Zetheumenidion abruptum, Selis, 2024
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5406.1.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:F4164A07-7B45-41E6-8611-A7EA6708E82E |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10624485 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/5C1587AE-575F-FB17-D5F4-FF10FB782A1D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Zetheumenidion abruptum |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Zetheumenidion abruptum sp. nov.
( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 , 12 View FIGURE 12 )
Diagnosis. Belonging to the group of species with subhorizontal face of propodeum and abruptly expanded base of T1 ( Fig. 1D View FIGURE 1 ), in which is recognized by lateral faces of propodeum deeply concave and forming an apical pit, propodeal valvula as long as basally wide, T 1 in dorsal view not widened near base and with width at level of spiracles equal to apical width, dorsal face of T1 evenly convex, apical lamella of T2 weakly reflexed and not reaching same height of preapical bulge ( Fig. 1D View FIGURE 1 ).
Material examined. HOLOTYPE: ♂ labeled “S AFRICA / Cape Province / Van Rhyn’s Pass / 11–21.xi 1931 //
Prof-T-D-A-Cockerell // Zetheumenidion / femoratum (Sch) / Giordani Soika det. 1967 // Zetheumenidion abruptum
/ HOLOTYPUS ♂ / Det. Marco Selis ” ( MSNVE) . PARATYPES, SOUTH AFRICA: Cape Province, Nieuwoudtville , XI.1931, 2♂ ( MSNVE, MSVI) .
Description. Male holotype. Body length 13.7 mm; fore wing length 9.8 mm.
Head 1.35× as wide as long in frontal view ( Fig. 1B View FIGURE 1 ). Clypeus as wide as long in frontal view, apical margin shallowly emarginate and wider than interantennal space, 0.35 × as wide as width of clypeus, apical angles more or less right-angled, with rounded apex and slightly pointing out; clypeus in lateral view distinctly convex in basal two thirds and then shallowly depressed, disc of basal half bulging. Interantennal space with a blunt longitudinal ridge. Distance from posterior ocellus to occipital carina 1.7× as long as the distance from posterior ocellus to inner eye margin; vertex in lateral view weakly sloping posteriorly, deeply furrowed along occipital carina; gena 0.8× as wide as eye at bottom of ocular sinus; occipital carina complete, strong and shortly lamellate for whole length, more highly lamellate at angle formed at level of antennal insertions. F1 2.45× as long as wide and 1.75× as long as F2; F2–4 distinctly longer than wide; F5–9 subquadrate to weakly transverse; F11 subconical and weakly curved at base, with strongly flattened apical half, reaching base of F9; F3–9 with weakly developed tyloids, linear on F3–8 and wide on F9. Mesosoma in dorsal view 1.3× as long as wide. Pronotum in dorsal view with converging sides; pronotal carina complete, forming a sharp translucent lamella on dorsal face; humeri rounded, obtuse in dorsal view; lateral faces short and markedly separated from dorsal face. Mesoscutum 0.8× as long as wide in dorsal view, weakly convex in lateral view. Scutellum weakly convex, anterior margin shallowly crenate on lateral fifths and deeply furrowed in the middle. Metanotum barely convex and nearly horizontal, weakly produced in the middle of the posterior margin. Tegula with strongly convex surface and outer margin, maximum width near middle, posterior lobe right-angled and sharp, not equaling parategula; parategula oblique and nearly straight in dorsal view, strongly flattened and forming a sharp vertical lamella. Mesepisternum strongly convex, sharply separated from epicnemium but without epicnemial carina. Propodeum long and forming a subhorizontal dorsal face behind metanotum, deeply furrowed in the middle and steeply rounded into posterior face, but without any sharp delimitation; lateral face deeply depressed, forming a deep pit above anterodorsal angle of propodeal valvula; posterior face subtriangular and deeply concave above orifice; all faces separated but not sharply, all carinae lacking; propodeal valvula about as long as basally wide and apically rounded. T 1 in dorsal view 5.3× as long as apically wide, sides strongly diverging in basal fourth, then nearly straight, width at level of spiracles equal to apical width; T 1 in lateral view abruptly expanded in basal third and then narrowing to apex, forming a distinct basal hump; dorsal face of T1 evenly convex. T2 bell-shaped with basal petiole wider than long, preapical area strongly bulging and nearly sharp, apical lamella preceded by a costulate depressed area, then weakly reflexed and reaching about half height of preapical bulge; T 2 in lateral view strongly convex behind basal petiole. S2 much less convex than T2, somewhat flattened in basal half, apical margin lamellate similar to T2, but preapical area shallowly bulging and rounded, and apical lamella shorter and not reflexed. T3 with a somewhat decolorate apical margin, but not lamellate. T7 weakly and evenly concave on disc; S7 evenly rounded and wide, mostly flattened. Hind femur enlarged, in lateral view 2.6× as long as wide and with dorsal margin weakly convex and ventral margin strongly convex with sinuate base, ventral face with an obliquely depressed elliptical area in basal half and a centrally placed spine-bearing pore ( Fig. 1C View FIGURE 1 ).
Clypeus deeply punctured, each puncture having a central deep pore from which a seta arise, interspaces narrow on disc and becoming wider on ventral third. Head very deeply and densely punctured, punctures smaller on frons and becoming larger and slightly sparser on vertex, interspaces narrower than puncture diameter and convex and shiny; gena more sparsely punctured, interspaces finely reticulate; area along occipital carina finely crenate. Mesosoma with deep punctures larger than those on vertex, interspaces flattened and reaching up to one puncture diameter on pronotum, scutellum and metanotum, narrower and somewhat convex on mesoscutum, mesepisternum and dorsal faces of propodeum. Tegula shiny with few sparse large punctures. Metaepisternum with fine transverse striae on upper plate, sparse deep punctures on lower plate. Posterior face of propodeum with very coarse irregular punctures; lateral face with dense and fine but strong striation, with few small punctures mixed, striae becoming finer around apical pit. T1 with small deep punctures, interspaces ranging from half to several puncture diameters, very finely and shallowly shagreened on base and on sides, sparsely and finely micropunctate on disc. T2 densely shagreened, macropunctures barely visible basally and becoming progressively larger and deeper apically, with a series of coarse punctures in front of the preapical bulge. T3–7 shagreened with very fine micropunctures, T7 with few sparse punctures. S2 more shiny than T2, punctures deep and sparse and becoming progressively stronger apically. S3–7 similar to respective tergites, S7 with dense small fine punctures. Outer face of hind femur shiny with few very sparse deep punctures, interspaces with very weak shagreen and very sparse barely visible micropunctures. Frons with long pale setae, longer than ocellar diameter; clypeus, gena and mesosoma with shorter pale setae; sides of propodeum with dense fine whitish setae; metasoma with very short brownish pubescence, short erect setae at base of T1 and at apex of S2–6, S7 with longer darker setae forming a sparse preapical brush.
Genitalia in Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 .
Black; following parts ferruginous-red: suffused markings on scape, most of mandible, irregular markings on dorsal face of pronotum, tegula, parategula, posterior half of scutellum (suffused with yellow), rounded spot on upper plate of mesepisternum, anterior half of dorsal face of propodeum, longitudinal lines on sides of T1, basolateral spots and suffused preapical margin on T2 and S2; following parts yellow to yellowish-orange: clypeus except narrow lateral margins of basal half, scape except dorsal face, basal triangle of mandible, narrow margin in ocular sinus, narrow anterior margin of pronotum, anterior and posterior spots on tegula connected by narrow outer margin, most of metanotum, spots at apex of dorsal faces of propodeum, posterior margin of spot on mesepisternum, narrow apical band on T1, bisinuate apical band on T2 partly covering apical lamella, sinuate apical bands on T3–6, regular narrow apical band on S2, irregular suffusions on S3–6; flagellum ferruginous at base of T1 and rapidly turning to black towards apex, F6–F10 with contrasting ivory spots on ventral face (weak and suffused on F6); legs mostly pale ferruginous, with pale yellow markings on lower face of mid and hind coxae, outer face of fore and mid femora, and outer face of all tibiae, hind femur brownish-black and turning to dark reddish-brown on inner face, apex weakly ferruginous. Wings infuscate and brownish, with weak purplish reflections.
Female. Unknown.
Variability. The two paratypes differ from the holotype in the following aspects: smaller size (body length 10.0– 12.8 mm; fore wing length 7.2–9.0 mm), black margins on clypeus wider, pronotum without dark-red markings and with narrower yellow anterior margin, markings on scutellum more yellow, markings on propodeum smaller, red markings on T1 darker and less visible. The smaller paratype has punctures on clypeus much sparser than in the other two specimens.
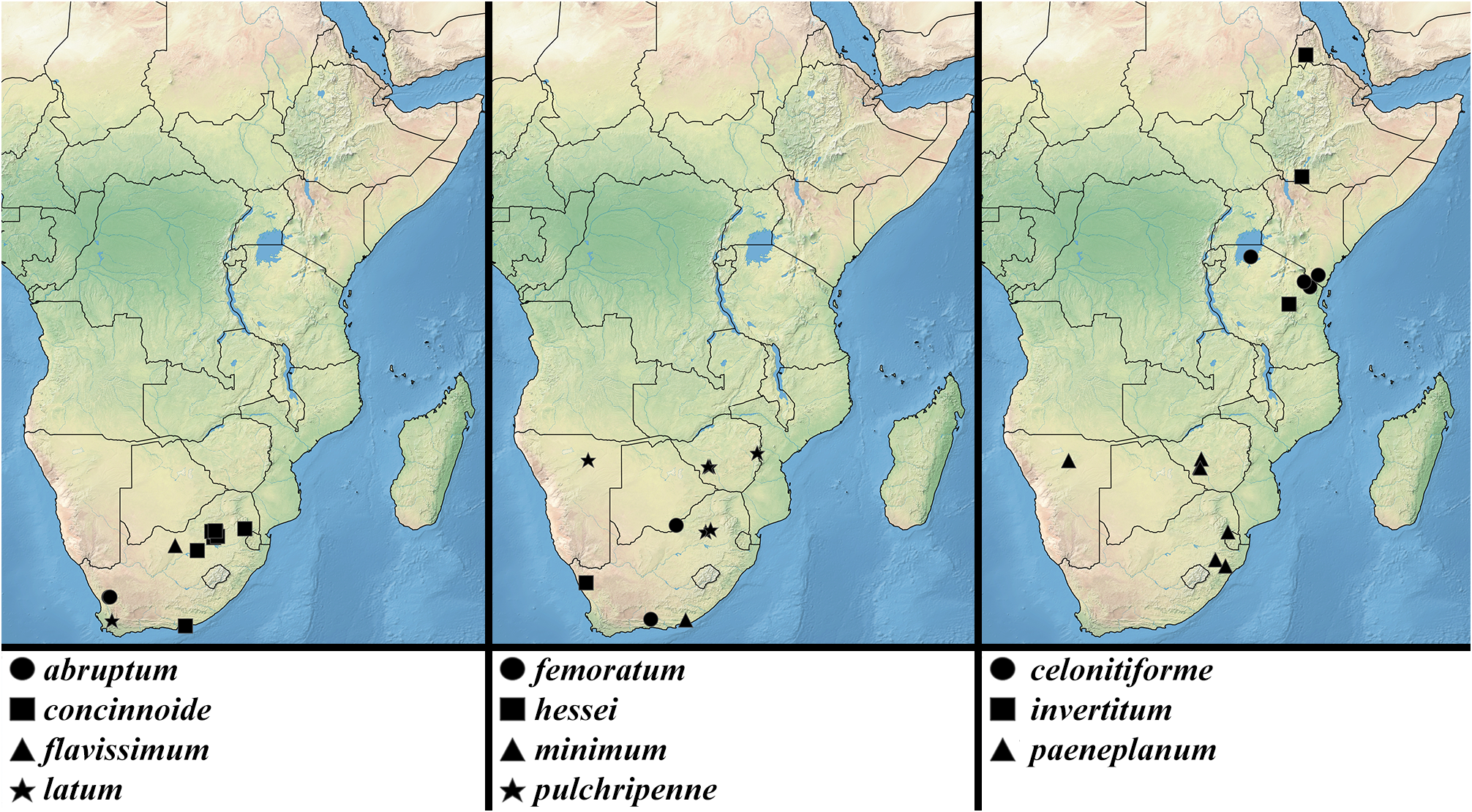
Distribution. South Africa: Northern Cape ( Fig. 13 View FIGURE 13 ).
Etymology. The species epithet refers to the abruptly expanded base of T 1 in lateral view.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |