Geddesia quadrata, Harris, 2014
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.3853/j.2201-4349.66.2014.1596 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3E5087BB-FFFC-3737-FE8A-FF3AFC7BE2DB |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Geddesia quadrata |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Geddesia quadrata sp. nov.
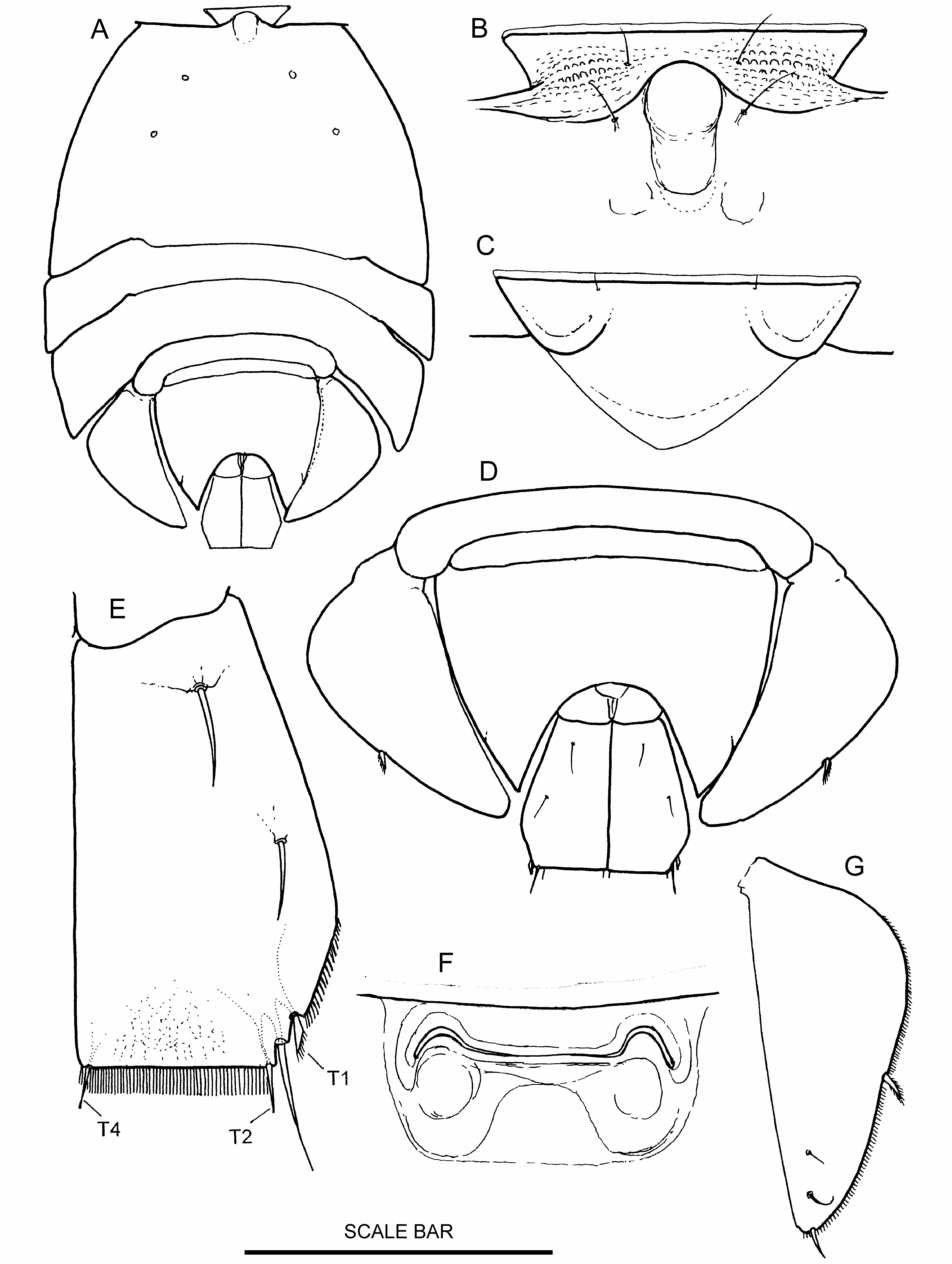
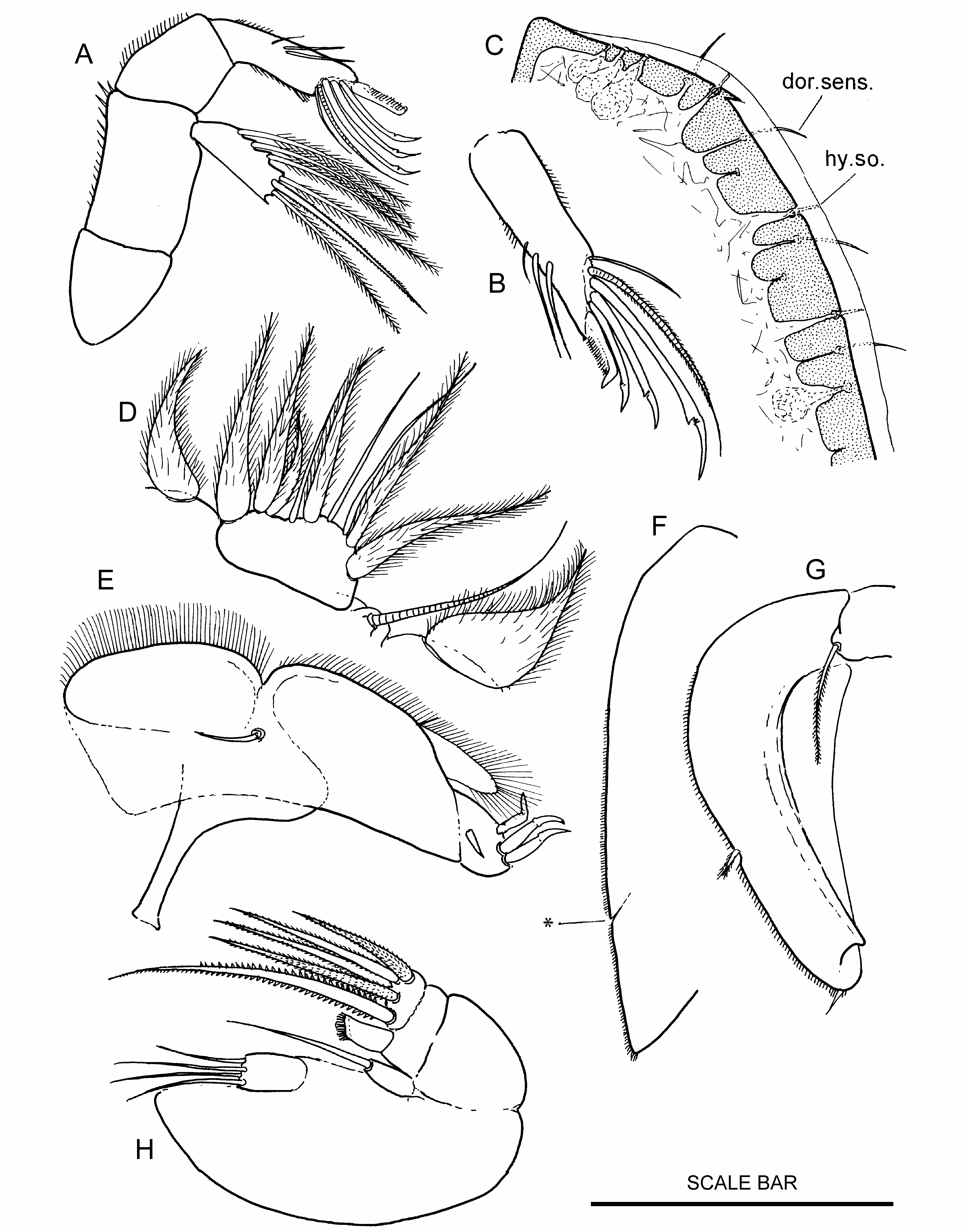
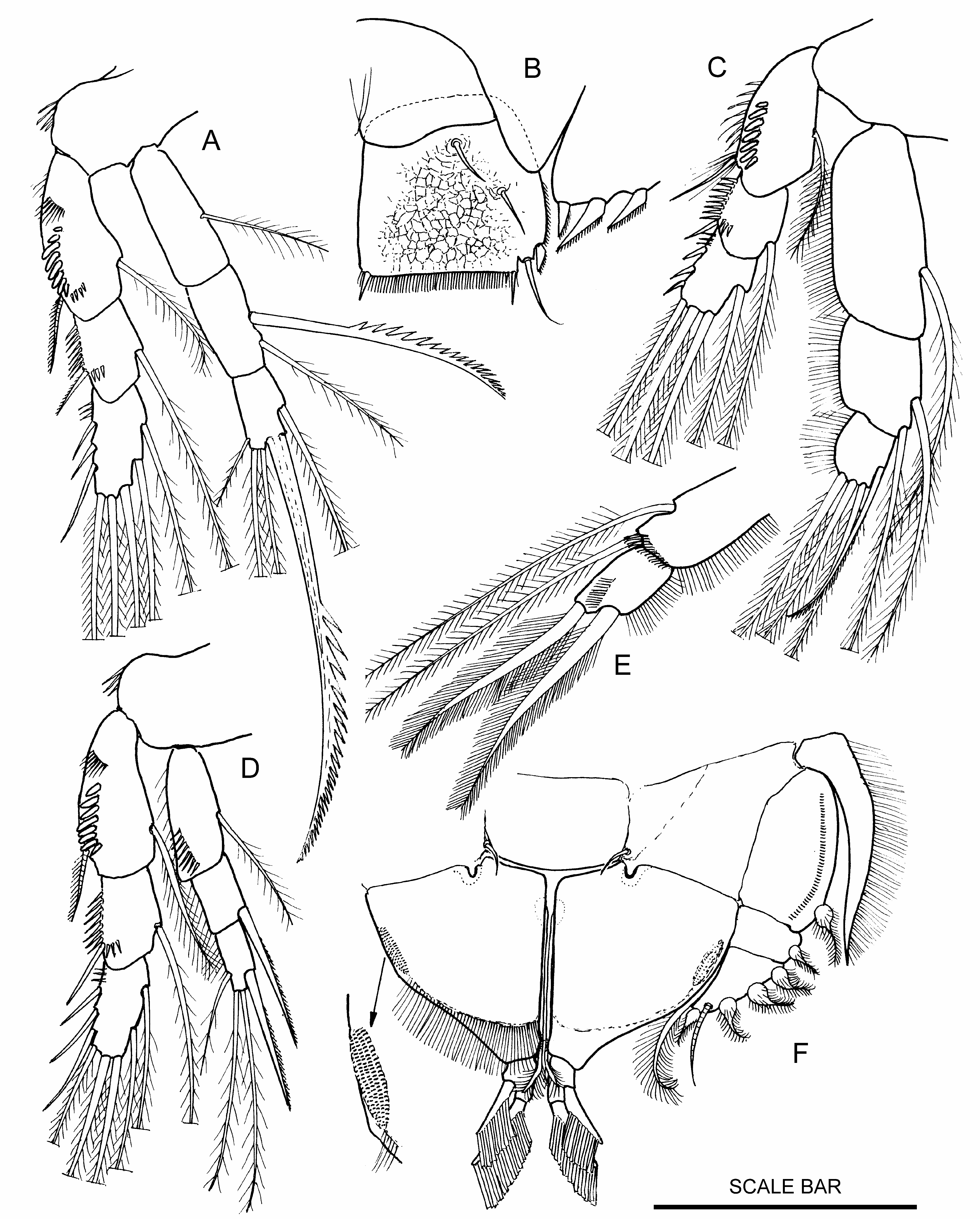
Figs 6–9 View Figure 6 View Figure 7 View Figure 8 View Figure 9
Type material. HOLOTYPE, adult male, length 0.86 mm, P81221 ; ALLOTYPE, adult female, length 1.06 mm, P81222 (both mounted on slide), deposited at AM, Sydney . PARATYPE female mounted on slide and deposited at NHM, London.All collected from seagrass ( Zostera sp?), Green Island , Great Barrier Reef, Queensland, Australia (16°41' S 45°56' E), V. A. Harris, 1973 .
Diagnosis. Female cephalosome hemi-ellipse sharply truncated, anterior edge straight, clear area (lens) above rostrum; male cephalosome deeplY concave anteriorlY; α and β setae on male caudal ramus and terminal setae T1, T2, T4, all verY short (<1/4 width of ramus); area of denticulate setules on P1 endopod resemble maize corn cob; male P2 with two terminal setae on endopod; falciform ventral ridge on female P5 exopod with deep posterior (apical) notch; female length 1.06 mm, colour yellow.
Biometric data. Females (N = 4): maximum length ( Lmax) 1.06 mm, body length ( Lurs) 0.98 mm; cephalosome width (W) mean 0.75 mm; rostrum width 0.16 mm; genital doublesomite width 0.33 mm, length 0.22 mm; caudal ramus length 0.15, width 0.08 mm.
Ratios: Lurs / W 1.3, W/R 4.7; genital double-somite w/l 1.5, arch 50% of length; caudal ramus 15% of Lurs, l/ w 1.8, Hicks’ index for α 80%, β 50%.
Males (N = 3): length ( Lmax) 0.86 mm [ 0.90 mm *], body length ( Lurs) 0.81 mm [ 0.85 mm *]; cephalosome width 0.70 mm, length 0.47 mm [ 0.50 mm *]; antennule fully extended 0.21 mm; spermatophore 0.21 × 0.09 mm. [* = Measured from shoulder. Due to the deeply concave anterior border of the male cephalosome, the length measured from the rostrum is very much shorter.]
Ratios: Lmax / W 1.2 [ 1.28 mm] cephalosome length 55% of Lmax; caudal ramus l/ w 1.0; antennule 23% of Lmax, segment 3+4 38%, dactYlus 27% of antennule length; spermatophore 25% of Lmax.
Description. Adult females ( Fig. 6A View Figure 6 ; Plate 1D, p. 172): colour lemon yellow, cephalosome hemi-ellipse strongly truncated anteriorly with small epaulette at shoulder, rostrum prominent ( Fig. 6B, C View Figure 6 ) with clear lens-like structure dorsal to rostrum. Dorsal pits very small ( 2 µm) near edge of cephalosome, hyaline border clear, 15 µm wide ( Fig. 7C View Figure 7 ). Labrum without setules or ridge plates. Genital doublesomite ( Fig. 7D View Figure 7 ) narrow (less than 1/2 width of bodY), verY small notch marks boundary between anterior and posterior lobes ( Fig. 7F View Figure 7 marked with *), posterior lobe about 1/4 length of anterior lobe, acutely pointed posteriorly, lateral edge with verY short border setules, arch less than 1/2 length of genital double-somite. Genital opening ( Fig. 6F View Figure 6 ). Caudal ramus ( Fig. 6E View Figure 6 ) pentagonal, widens posteriorlY, maximum width 2/3 down ramus, dorsal surface with fine reticulation. Bevelled edge with setules, posterior edge straight, 3/4 of maximum width, 90° to medial edge, posterior border setules conspicuous. Beta seta half waY down ramus, T1, and γ close together near posterior end of bevelled edge, T3 absent, T4 small at medial corner. Structure and setation of mouthparts and ambulatory limbs tYpical of familY.Antenna ( Fig. 7A, B View Figure 7 ) with fine setules along edge of basis and endopod segment 1, exopod with five plumulose setae and one serrulate spinous seta, geniculate setae on endopod segment 2 with plain terminal section, claw comb-like. Setae on mandible endopod unusually long ( Fig. 7D View Figure 7 ). Maxillule with six setae on endopod. Claw on maxilla with distal edge comb-like ( Fig. 7H View Figure 7 ). Maxilliped ( Fig. 7E View Figure 7 ). P1 ( Fig. 8F View Figure 8 ), exopod segment 1 with single row of denticles parallel to edge, endopod segment 1 short, broad (w/l = 0.9) with elongate patch of denticulate setules that resemble maize corn cob at lateral end of fimbriate crescent. Setules along external edge of segment 1 on P2, P3 and P4 exopods unusually strong ( Fig. 8A, C, D View Figure 8 ). Serrate spinous seta on segment 2 of P3 endopod strong, almost as long as endopod (0.9:1), large serrate spinous seta on segment 3 longer than endopod (1.35:1, Fig. 8A View Figure 8 ). Seta on endopod of P4 segment 2 and internal seta of segment 3 strong serrulate spinous setae 1/2 length of endopod ( Fig. 8D View Figure 8 ). P5 exopod ( Fig. 6G View Figure 6 ) lanceolate, apex rounded (not acute), apical end of ventral falciform ridge terminates in notch ( Fig. 7G View Figure 7 ), two dorsal and one apical seta present (not pinnate), P5s extend beyond genital double-somite but are separated by full width of caudal rami. Females carry six eggs.
Adult males ( Fig. 9A View Figure 9 ), colour lemon yellow, cephalosome truncated hemi-ellipse, posterior half of body semi-circular. Anterior of cephalosome strongly concave, convex medial prominence above rostrum with clear, lens-like, structure in rostrum ( Fig. 9D View Figure 9 ), small epaulette present ( Fig. 9B View Figure 9 ). Dorsal pits and hyaline border as for female. Caudal ramus ( Fig. 8B View Figure 8 ) square (l/w = 1), dorsal surface with reticulate markings, lateral edge slightly convex with border setules along posterior half, α and β setae about 1/4 width of ramus or less, β seta half waY down ramus. Medial corner 90° with T4 at corner, setae T1 and γ recessed at lateral corner (no bevelled edge), T3 absent, posterior border straight with conspicuous row of setules, distance between T2 and T4 80% of ramus width. Antennule ( Figs 9E, F View Figure 9 ) without denticle or comb on segment 3, prominent peg-like ventral process present (marked * on figures), segment 4 with two small serrated denticles and two bulbous structures ( Fig. 9E, F View Figure 9 ). Dactylus cylindrical, as long as segment 3+4.Two plumose terminal setae on P2 endopod ( Fig. 8E View Figure 8 ), setae on P4 endopod plumose (not spinous). P5 exopod ( Fig. 9C View Figure 9 ) trapezoidal, lateral seta same size and shape as five terminal setae, row of 20 ventral setules, no setules at base of terminal setae. Spermatophore 1/4 length of bodY.
Etymology. The specific name refers to the straight posterior border of the caudal ramus which makes an angle of 90° with the medial edge, (L. quadratus = made square).
Remarks. The female animal described by Geddes (1968) as Porcellidium trisetosum lacks the T3 seta on its caudal ramus and the female cephalosome is truncated anteriorly: two features that exclude it from the genus Porcellidium . The male antennule is not described, but the maxillule is stated to be the same as Sars (1904) described for P. fimbriatum , which has six setae on the endopod. Therefore, Geddes’ trisetosum fits the diagnosis of Geddesia and should be moved to that genus as Geddesia trisetosa ( Geddes, 1968) comb. nov.
The latter differs from G. quadrata in the following features: size of female ( Lmax 0.78 mm), colour (red-brown), male P2 endopod with three terminal setae, female Hicks’ index for α 70%, length of spinous setae on female P4 endopod as long as endopod, male P5 with setules at base of each terminal seta.
Distribution. Type series collected from sea grass Zostera capricornia on the reef side of Green Island, Cairns, Great Barrier Reef, Australia, 6 ♀♀, 2 carrYing eggs, 8 ♂♂, 2
juveniles, V. A. Harris, 1973. Geddes’ animals come from the Bahamas.
| AM |
Australian Museum |
| V |
Royal British Columbia Museum - Herbarium |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.