Sangabasis carmelae, Villanueva, R. J. T. & Dow, R. A., 2014
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3815.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:85DD7449-EBB5-4BDF-AB6A-465D926B21EA |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5671756 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/4370710E-D762-FFE7-FF2A-D02CFC80FCED |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Sangabasis carmelae |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Sangabasis carmelae View in CoL sp. nov.
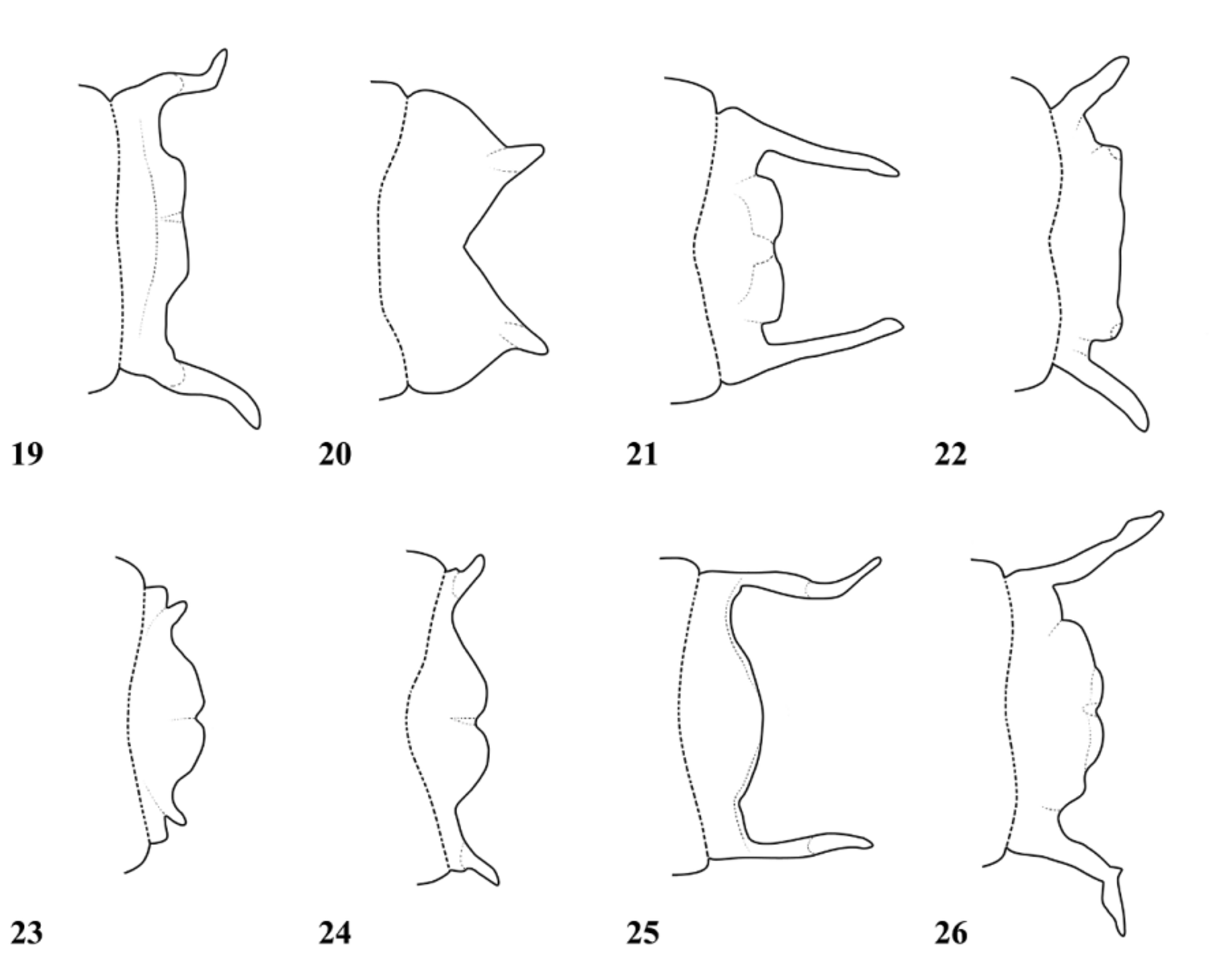
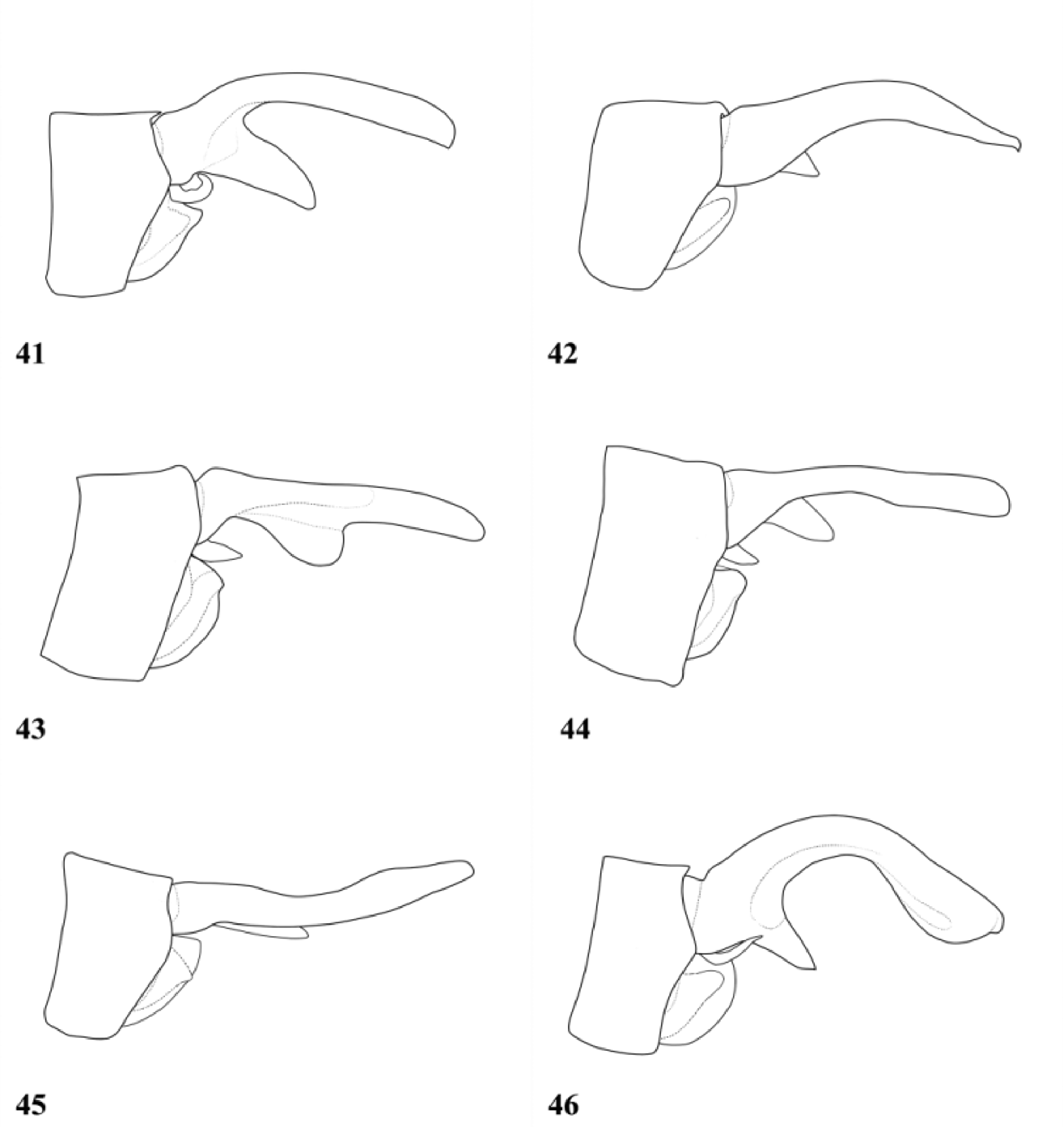
( Figs. 7 View FIGURES 6 – 7 , 21 View FIGURES 19 – 26 , 31 View FIGURES 27 – 32 , 45 View FIGURES 41 – 46 , 57 View FIGURES 53 – 58 , 65 View FIGURE 65 )
Amphicnemis sp.n.;— Villanueva (2010a: 8, photograph ♂).
Amphicnemis View in CoL sp.n. 1;— Villanueva (2010b: 6).
Type material. Holotype: ♂, Philippines, Quezon Province, Polillo Island, Polillo, Anawan area, 24 iv 2009, in RMNH, leg. RJTV. Paratypes: 3 ♂, 4 ♀, data as holotype, in coll. RJTV.
Other material: 2 ♂, 6 ♀, data as holotype, in coll. RJTV; 3 ♂, same location, 2 iv 2010, in coll. RJTV, leg. RJTV & HC.
Etymology. Carmelae , a noun in the genitive case. This species is dedicated to Ms. Carmela Espanola in appreciation of her invaluable advice on fieldwork in Luzon.
Description of holotype male. Head: Labium and most of mandible bases pale. Labrum shiny black except for yellow distal third. Genae pale, pale colour continued to eye margin and narrowly along eye margin from ridge of frons to level of antennal sockets. Anteclypeus largely dark with pale lateral marks adjacent to labrum. Postclypeus black. Frons black, with distinct ridge, anterior face with paired transverse yellow streaks separated centrally. Vertex black with metallic reflection, broad vertical pale streak on antennal socket, top of scape pale, pale streak along anterior and posterior faces of pedicel, rest of antennae brown. Remainder of head dark metallic green. Broad tubercle situated anteriorly beside eye margin in postocular area.
Thorax: Prothorax dark metallic green except for pale transverse streak on crest of anterior lobe, pale lower part of propleuron and brownish tips of horns of posterior pronotal lobe. Shelf of posterior lobe ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 6 – 7 ) short, approximately rectangular. Horns of posterior lobe long, flattened, rearward directed, running parallel to dorsum of synthorax. Synthorax ( Fig. 31 View FIGURES 27 – 32 ) with dorsal carina almost smooth. Mesinfraepisternum metallic green with intermittent and irregular pale borders, with long conical tubercle in upper anterior corner, clearly visible in dorsal view ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 6 – 7 ). Mesepisternum almost entirely metallic green, bearing low tubercle covered in setae, on each side just above posterior corner of mesinfraepisternum. Mesepimeron mostly metallic green with pale streak along interpleural suture, extending upward near to, but not reaching, antealar carina ( Fig. 31 View FIGURES 27 – 32 ). Metepisternum pale, large metallic green marking adjacent to antealar carina, slightly separated from small dark mark spanning metapleural suture, metepimeron otherwise pale. Legs with coxa and trochanter pale, femur and tibia pale with dark spines, blackish streaks on extensor surfaces and dark markings around joint. Tarsi without denticle. Wings hyaline with black veins. Arc at level of Ax2, Ac near Ax2, petiolation ceases before level of Arc. R4 arising at subnodus; IR3 distal to subnodus. 13 Px in Fw, 12 Px in Hw. Pt brown, rectangular, costal side a little shorter than subcostal side.
Abdomen: S1–2 black dorsally, becoming pale lower on sides; S3–7 dark brown becoming black apically, paler laterally with narrow pale basal ring. S8–9 black, pale laterally. S10 black with pale bluish patch occupying most of lower half of sides. Cerci brownish, becoming paler apically, more than twice length of S10. Fork of upper branch at ca 1/3 of the length of upper branch ( Fig. 57 View FIGURES 53 – 58 ). In lateral view upper branch shaped as in Fig. 45 View FIGURES 41 – 46 , with small black internal tooth at tip, in dorsal view slightly expanded and hollowed toward tips. Spur shorter than distance from S10 to base of fork in dorsal view, tuft of dense setae at tip; visible in lateral view. Lower branch very short, barely visible in lateral view. Paraprocts typical for genus.
Measurements (mm): abdomen including cerci: 40, Hw 22.
Variation in paratype males. Anteclypeus pale except for central black mark adjacent to postclypeus in paratypes. Horns of posterior pronotal lobe sometimes bent.
Measurements (mm): abdomen including cerci 39–41, Hw 22.
Female. Similar to male except: labrum with more extensive yellow; horns of posterior pronotal lobe gently angled upward ( Fig. 21 View FIGURES 19 – 26 ); S8 laterally blue; S9 whitish blue except black dorsal line, broader apically; S10 pale blue laterally.
Measurements (mm): abdomen 38, Hw 23.
Diagnosis. The species is easily recognized by the almost smooth dorsal carina and distinct conical process on mesinfraepisternum. S. janvantoli has a small, inconspicuous conical process on the mesinfraepisternum, but this cannot be confused with the much longer process of S. carmelae .
| RMNH |
National Museum of Natural History, Naturalis |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
Sangabasis carmelae
| Villanueva, R. J. T. & Dow, R. A. 2014 |
Amphicnemis
| Villanueva 2010: 6 |