Dasypoda (Microdasypoda) Michez, 2004
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5188.1.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:4E9B2842-2454-4CA6-9E2F-86693CCFE663 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7105569 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3A393D28-FFED-FFD4-FF6D-DF8E9FE1FC57 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Dasypoda (Microdasypoda) Michez, 2004 |
| status |
|
Key to the males of Dasypoda (Microdasypoda) Michez, 2004
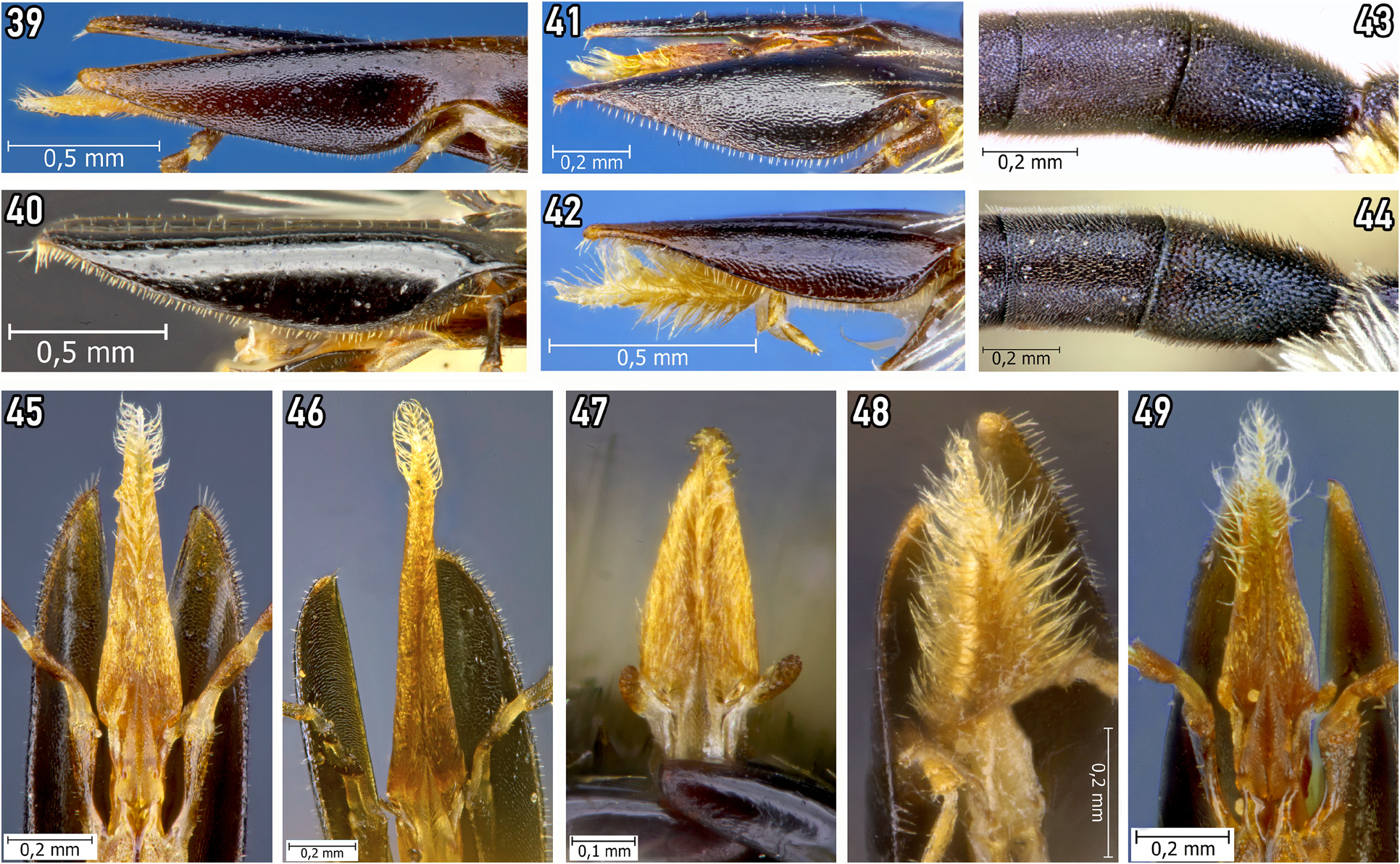
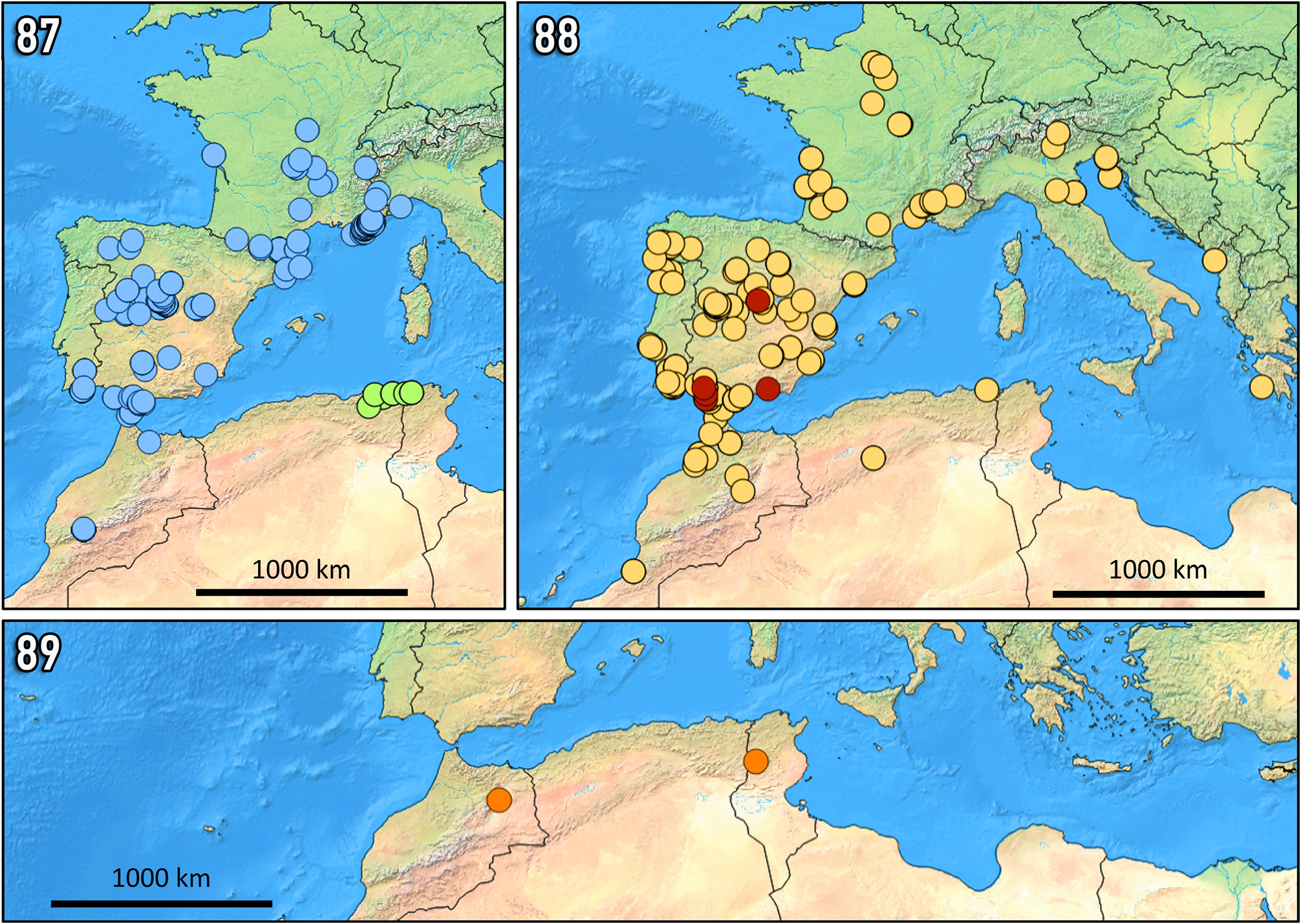
1. Galea black, smooth, polished, shiny, with very sparse punctures ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 39–49 ). Glossa narrow and relatively long, 5 times as long as wide ( Fig. 46 View FIGURES 39–49 ). S6 with brown apical pilosity directed laterally ( Figs 51, 56 View FIGURES 50–64 ). Marginal edge of S6 strongly bent outside ventrally, especially at the lateral angles ( Fig. 56 View FIGURES 50–64 ). S7 marginal part deeply notched centrally, its lateral apodemes relatively short ( Fig. 61 View FIGURES 50–64 ). Dorso-apical part of S8 with two wide, partly separated outgrowths ( Fig. 71 View FIGURES 65–86 ); lateral apodemes before pregladular area of this sternum rectangularly widened on the sides ( Fig. 66 View FIGURES 65–86 ). Gonostylus strongly widened and not rounded apically; inner basal part of gonostylus with very short tooth; penis valvae narrower than gonostylus ( Figs 76, 82 View FIGURES 65–86 ). Mid and hind legs with the last article often yellow. Distribution: species mostly distributed in the western part of the Mediterranean basin ( Fig. 88 View FIGURES 87–89 )............................................................................. Dasypoda cingulata Erichson, 1835 View in CoL
– S6 with apical pilosity directed radially ( Figs 50, 52–54 View FIGURES 50–64 ). Latero-apical angles of S6 flat, not curved outward ventrally ( Figs 55, 57–59 View FIGURES 50–64 ). Dorso-apical part of S8 with entire transverse carina ( Figs 70, 72, 74 View FIGURES 65–86 ) or with two semicircular, completely separated outgrowths ( Fig. 73 View FIGURES 65–86 ); lateral apodemes before pregladular area of this sternum more beveled on the sides ( Figs 65, 67–69 View FIGURES 65–86 ). Inner basal part of gonostylus with longer tooth or lobe-like projection, or penis valvae are wider than gonostylus. Galea brown to dark brown, tightly covered with small tubercles that in some places form the thin wavy striae ( Figs 9 View FIGURES 1–13 , 39, 41, 42 View FIGURES 39–49 ). Glossa wider and relatively shorter, 2.5-3.5 times as long as wide ( Figs 45, 47–49 View FIGURES 39–49 ). Mid and hind legs with last article brown to black .................................................................................................... 2
2. Marginal part of S6 very slightly notched centrally and with white pilosity ( Figs 53, 58 View FIGURES 50–64 ). Apical third of S7 strongly widened, its marginal part slightly notched centrally ( Fig. 63 View FIGURES 50–64 ); dorso-apical part of S8 with two deeply separated semicircular outgrowths ( Fig. 73 View FIGURES 65–86 ). Penis valves narrower than gonostyle; inner basal part of gonostylus with a long spine-like tooth ( Figs 78, 84 View FIGURES 65–86 ). Pilosity of the body silver-white. Distribution: species endemic to central and southern Spain ( Fig. 88 View FIGURES 87–89 )......................................................................................... Dasypoda iberica Warncke, 1973 View in CoL
– Marginal part of S6 strongly triangularly notched centrally, forming two separate projections covered with a brown pilosity ( Figs 50, 52, 54 View FIGURES 50–64 ). Apical third of S7 narrowed, its marginal part strongly notched centrally ( Figs 60, 62, 64 View FIGURES 50–64 ); dorso-apical part of S8 with entire transverse carina very slightly notched centrally ( Figs 70, 72, 74 View FIGURES 65–86 ). Inner basal part of gonostylus with a small tooth or bilobed without a long spine-like tooth. Penis valves as wide as the gonostyle ( Figs 75, 77, 79 View FIGURES 65–86 ). Pilosity of the body mostly yellowish to brownish............................................................................ 3
3. Face with a patch of pure white hairs surrounded by a pure black pilosity. S6 apical projections with right angles on the inner edges ( Figs 52, 57 View FIGURES 50–64 ). Gonostylus narrowed at apex, lanceolate, with a small tooth at the base ( Figs 77, 83 View FIGURES 65–86 ). Distribution: species bound to the western part of the Mediterranean basin ( Italy, France , Spain, Portugal and Morocco; Fig. 87 View FIGURES 87–89 )...................................................................................... Dasypoda crassicornis Friese, 1896 View in CoL
– Hair of the face with a different colour pattern. Apical projections of S6 with rounded angles on the inner edges ( Figs 50, 54 View FIGURES 50–64 ). Gonostyli bilobed without spine-like tooth at the base ( Figs 75, 79 View FIGURES 65–86 )............................................. 4
4. 1 st flagellomere relatively shorter, conical, 1.4 times as long as wide at the apex ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES 39–49 ). Face with a yellowish pilosity intermixed with black hairs especially on the paraocular areas. Apical projections of S6 with rounded angles on the outer edges ( Fig. 55 View FIGURES 50–64 ). S8 not notched laterally before the widened basal part ( Fig. 65 View FIGURES 65–86 ). Gonostylus with a well-developed internal lobe strongly thickened in the middle and with very dense long pubescence on the side facing the penis valvae; external lobe rounded at the top ( Figs 75, 80, 81 View FIGURES 65–86 ). Distribution: species only recorded in the northern parts of Algeria and Tunisia ( Fig. 87 View FIGURES 87–89 )............................................................................. .. Dasypoda brevicornis Pérez, 1895 View in CoL
– 1 st flagellomere relatively longer, partly cylindrical in apical half, 1.7 times as long as wide at the apex ( Fig. 44 View FIGURES 39–49 ). Face with a white pilosity except vertex and adjacent parts that intermixed with black hairs. Apical projections of S6 with right angles on the outer edges ( Fig. 59 View FIGURES 50–64 ). S8 deeply notched laterally before the widened basal part ( Fig. 69 View FIGURES 65–86 ). Inner lobe of gonostylus widened in a circular shape and flat at the apical half, racquet-like with a widened base, and covered with very sparse long setae on surface facing penis valves; external lobe of gonostylus wide, its apex oblique truncated ( Figs 79, 85, 86 View FIGURES 65–86 ). Distribution: species currently known from Morocco and Tunisia ( Fig. 89 View FIGURES 87–89 )................ Dasypoda schwarzi Radchenko & Michez sp. nov.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Apoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |