Scotophilus andrewreborii, Brooks & Bickham, 2014
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.6397752 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6580626 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/4C3D87E8-FF79-6AC7-FA80-9AF91C6ABDDE |
|
treatment provided by |
Conny |
|
scientific name |
Scotophilus andrewreborii |
| status |
|
284. View Plate 66: Vespertilionidae
Andrew Rebori’s Yellow Bat
Scotophilus andrewreborii View in CoL
French: Scotophile de Rebori / German: Andrew-Rebori-Hausfledermaus / Spanish: Scotofilo de Rebori
Other common names: Andrew Rebori's House Bat
Taxonomy. Scotophilus andrewreborii Brooks & Bickham, 2014 View in CoL ,
“ Kenya: Rift Valley Province, Nakur District, 12 km S, 4 km E Nakuru (0°24'S, 36°07'E).” GoogleMaps
Scotophilus andrewreborii and S. dinganit have 9-3% sequence difference in cytochrome-b. Monotypic.
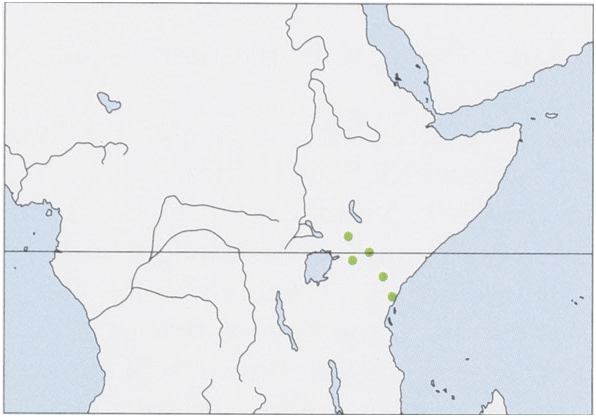
Distribution. Known only from a few localities in Kenya. View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head-body 74-986- 5 mm, tail 42.9-50- 3 mm, ear 8-8 10- 8 mm, hindfoot 9-10- 2 mm, forearm 46-5-64- 1 mm. Dorsal fur is red to mahogany; venter is tan to orange, darker on chin and sides of abdomen. Ears are separated and have semi-rounded tips. Ventral plagiopatagium is hairy proximal to body and forearm. Dorsal plagiopatagium, uropatagium, dactylopatagium,tail, legs, and feet are naked. Skull is broad with wide orbits; premaxillae are deeply notched and wide;sagittal crest is well developed; zygomatic arch is thin; vomer has well-developed central process; palatine bones are angled inward anteriorly; tympanic bullae are round to oval and well developed; foramen magnum is round; and occipital condyles are developed. All mandibular processes are well developed; coronoid processis triangular pointing upward; and angular process extends to same level as mandibular condyle. I? is bilobed, with inner cusp longer than outer cusp; paracone of P*is longer than metacone that is longer than hypocone; P* has smaller diameter but longer paracone than M' and M?; M! and M? are similar in size and structure, with ellipsoidal triangular outline in occlusal view, and interior edge is shortest; paracone and metacone of M! and M? are similar in length, being longer than hypocone; M? is highly reduced,less than one-half the diameter of M' and M* with an ellipsoidal rectangular outline in occlusal view; lower incisors are small, with I, and k; well developed and trilobed; and P, 1S shorter than C, and slightly longer than paracone of M,. M, and M,are similar in size and structure, with rectangular trapezoid outline in occlusal view, and exterior edge is shortest; M, is similar to M, and M, structurally and only slightly reduced in size; and paracone of lower molars is longer than metacone, which is longer than hypocone.
Habitat. Wide range of savannas and woodlands at elevations of ¢. 332-1905 m.
Food and Feeding. No information.
Breeding. No information.
Activity patterns. No information.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. No information.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Least Concern on The IUCN Red List. Combined localities encompass ¢. 38,653 km?.
Bibliography. Brooks & Bickham (2014).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Scotophilus andrewreborii
| Don E. Wilson & Russell A. Mittermeier 2019 |
Scotophilus andrewreborii
| Brooks & Bickham 2014 |