Ctenomys leucodon, Waterhouse, 1848
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6588177 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6588119 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/59304B44-1B0C-FFC0-FF16-FB5FF7F1FE8B |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Ctenomys leucodon |
| status |
|
45. View Plate 32: Ctenomyidae
White-toothed Tuco-tuco
French: Tuco-tuco a dents blanches / German: \WeiRzahnkammratte / Spanish: Tuco tuco de dientes blancos
Other common names: Titicaca Tuco-tuco
Taxonomy. Ctenomys leucodon Waterhouse, 1848 View in CoL ,
“San Andrés de Machaca, ... south of the Lake Titicaca, Department of La Paz, Bolivia.” Restricted by O. Thomas in 1927 to “ca. 4,000 m, 16°44’ S 69°01’ W.”
Ctenomys leucodon is not classified in any species group. Chromosomal complement is 2n = 36 and FN = 68, and sperm form is unknown. Monotypic.
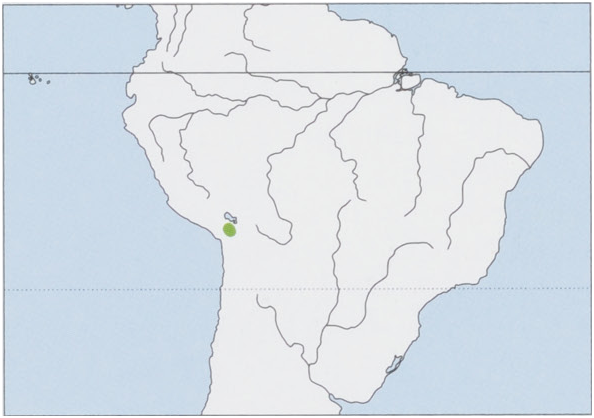
Distribution. Andean altiplano, in S Peru (Puno Region) and W Bolivia (La Paz Department). View Figure
Descriptive notes. Head—body 115-172 mm, tail 79-85 mm, ear 3-8, hindfoot 27-34 mm. No specific data are available for body weight. The White-toothed Tuco-tuco is medium-sized. Dorsum is clay colored, with hairs of slate-gray at bases, clay-colored bands in middle, and ending in black tips. Tail is dark brown above and slightly paler below. Venter is near tawny-olive, and chest is reddish. Head and sides of muzzle are darker, and cheeks are buckthorn brown. Upper incisors of the White-toothed Tucotuco are quite different from other species of tuco-tucos, strongly procumbent and covered with white or pale yellowish white enamel.
Habitat. Altiplano open grasslands in primary habitat and areas disturbed by grazing. The White-toothed Tuco-tuco is fossorial and herbivorous; it eats underground tubers and roots. Colonies are found in areas with friable soils.
Food and Feeding. There is no information available for this species.
Breeding. A single pregnant White-toothed Tuco-tuco with one embryo was observed in August in Bolivia.
Activity patterns. There is no information available for this species.
Movements, Home range and Social organization. White-toothed Tuco-tucos seems to be particularly non-vocal. They make large earthen mounds.
Status and Conservation. Classified as Least Concern on The IUCN Red List.
Bibliography. Anderson (1997), Anderson et al. (1987), Bidau (2015), Contreras & Bidau (1999), Parada et al. (2011), Pearson (1959b), Sanborn & Pearson (1947), Thomas (1927a).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.