Scutacarus pseudoapodemi Navabi & Hajiqanbar, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4531.4.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:BD0BADCE-2CB7-471A-B3E3-741585CF80A0 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5974827 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/521D2D31-9A6A-FFF1-DCEF-FCAB798CDAE3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Scutacarus pseudoapodemi Navabi & Hajiqanbar |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Scutacarus pseudoapodemi Navabi & Hajiqanbar sp. nov.
( Figs. 1–4 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 )
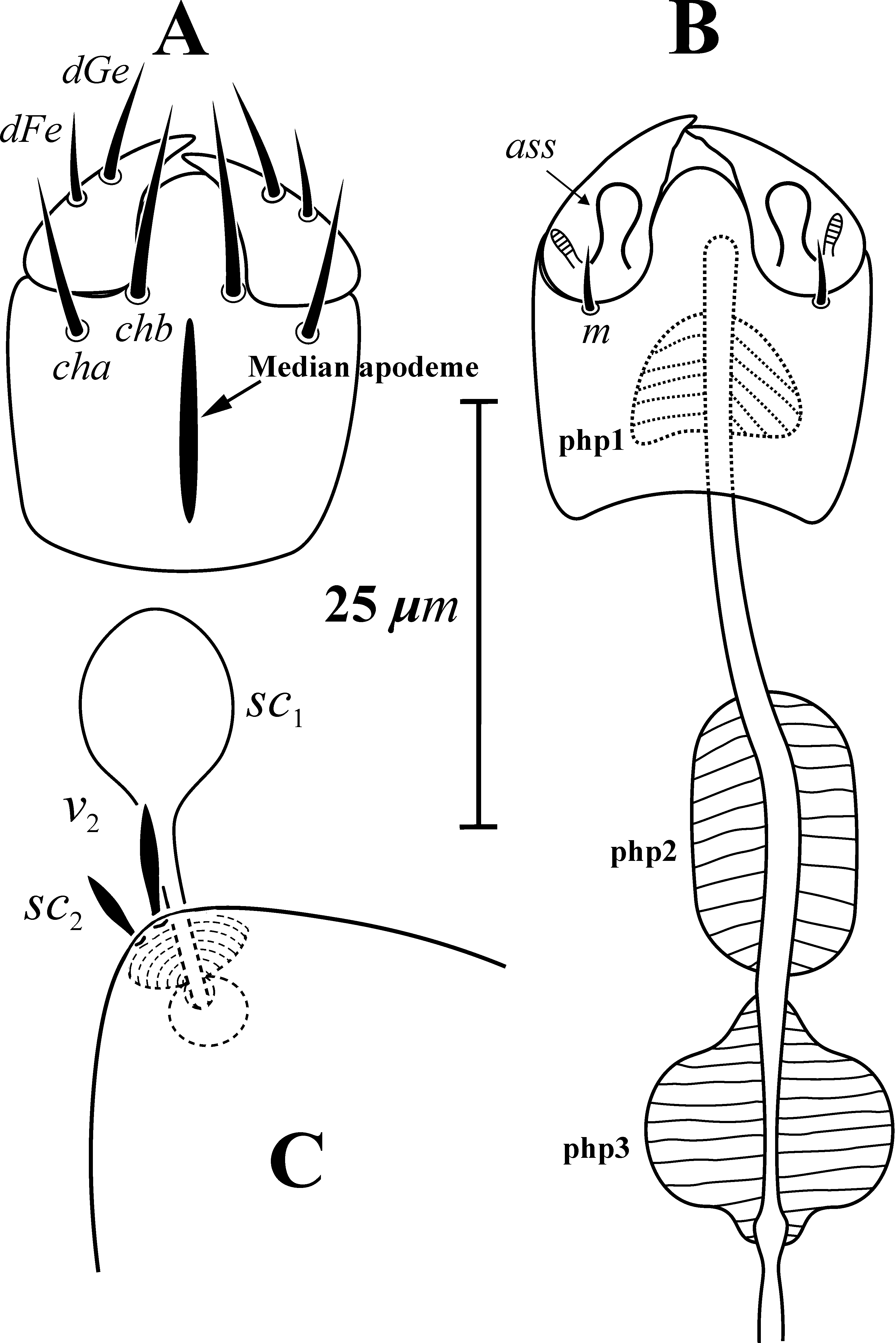
Description. FEMALE (n=5). Body oval. Tergites smooth. Length of idiosoma 193 (188–207), width 137 (131– 143). Gnathosoma ( Figs. 2A, B View FIGURE 2 ). Gnathosomal capsule oval in dorsal aspect, with well-developed dorsal median apodeme, dorsally with two pairs of smooth and pointed setae ( cha, chb); setae chb slightly longer than cha, postpalpal setae ( pp) not evident. Palps dorsolaterally with two pairs of setae ( dFe, dGe); setae dGe longer than dFe. Palps ventrally with large mushroom-like accessory setigenous structure ( ass). Palpal solenidion hardly visible. Gnathosomal venter with one pair of pointed subcapitular setae m and pair of round pits situated posteriorly to bases of setae m. Pharyngeal pumps 1–3 ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ) transversely striated. Pharyngeal pump 1 oval, pharyngeal pump 2 oval and two times longer than pump 1, pharyngeal pump 3 heart-like and longer than pump 1.
Idiosomal dorsum ( Figs. 1A View FIGURE 1 , 2C View FIGURE 2 ). Prodorsum completely covered by tergite C, with two pairs of smooth and needle-like setae v 2 and sc 2, one pair of capitates, smooth trichobothria ( Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ), and one pair of oval stigmata associated with long tracheal trunks. Lateral propodosomal spine absent. All dorsal shields smooth. All dorsal setae pointed and barbed. Cupules ia and ih on tergites D and H small, round, ia situated anterolaterally to bases of setae d and ih anteriorly to bases of setae h 2. Bases of setae c 1, c 2, d, f and h 1 associated with alveolar canals. Lengths of dorsal setae: c 1 34 (35–40), c 2 31 (31–37), d 40 (41–46), e 28 (28–31), f 42 (44–51), h 1 50 (49–56), h 2 29 (30–32). Distances between setae: c 1 – c 1 48 (49–55), c 2 – c 2 108 (113–120), c 1 – c 2 32 (32–36), d–d 81 (80–88), e–e 120 (122– 130), f–f 66 (67–72), e–f 34 (35–41), h 1 – h 1 41 (42–47), h 2 – h 2 100 (103–108), h 1 – h 2 34 (35–40).
Idiosomal venter ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ). All ventral plates smooth. Apodemes 1 (ap1) well developed and joined with prosternal apodeme (appr), apodemes 2 (ap2) w-like, joined with appr; sejugal apodeme (apsej) well developed and joined with appr. Secondary transverse apodeme (sta) absent. Apodemes 3 (ap3) well developed and weakly sclerotized, joined with poststernal apodeme (appo), ap4 short, joined with appo. Apodemes 5 absent. All setae of anterior and posterior sternal plates barbed and pointed. Setae 4 a situated slightly anteriorly to 4 b, setae 4 b reaching to posterior margin of aggenital plate. Distance 4 a –4 a (18) longer than distance 4 a –4 b (8). Anterior genital sclerite ( ags) bell-like, posterior genital sclerite ( pgs) large, triangular. Pseudanal segment with three pairs of setae ( ps 1, ps 2 and ps 3), setae ps 1 and ps 2 barbed and pointed; setae ps 3 smooth and thin. Lengths of ventral setae: 1 a 29 (31–36), 1 b 24 (22–27), 2 a 27 (29–34), 2 b 19 (20–22), 3 a 31 (34–38), 3 b 34 (36–41), 3 c 30 (31–37), 4 a 21 (20–23), 4 b 68 (70–75), 4 c 45 (43–49), ps 1 29 (30–35), ps 2 19 (21–22), ps 3 7 (8–9).
Legs ( Figs. 3 View FIGURE 3 , 4 View FIGURE 4 ): Leg I ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ). Thicker than other legs. Leg chaetotaxy: Tr-1, Fe-3, Ge-4, TiTa-16(4). Tibiotarsus: with large tarsal claw, pointed distally; seta k and tarsal eupathidia ( p”, ft’, ft”, tc’, tc”) blunt-ended; setae of the segment barbed (except eupathidia); solenidion ω 1 finger-shaped, other solenidia almost clavate, lengths of solenidia: φ 2 3 (3–4) < ω 2 5 (4–6) < φ 1 8 (7–8) = ω 1 8 (7–8); eupathidium tc ″ situated on long pinnaculum, tc ′ on short protuberance, tc ″ longer than tc ′, ft’ longer than ft”; seta d longest on tibiotarsus. Genu: with seta v′ longer than others, l” shortest; v” slightly longer than l′; all setae of the segment barbed. Femur: with subequal blunt-ended setae d and l′, both longer than v”; seta d barbed, setae l’ and v” smooth. Trochanter: with one barbed seta v′. Leg II ( Fig. 3B View FIGURE 3 ). Leg chaetotaxy: Tr-1, Fe-3, Ge-3, Ti-4(1), Ta-6(1). Tarsus: with large padded claws and well-developed flipper-like empodium; solenidion ω 8 (8–9) finger-shaped; setae pl" spine-like, blunt and barbed, u ’ sparsely barbed in distal half. Tibia: with solenidion φ 4 (4–5) weakly clavate; seta v′ longest on leg. Genu: seta l” longest, v’ longer than l’. Femur: with subequal setae l′ and v”, both shorter than d. Leg III ( Fig. 3C View FIGURE 3 ). Leg chaetotaxy: Tr-1, Fe-2, Ge-2, Ti-4(1), Ta-6. Tarsus: Claws of same shape as on tarsus II; setae pl" spine-like, blunt and barbed, u ’ barbed in distal half, setae tc’ and tc” subequal and longer than other tarsal setae, tc” smooth. Tibia: with solenidion φ 3 (3–5) weakly clavate; with subequal setae v’ and l′. Genu: with subequal setae v’ and l′. Femur: setae d longer than v’. Trochanter: with one seta v′ longest on leg. Leg IV ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ). Leg chaetotaxy: Tr-1, Fe-2, Ge- 1, TiTa-6. Tibiotarsus: short, only slightly longer than its width; setae d and pv” subequal and half as long as bluntly ended seta tc’, seta pv’ shortest on leg; seta v’ about two times longer than genual seta v’.
Type material. Female holotype (slide AN 07072016 -I) and 4 paratypes, IRAN, western Iran, Lorestan Province, Borujerd city, Goldasht village ( 33°54'19.39"N, 48°42'9.83"E), 7 April 2016, removed from a vial containing more than 50 Camponotus oasium Forel ( Hymenoptera : Formicidae ).
Etymology. The species epithet refers to the similarity of the new species to S. apodemi Mahunka, 1963 .
Differential diagnosis. The new species is most similar to S. apodemi Mahunka, 1963 due to the similar length of the dorsal and ventral setae, but is distinguished from it by its pointed idiosomal dorsal setae c 1, c 2, d and f ( c 1, c 2, d and f blunt-ended in S. apodemi ) and barbed ventral idiosomal setae 2 b and 4 a (2 b and 4 a smooth in S. apodemi ). In addition, solenidia φ 2 < ω 2 < φ 1 = ω 1 ( ω 1 > ω 2 < φ 1 > φ 2 in S. apodemi ), seta d FeI is seta-like ( d FeI spine-like in S. apodemi ), and the length and width of tibiotarsus IV is almost equal (tibiotarsus IV about twice longer than its width in S. apodemi ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |