Agalma clausi (Bedot, 1888)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4441.2.7 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:1F81A5B9-5FCB-43F4-B85B-5398AB16E09E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5974011 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/583E5976-4E20-DE61-32CD-8BDEFD250449 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Agalma clausi (Bedot, 1888) |
| status |
|
Agalma clausi (Bedot, 1888) View in CoL
Synonyms.
Agalma sarsii ( Fewkes, 1880) View in CoL p. 628.
Crystallodes Clausi View in CoL (Bedot, 1888, post-scriptum) p. 20.
Stephanopsis Clausi ( Bedot, 1896) p. 406.
Stephanomia sarsii ( Schneider, 1898) p. 121–122.
? Agalma eschscholtzii (Haeckel, 1888) p. 226 and Plate XVIII, Fig. 8–17 View FIGURE 8 View FIGURE 9 View FIGURE 10 View FIGURE 11 View FIGURE 12 View FIGURE 13 View FIGURE 14 View FIGURE 15 View FIGURE 16 View FIGURE 17 .
? Agalma haeckeli ( Bigelow, 1911) p. 274–277.
Systematics. Agalma clausi View in CoL belongs to the Family Agalmatidae Brandt, 1834 View in CoL that is nested within the historically recognized Physonectae, a suborder that groups all siphonophores sharing particular body plan i.e., possessing pneumatophore, nectosome, and siphosome. However, Physonectae were shown to be polyphyletic (Dunn et al. 2005) and following the most recent phylogeny ( Munro et al. 2018) agalmatid siphonophores are placed within a newly erected, monophyletic clade Euphysonectae. Although this phylogenetic hypothesis is well supported, as the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature ( ICZN 1999) does not recognise clades we decided to maintain the name Physonectae throughout this text.
Type specimens. There is no known type specimen, thus we designate the specimen from BWP Dive 1044-15 as a neotype. It will be deposited at the United States National Museum ( Smithsonian Institution ), Washington, DC under accession number USNM 1422474 About USNM . It was collected close to the surface by a SCUBA diver on 14th July, 1983 at 3°56.9'N, 37°15.8'W.
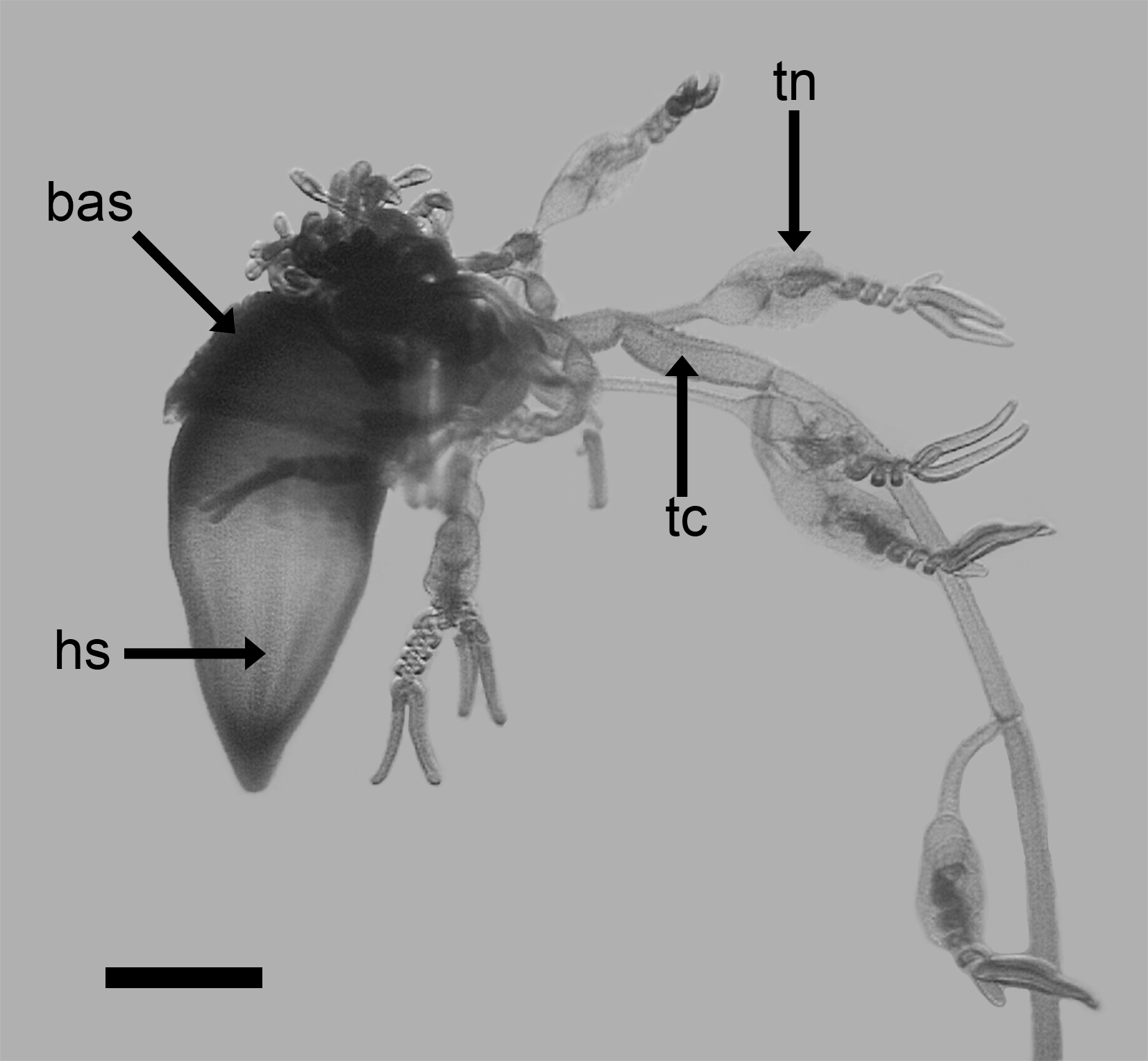
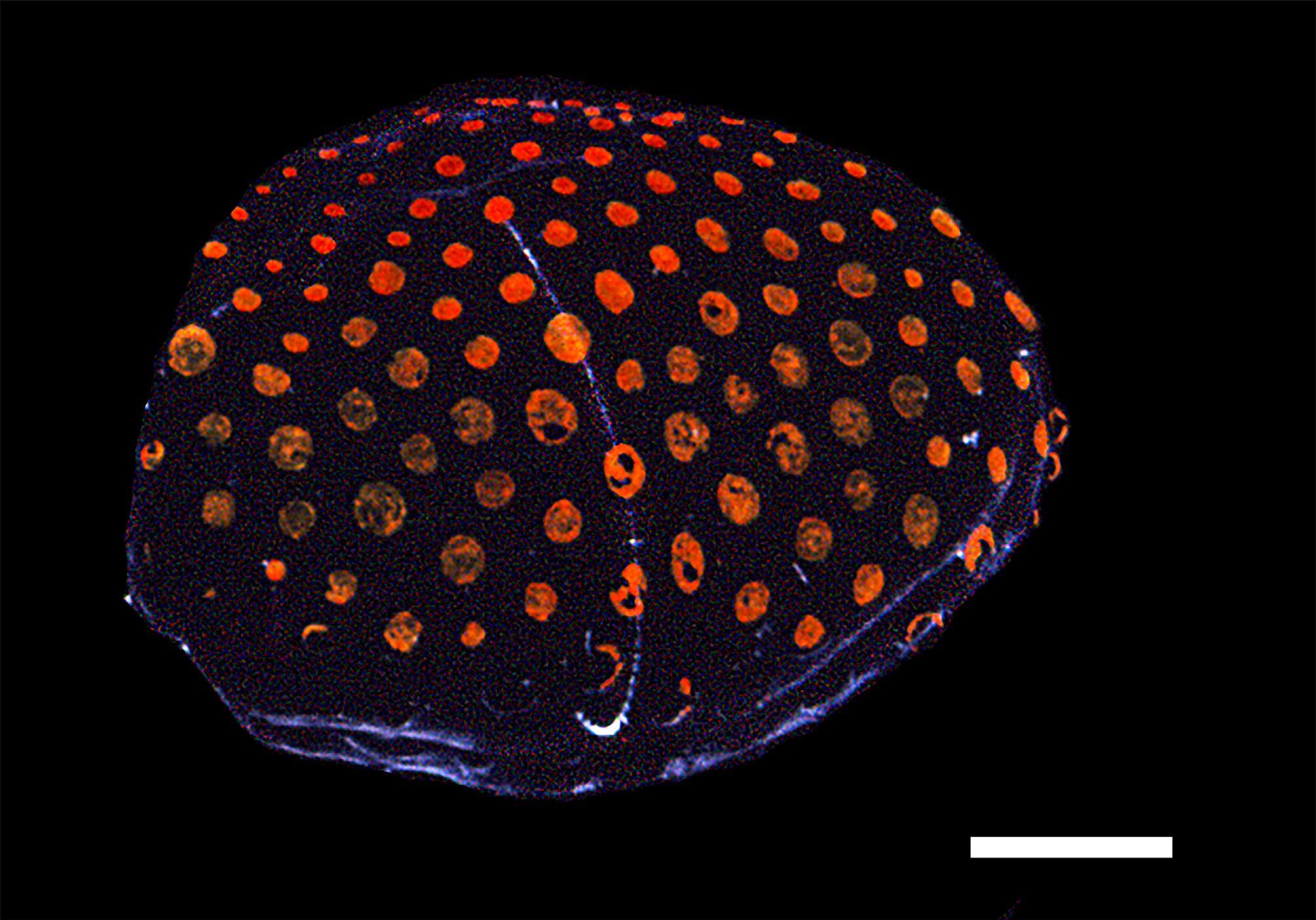
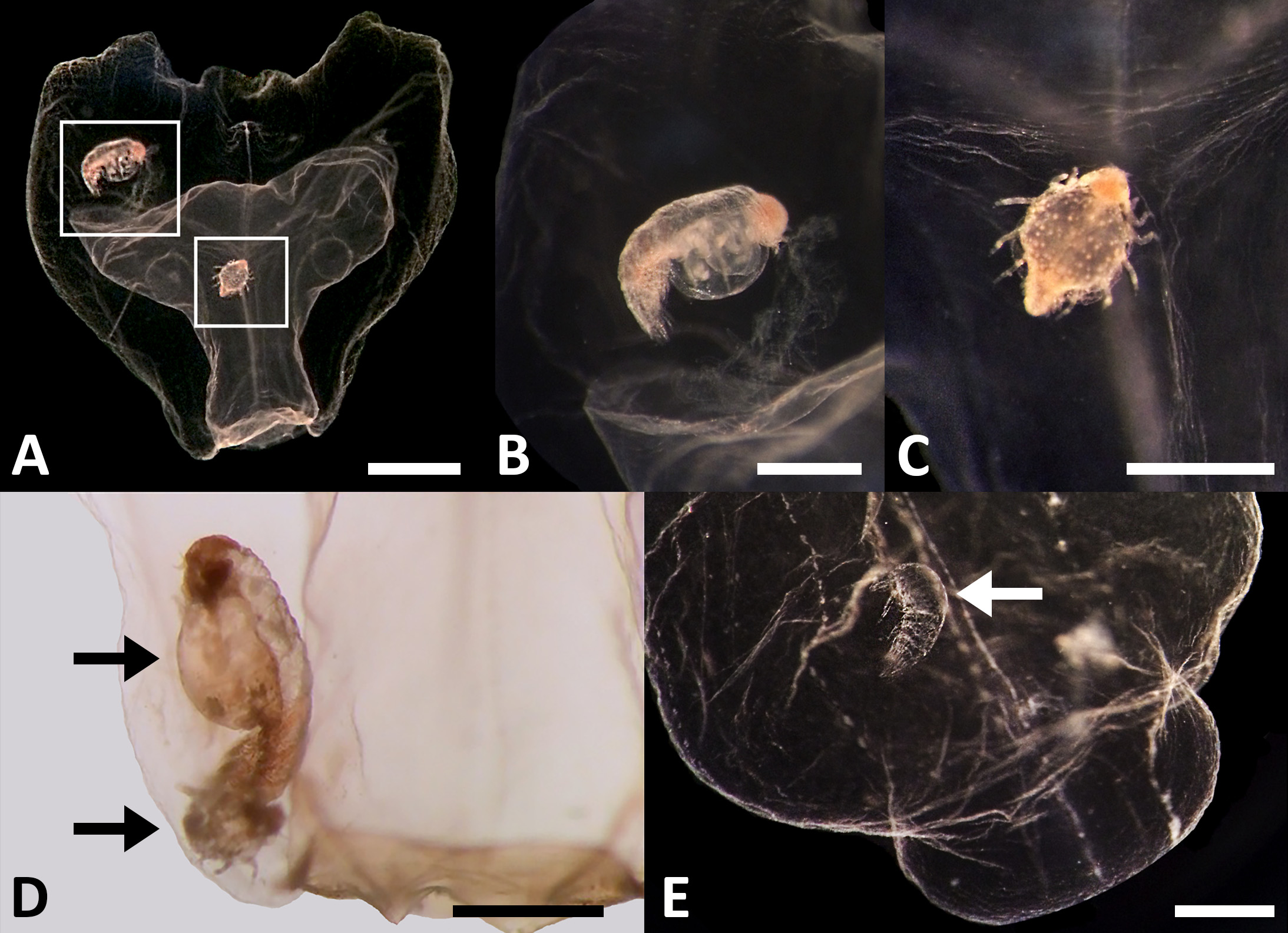
Diagnosis. Rigid-stemmed, monoecious agalmatid siphonophore of prismatic appearance, with nectophores arranged biserially and some bracts showing carmine pigmetation in living animal. Nectophores with short axial wings and size-dependent ridge pattern, incomplete laterals discernible only in younger zooids, but upper and lower lateral ridges present throughout development, but very weak in largest nectophores. No vertical lateral ridges. Thrust block small on mature nectophores; lateral ostial processes also small and packed with nematocysts. Typical Agalma course of lateral radial canals. Cormidia bearing gastrozooids (often flask-shaped), with tentacle, several gonophores of both sexes, bracts and palpons. Involucrum of tentillum voluminous, able to contain the cnidoband, the two terminal filaments and the central ampulla. Palpacle of palpon originates not at its base but, on the fully mature palpon, almost at its mid-length. Six types of bracts, of which one is able to discharge a coloured, probably fluorescent, fluid when stimulated.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SubOrder |
Physonectae |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
Agalma clausi (Bedot, 1888)
| Mańko, Maciej K. & Pugh, Philip R. 2018 |
Stephanopsis Clausi ( Bedot, 1896 )
| Clausi (Bedot 1896 |
Agalmatidae
| Brandt 1834 |