Heteromys catopterius, Anderson & Gutierrez, 2009
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6611160 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6607902 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3C3D87A6-874A-B110-1B9E-57C7FD32F335 |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Heteromys catopterius |
| status |
|
Overlook Spiny Pocket Mouse
Heteromys catopterius View in CoL
French: Souris-a-ajaboues de la Costa / German: Aragua-Stacheltaschenmaus / Spanish: Raton espinoso de altura
Taxonomy. Heteromys catopterius R. P. Anderson & Gutiérrez, 2009 View in CoL ,
Rancho Grande, Near Biological Station, 13 km NW Maracay, 10°21'N, 67°40'W, 1090 m, Aragua, Venezuela.
With the exception of H. desmarestianus in the north-western corner of Colombia, the South American spiny pocket mice all belong to the anomalus species group: H. anomalus , H. catopterius , H. oasicus , H. australis , and H. teleus . Only H. australis exists outside of South America, in eastern Panama. Monotypic.
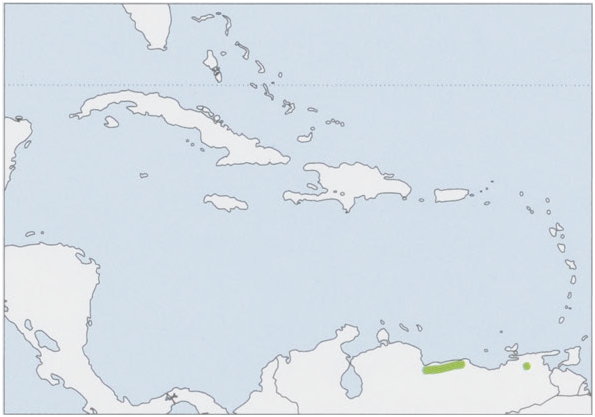
Distribution. NC & NE Venezuela (Cordillera de la Costa, 350-2425 m). View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body mean 132 mm, tail mean 166 mm, ear mean 19 mm, hindfoot mean 36 mm. No specific data are available for body weight. There is no significant secondary sexual dimorphism. The Overlook Spiny Pocket Mouse is a scansorial rodent, medium-sized for the genus, with coarse adult pelage having abundant stiff, flattened spine-like hairs on dorsal and lateral surfaces of body. It is typically moderately spiny but soft in some populations. Upper parts are dark slate gray or black, interspersed with dark spines and ocherous hairs. There is no buffy lateral line, and belly is white. Distinctive patch of dark color occurs on dorsal and external surfaces of forearms. Ears are moderately large, dark gray to blackish. Posterior parts of soles of hindfeet are naked. Tail is moderately haired, strongly bicolored (darker on upper part), and relatively long. Cheekteeth have high crowns, and lower premolar has 3-4 lophids. Auditory bullae are only moderately inflated. Chromosomal complement has 2n = 60 and FN = 68. Compared with the dark slate gray dorsal pelage, only moderately grizzled with ocherous hairs and a gray or black patch on forearm in the Overlook Spiny Pocket Mouse, the Trinidad Spiny Pocket Mouse ( H. anomalus ) with which it comes into contact in several areas has a palebrown dorsal pelage, strongly grizzled with ocherous hairs and paler, brownish patch on forearm and distinctive rounded ears. The Overlook Spiny Pocket Mouse also has longer, darker mystacial vibrissae. Skull of the Overlook Spiny Pocket Mouseis larger and relatively wider, with a more inflated braincase, wider interorbital constriction, and relatively wider interparietal. Incisive foramina tend to be wider, often short, and anteriorly tapering compared with longer, thinner, and more parallel-sided foramina of the Trinidad Spiny Pocket Mouse.
Habitat. Deciduous and evergreen forested habitats, including cloud forest, but not grassy and brushy areas. The Overlook Spiny Pocket Mouse occurs in upper elevations of the Cordillera de la Costa of north-central and north-eastern Venezuela, 350-2425 m but usually above 700 m. It has been found in all four major subranges of the Cordillera: main Aragua-Carabobo chain, El Avila massif, Serrania del Interior, and Macizo Oriental. In a cloud forest, the Overlook Spiny Pocket Mouse was associated with areas of palms, in rock or bamboo cover, and was commonly trapped at bases of palms. While commonly taken in bamboo and rock cover, it was rarely found in grass or other microhabitats. The Overlook Spiny Pocket Mouse occupies higher, wetter, more mature, and less disturbed habitats than the Trinidad Spiny Pocket Mouse where they occur in very narrow zones of sympatry. At two such zones, one and two specimens (respectively) were morphologically intermediate and perhaps represented hybrids between the species. The two species are largely parapatric.
Food and Feeding. In captivity, the Overlook Spiny Pocket Mouse will eat a variety of native and exotic foods, including corn, avocados, tomatoes, bread, rolled oats, cabbage, and cheese. Native foods include nuts of stilt palms (/riartea Arecaceae ) and likely a variety of seeds, green vegetation, fruits, and insects. Food is transported in external, furlined cheek pouches.
Breeding. Reproductive activity probably peaks in April-May, corresponding to onset of the rainy season. Litter sizes are 1-3 young, and young at birth weight an average of 3-3 g. Weaning occurs at ¢.48 days.
Activity patterns. The Overlook Spiny Pocket Mouse is typically nocturnal.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. Captive adult male Overlook Spiny Pocket Mice, but not adult females or juveniles, exhibited aggression toward humans. A clear dominance structure was observed in captive individuals, with adult males aggressive toward females unless females were in estrus, and dominant over adult females and juveniles; adult females were dominant over juveniles of both sexes. Dominance among adult males was determined after brieffights.
Status and Conservation. The Overlook Spiny Pocket Mice has not been assessed on The IUCN Red List.
Bibliography. Anderson & Gutiérrez (2009).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Castorimorpha |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Heteromys catopterius
| Don E. Wilson, Thomas E. Lacher, Jr & Russell A. Mittermeier 2016 |
Heteromys catopterius R. P. Anderson & Gutiérrez, 2009
| Anderson & Gutierrez 2009 |