Pseudokanakia
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4092.3.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:F7969BB5-D279-439E-8EC0-3BAAF23D3B8F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6070298 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/427887EF-EC0F-BB0A-97C6-FB6B4BA2587D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Pseudokanakia |
| status |
gen. nov. |
PSEUDOKANAKIA Delorme View in CoL gen. nov.
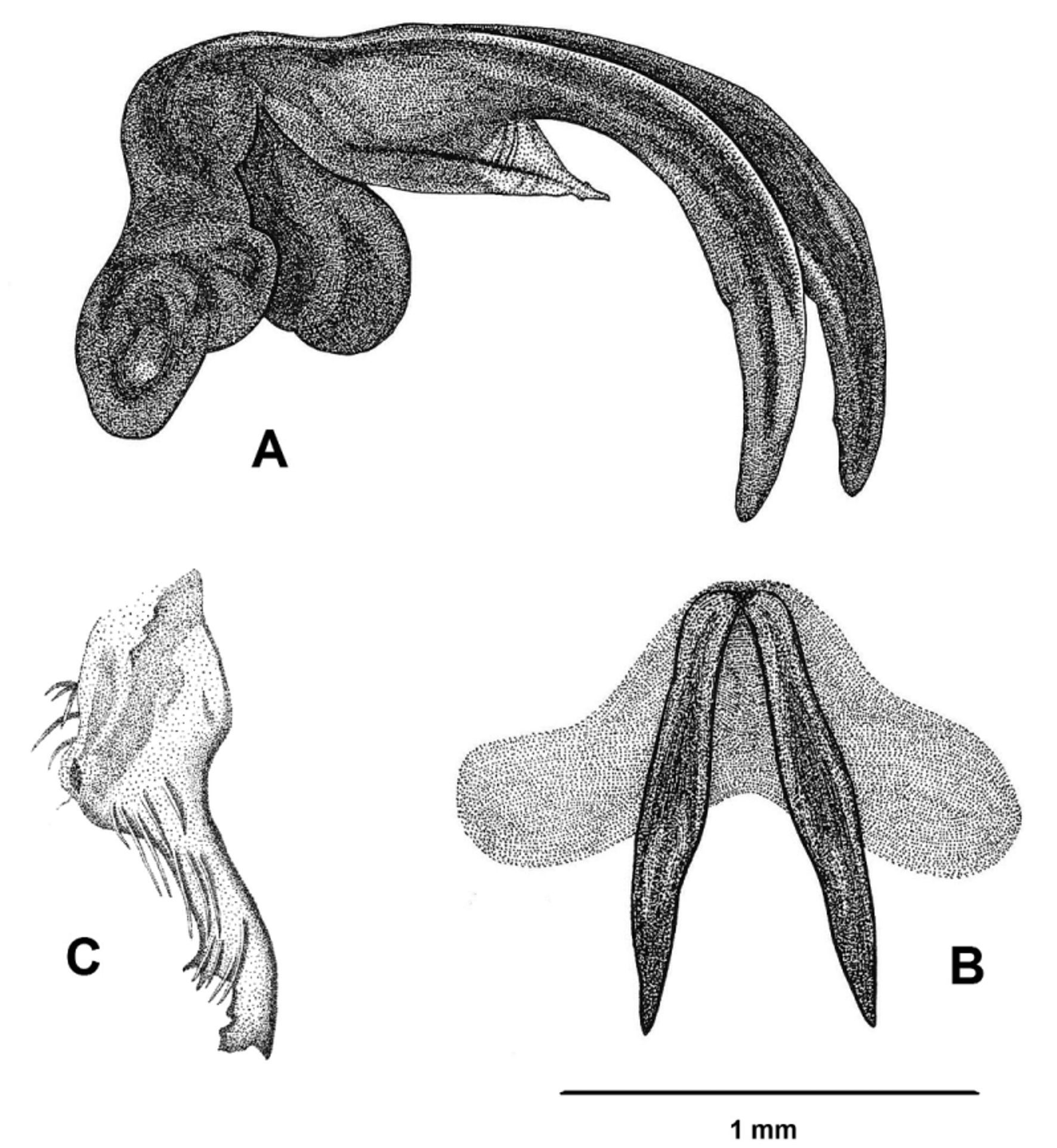
( Fig. 34 View FIGURE 34 )
Type species. Pseudokanakia flavoannulata (Distant, 1920) comb. nov.
Included species. Only one species coming from New Caledonia: Pseudokanakia flavoannulata (Distant, 1920) .
Derivation of name. Means “close to Kanakia ”. The genus is feminine.
Diagnosis. Big sized cicada (male body length around 30 mm), more or less close to the genus Kanakia Distant, 1892 with which it shares a similar shape and wing venation, but differs mainly in claspers morphology (flattened and serrated ( Fig. 34 View FIGURE 34 c)) and aedeagus shape (thecal pseudoparameres originating near thecal base ( Fig. 34 View FIGURE 34 a)).
Material examined. Holotype male, Nouvelle-Calédonie, Plaine des lacs, (BMNH). Province Sud, Boulouparis, Mont Do, 1 male, Salesne rec, 15/I/2009 (MNHN). Province Sud, Dumbéa, Monts Koghi, 1 male Delorme rec, 13/I/2013 (MNHN). Province Sud, Dumbéa, Monts Dzumac, 1 male Delorme rec, 16/I/2013 (MNHN).
Head. About as wide as mesonotum between wings; head length shorter than pronotum length. Dorsal postclypeal area wider than long; anterior border not prominent from curve of supra-antennal plate. Postclypeus anterior profile in dorsal view well rounded giving the head an angular appearance. Big sized ocelli; distance between lateral ocelli longer than distance between lateral ocellus and median ocellus. Distance between lateral ocelli twice as wide as ocelli and about equal to distance between lateral ocellus and eye. Epicranial suture very deep. Postclypeus bears at least six transversal grooves and no longitudinal furrow.
Thorax. Paranotum (lateral margin of pronotal collar) when viewed dorsally with a rounded lateral lobe and an anterior lateral tooth. Male operculum, covering rim of distal margin of tympanal cavity, overlapping, almost joining, directed towards distomedial margin of tympanal cavity, apically broadly rounded.
Wings. Forewings with eight apical cells; radial crossvein oblique. Forewing veins M and CuA meeting basal cell clearly separated, immediately diverging; distance between r and r-m much less than distance between r-m and m; forewing infuscation present on crossveins r and r-m. Base of first apical cell located close after pterostigma mid-length; slender and briefly reduced at tip, terminally sharpen and more than half as long as costal vein. Hind wings with six apical cells; anal cell almost reaching distal margin of anal cell 2.
Legs. Forelegs with femur bearing three developed black spines and a forth one (aborted) on the anterior base of the third spine. Primary spine strong and oblique, isolated, almost as long as distance separating primary and secondary spines. Secondary spine sharp, sub-perpendicular distinctly shorter than primary spine; apical spine oblique, triangular, distinctly shorter than second spine. Hind legs similar to mid legs, with three tibial laterointernal spurs and two latero-external spurs.
Abdomen. Swollen, much larger than mesonotum. Timbals broad, bearing four long ribs fused dorsally; ribs 1 to 3 fused ventrally; three intercalary ribs. Male sternite 1 with large rounded bulge; sternite 7 about as long as wide, apically roundish.
Genitalia. Upper lobe of pygofer flat, well developed, longer than wide dominating pygofer between basal lobes and dorsal beak; basal lobes undivided, moderately developed, rounded in lateral view, abutted against or partly tucked behind pygofer margin; dorsal beak present as a developed apical spine or pointed apex and a part of chitinized pygofer. Median lobe of uncus obtuse with median furrow, longer than wide. Thecal pseudoparameres thick, dorsal of theca, originating near thecal base. Claspers serrated posteriorly. Pseudoparameres apically straight and obtuse. Aedeagal basal plate in lateral view angled at about 90°.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Cicadoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Cicadettinae |
|
Tribe |
Taphurini |