Amphoriscus semoni Breitfuss, 1896
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4426.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:18929E20-5296-4458-8A8A-4F5316A290FD |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5966762 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/386CC616-DCF3-A5B2-FF67-8C5CFC6DFA1C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Amphoriscus semoni Breitfuss, 1896 |
| status |
|
Amphoriscus semoni Breitfuss, 1896 View in CoL
Figs 80a–e View FIGURE 80 , 81a–d View FIGURE 81
Amphorisus semoni Breitfuss, 1896: 435 View in CoL ; Breitfuss 1898: 221; Van Soest & De Voogd 2015: 93, figs 68a–f.
Material examined. ZMA Por. 10527, Seychelles, NE of Aride Island, 4.1667°S 55.7333°E, depth 55 m, Agassiz trawl, coll. R.W.M. van Soest, field nr GoogleMaps . NIOP-E stat. 714/ 01, 19 December 1992.
Description. The sample consists of a dozen small thin tubes ( Fig. 80a View FIGURE 80 ), which are mostly loose, but two tubes are attached together to a small stone. It is likely the tubes were in contact on the substratum. Live color reported as white, in alcohol they become beige. Size of individual tubes 1–3 cm high, 5–9 mm in diameter. Apical oscules naked. Consistency soft.
Aquiferous system. Syconoid.
Skeleton. ( Figs 80b–e View FIGURE 80 ) Inarticulate ( Fig. 80b View FIGURE 80 ). The cortical skeleton ( Figs 80c–d View FIGURE 80 ) is formed by the unpaired and paired actines of giant tetractines. The apical actines of the ectosomal tetractines form the choanosomal skeleton together with the unpaired actines of subatrial sagittal triactines. The subatrial skeleton is formed by the paired actines of sagittal triactines and all actines of smaller triactines. The atrial skeleton ( Fig. 80e View FIGURE 80 ) is formed by small tetractines, the apical actines of which protrude into the atrial lumen.
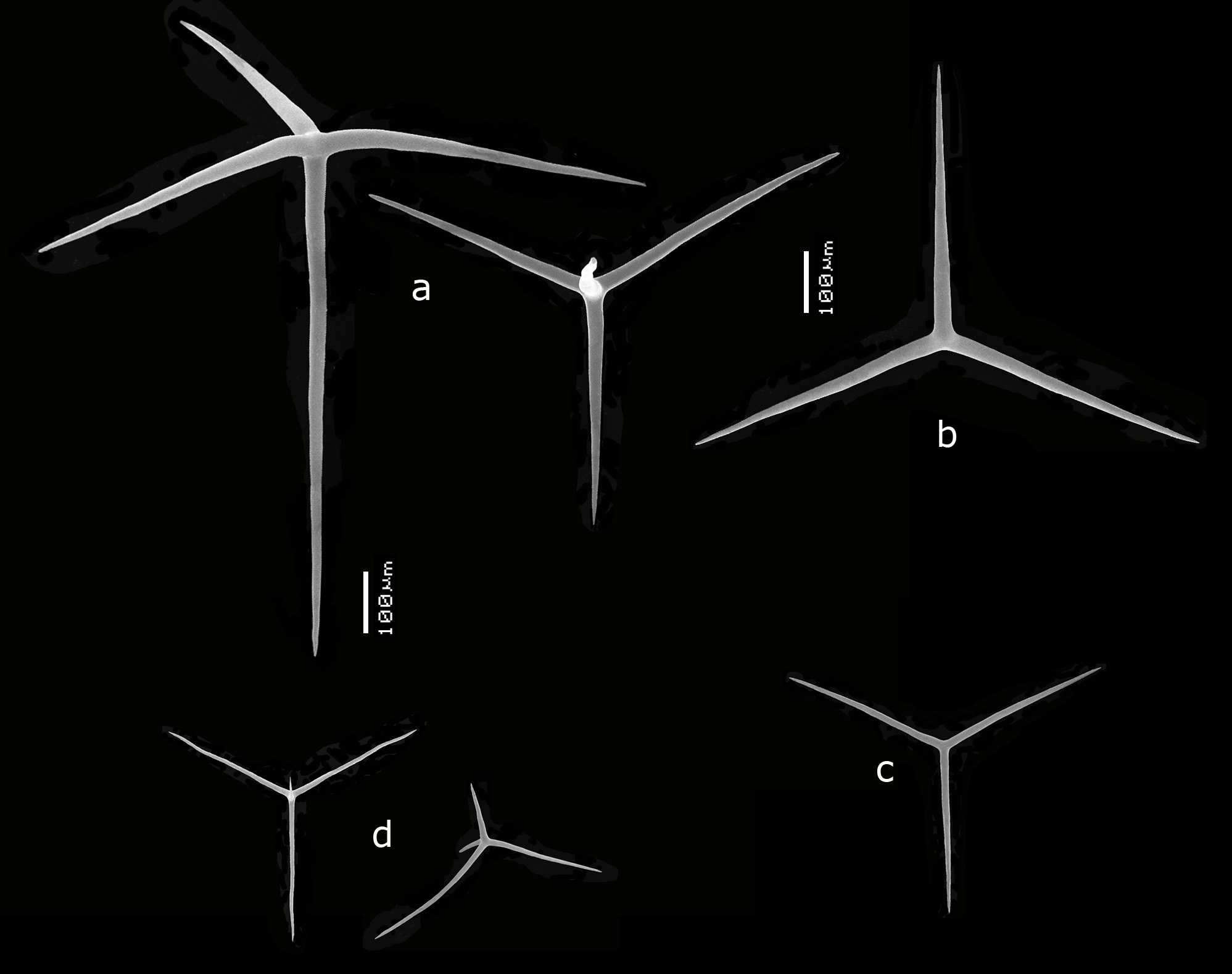
Spicules. ( Figs 81a–d View FIGURE 81 ) Giant tetractines, triactines, small tetractines.
Giant tetractines ( Fig. 81a View FIGURE 81 ), with straight or curved actines of rather variable length and thickness, unpaired actines 162– 264 –487 x 12 – 20.1 –31 µm, paired actines 210– 336 –552 x 12 – 21.1 –29 µm, apical actines 239– 425 –882 x 13 – 21.8 –31 µm.
Triactines ( Figs 81b–c View FIGURE 81 ), divisible in overlapping larger and smaller spicules:
Large triactines ( Fig. 81b View FIGURE 81 ), sagittal, usually with unpaired actines slighty shorter; unpaired actines 200– 266 –342 x 13 – 14.8 –18 µm, paired actines 279– 309 –336 ≈ 12– 13.3 –15 µm.
Small triactines ( Fig. 81c View FIGURE 81 ), slightly sagittal, unpaired actines 48– 137 –180 x 7 – 9.4 –14 µm, paired actines 88– 178 –246 x 6 – 8.8 –11 µm.
Small tetractines ( Figs 81d View FIGURE 81 ), sagittal, often with curved or wobbly paired actines; unpaired actines 81– 150 –241 x 7 – 9.4 –11 µm, paired actines 121– 214 –269 x 7 – 9.8 –12 µm, apical actines 15– 54 – 94 x 3 – 5.2 –7 µm.
Distribution and ecology. Indonesia, Seychelles, shallow-water down to 55 m.
Remarks. We assign this material to the Indonesian species A. semoni because of overall similarity with recently described material (cf. Van Soest & De Voogd 2015). However, there are several discrepancies: the tubes of the Indonesian ZMA Por. 0 8073 were described as green in life, and they also appeared slightly different in shape as their diameter gradually narrowed down towards the substratum, whereas our present specimens were white in life and and remain cylindrical over most of their length. The apical actines of the giant tetractines of the Indonesian specimens penetrated through the atrial wall, which we do not observe in the present specimens. We consider these differences as minor and subject to variation.
The South African Amphoriscus kryptoraphis Urban, 1908 , from deeper water ( 155 m) differs from the above a.o. by the possession of trichoxeas. Unfortunately, our attempt to obtain partial 28S sequences failed.
| ZMA |
Universiteit van Amsterdam, Zoologisch Museum |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Amphoriscus semoni Breitfuss, 1896
| Van, Rob W. M. & De, Nicole J. 2018 |
semoni
| Breitfuss, 1896 : 435 |