Trichromothrips indicu s (Bhatti)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4544.1.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:FD830F37-624A-47F4-B299-3C4FAD758C13 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4607985 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/473F87EB-EB73-FFFE-FF19-2DBAFE26FAD0 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Trichromothrips indicu s (Bhatti) |
| status |
|
Trichromothrips indicu s (Bhatti)
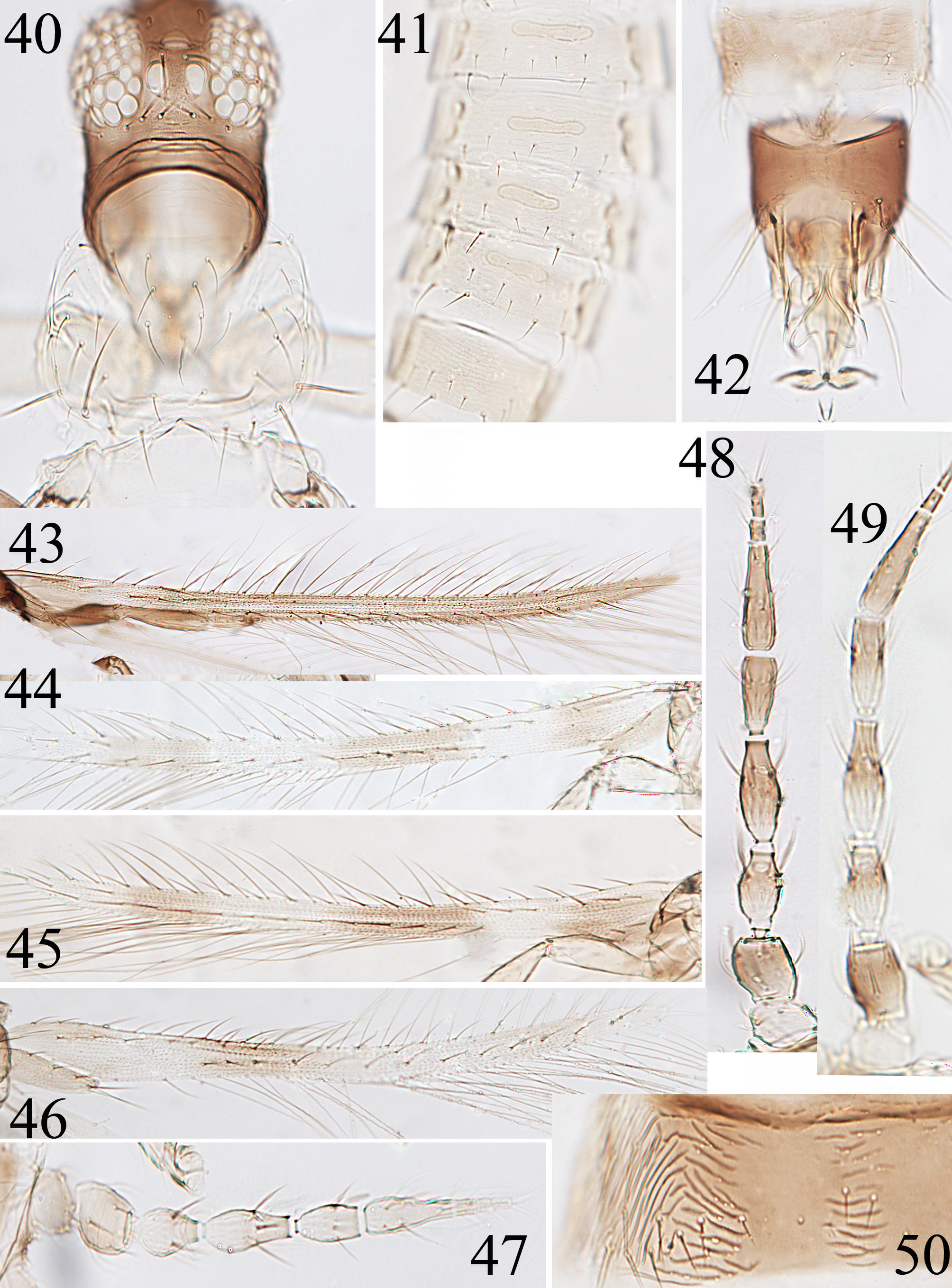
( Figs 5 View FIGURES 1–12 , 39 View FIGURES 31–39 , 41, 46 View FIGURES 40–50 )
Bhatti (2000) divided Trichromothrips genus into ten sections, and placed five species ( caespitis, cyperaceae, indicus , obscuriceps and walteri) in the caespitis -section. Members of this section have discal setae present on the abdominal sternites ( Fig. 41 View FIGURES 40–50 ), and sternite VII of females with all major setae in front of the posterior margin. The shaded fore wing is similar to walteri described from North America, but that species has 2-segmented maxillary palps, and the fore wing with one dark brown area before the middle. Collected originally from grass in India, indicus is here recorded for the first time in China.
Specimens examined. China, Yunnan, Jinghong City , 1 macropterous female, 2 apterous males from grasses, 30.ix.2011 (Shiqin Sun).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |