Foenobethylus zhejiangensis Liu, Chen et Xu
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.277079 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6183000 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/4659B72E-FFA0-BE02-FF06-FCFAC10CE61D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Foenobethylus zhejiangensis Liu, Chen et Xu |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Foenobethylus zhejiangensis Liu, Chen et Xu , sp. nov.
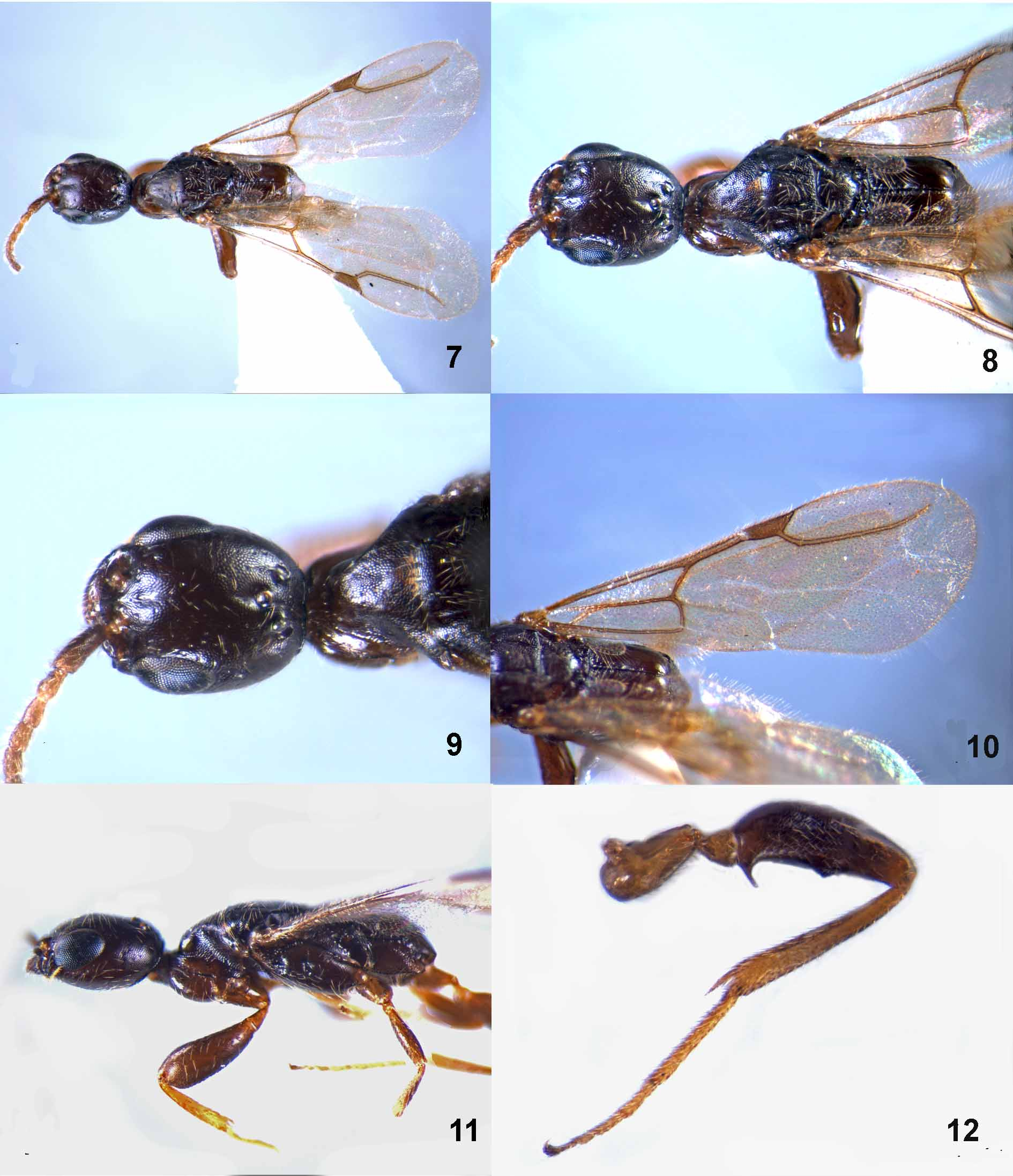
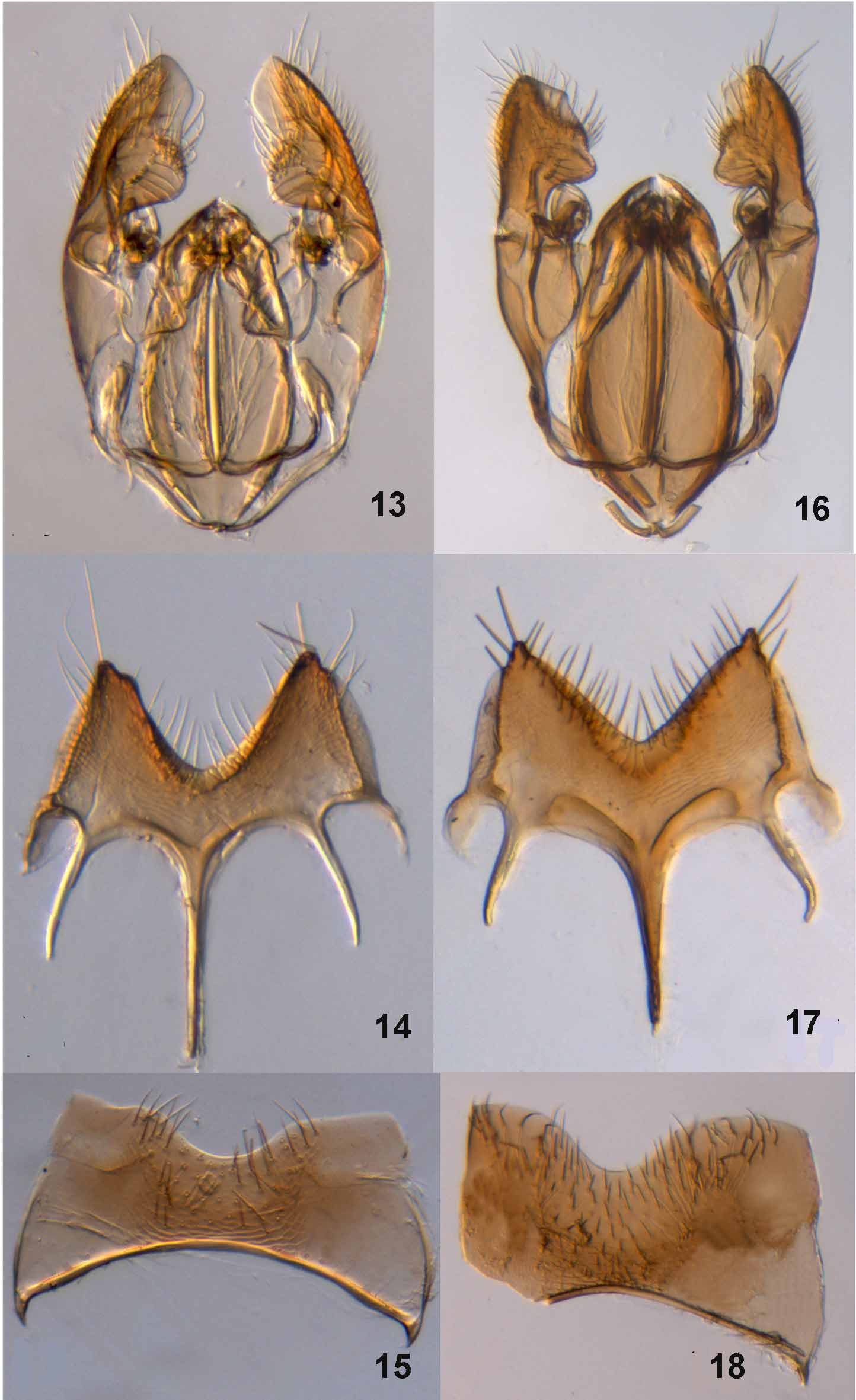
( Figs 7–12 View FIGURES 7 – 12 , 16–18 View FIGURES 13 – 18 )
Type material. Holotype, male. CHINA: Zhejiang, Anji, Mt. Longwangshan ( 30º46'N, 119º36'E), 24.VI.1996, Qiang LI, No. 963099.
Diagnosis. This species can be distinguished from Foenobethylus bidentatus Várkonyi et Polaszek, 2007 by having the distance between posterior margin of compound eye and occipital carina 1.3 times the length of compound eye in dorsal view (equals to the length of compound eye of the latter), terminal segment of maxillary palpus 3.5 times as long as wide (over 4.0 times of the latter) and eighth sternum with distal margin strongly emarginate (with distal margin of eighth sternum narrowly emarginate of the latter).
Description. Holotype. Male. LH 0.7 mm, WH 0.60 mm, WF 0.4 mm, LM 1.5 mm, LPD 0.47 mm, WPD 0.4 mm, LFW 2.5 mm.
Head. Head ( Figs 7–9, 11 View FIGURES 7 – 12 ) in dorsal view 1.16 times as long as wide, broadly rounded towards occipital carina; frons and vertex coriaceous and sparsely punctate. Ocellar triangle forms slightly obtuse angle at the anterior ocellus. Mandible with five teeth. Median lobe of clypeus rounded. Antennae broken, only the left with the basal seven segments remaining, ratio of length to width of first to seventh segments as follows: 20:7, 7:5, 8:5, 8:5, 8:5, 8:5, 8:5, scape incrassate apically. Compound eyes small and bare. Distance between posterior margin of compound eye and occipital carina 1.3 times the length of compound eye in dorsal view. Distance between occipital carina and posterior ocelli 2.0 times the length of maximum diameter of the latter. POL: OOL: OL: DAO =10: 20: 3: 4. Terminal segment of maxillary palpus 3.5 times as long as wide
Mesosoma. Mesosoma ( Figs 8, 9, 11 View FIGURES 7 – 12 ) 3.0 times as long as depth and 2.4 times as long as wide. Pronotum coriaceous, elongate and narrowed anteriorly, without narrow horizontal shelf protruding above base of propleuron. Mesoscutum transverse, 0.5 times as long as wide; notauli complete; parallel lines weakly present. Scutellum flat and coriaceous as mesoscutum. Metanotum emarginated centrally. Propodeum finely coriaceous, nearly smooth; propodeal disc 1.2 times as long as wide; median carina of propodeum strong and reaching to apical margin of propodeum, rugose on its lateral sides.
Wings. Fore wing ( Figs 7, 10 View FIGURES 7 – 12 ) with costal, median and submedian cells closed. Radius long, with a weak node on basal 1/7.
Legs. Fore femur ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 7 – 12 ) moderately swollen, 2.5 times as long as its maximum width. Hind trochanter without ventral tooth; hind femur ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 7 – 12 ) with a long basal spine on its inner edge and with a short and broad median tooth on middle.
Metasoma. Eighth sternum ( Fig. 18 View FIGURES 13 – 18 ) with distal margin strongly emarginate, centrally with dense setae. Subgenital plate deeply notched ( Fig. 17 View FIGURES 13 – 18 ).
Male genitalia. Distal part of parameres ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 13 – 18 ) with long setae, central part weakly narrowed. Volsella with digitus clearly visible. Aedeagus as illustrated ( Fig. 16 View FIGURES 13 – 18 ).
Colour. Head and mesosoma black. Antennae dark brown. Legs dark brown, with tibia and tarsus brown. Wings hyaline, veins brown, stigma blackish brown.
Ditribution. China (Zhejiang).
Etymology. The specific name refers to the type locality.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |