
Tropic of Cancer, is ~ 1,306 km ( 816 mi) long,
304 km ( 190 mi) wide, and extends from south-
ern Nuevo León / Tamaulipas, Mexico, to Alta and
Baja Verapaz Depts., Guatemala. Sixteen species
have been described from this region, eight known
only from caves, and we add records in the Ap-
pendix to those reported by Shear (1982, 1986),
Hoffman (1999), and Bueno-Villegas et al. (2004).
The European distribution follows Kime
(2000), to which we add the Caucasus region, the
Middle East, Mediterranean Islands, coastal
northwestern Africa, and the Canary Islands ( Fig. View Figure 7-9
9, 11). Works with or without maps cover the
Balearic Islands ( Mauriès and Vicente 1976), Brit-
ish Isles ( Blower 1985), Canary Islands ( Golovatch
1987a, Golovatch and Enghoff 2003), Caucasus
( Golovatch 1989a, b, 1990b), Cyprus and Greece
( Mauriès and Karamaouna 1984; Thaler 1987, Figure 12. Distributions of Oniscomorpha and Glomerida 2000 ), Iran ( Golovatch 1981a, 1989a, b, 1990b; in Central Asia.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.