Truljalia formosa He
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.211315 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6172467 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/714E87E1-FFC7-AA5C-2DBA-98D3FC18EC26 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Truljalia formosa He |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Truljalia formosa He sp. nov.
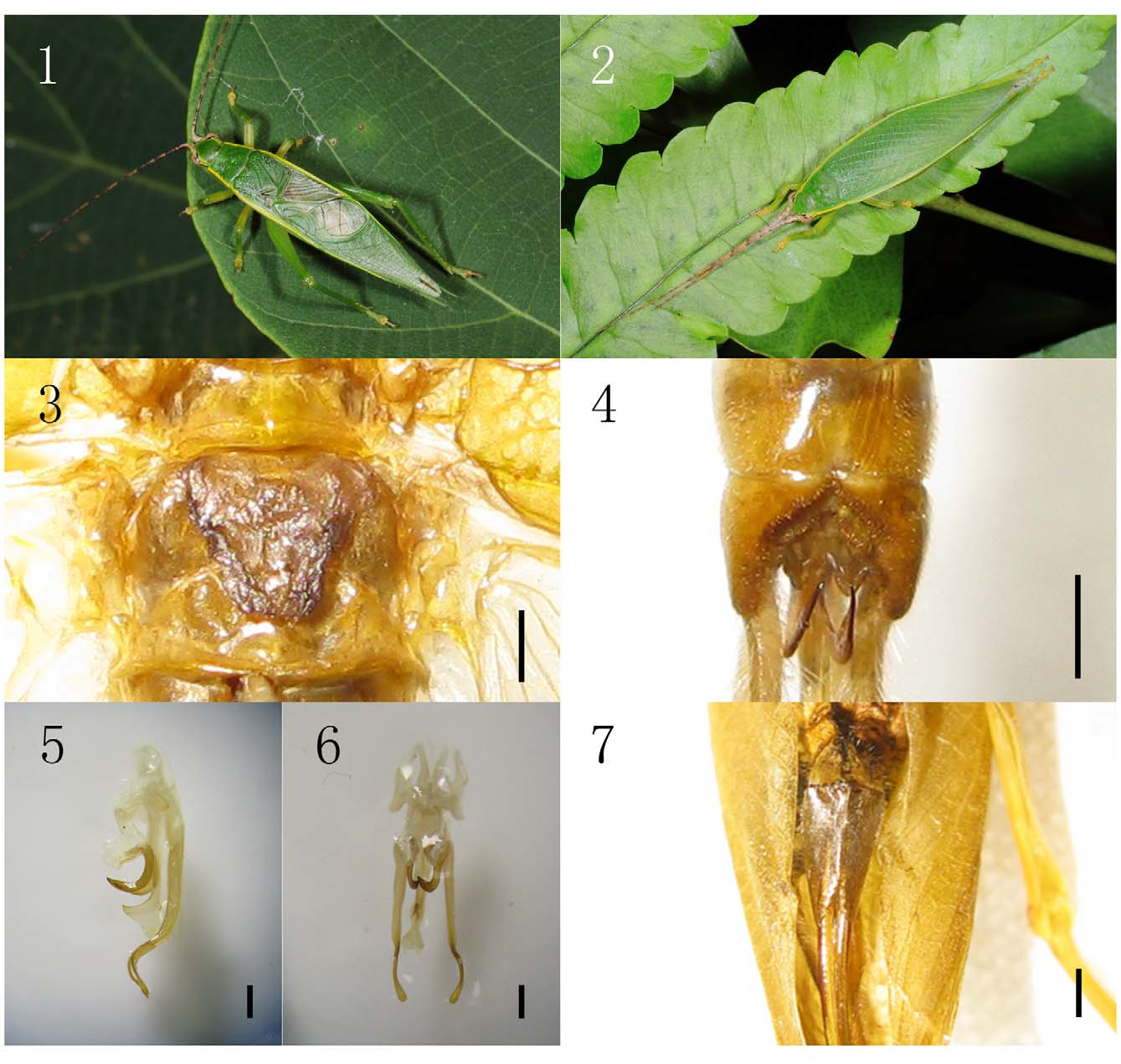
Figs. 1–11 View FIGURES 1 – 7 View FIGURES 8 – 10 View FIGURES 11 – 13
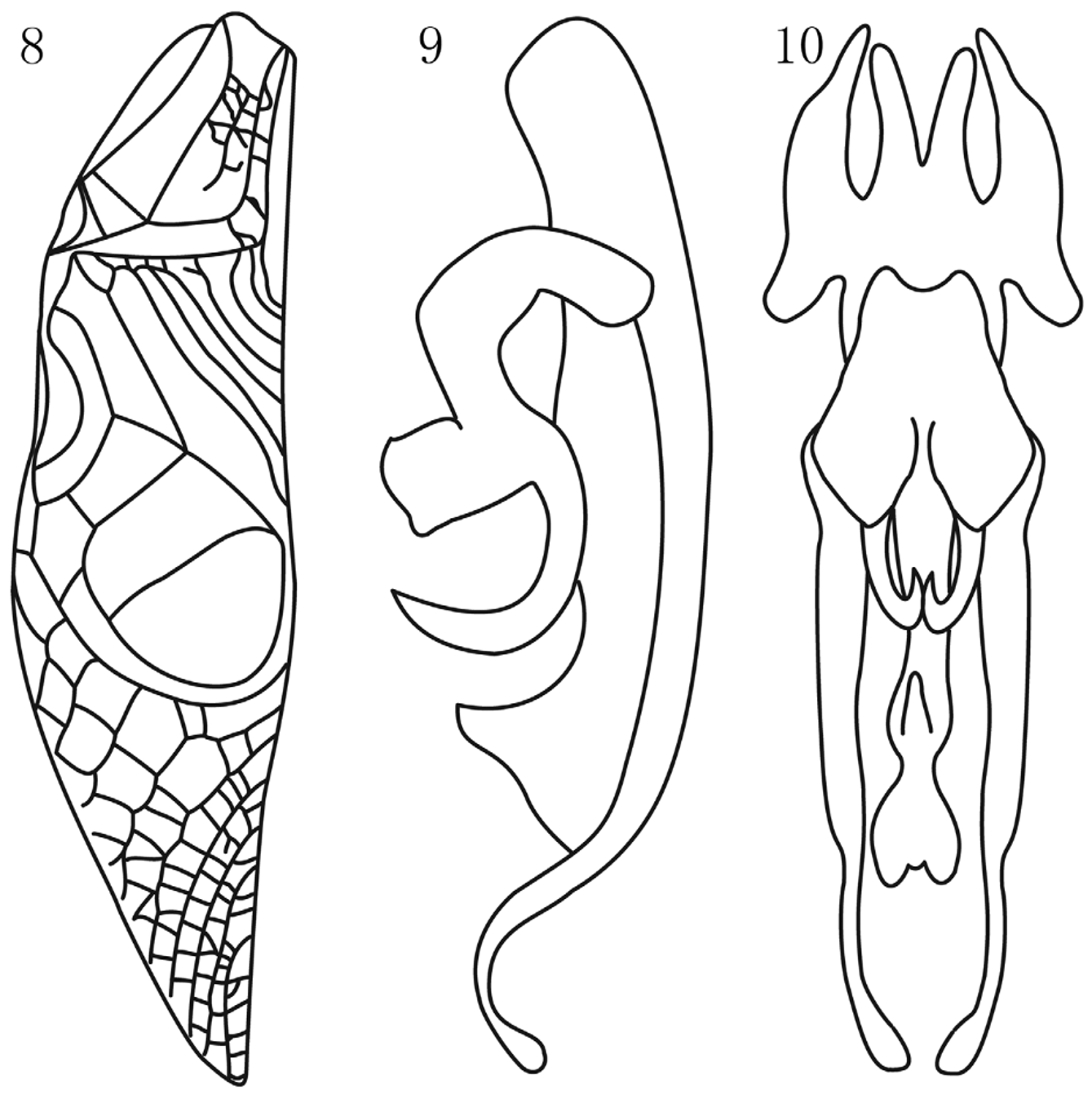
Description. Male. Medium size, slim body and nearly glabrous. Head is small and round. Frontal rostrum is little narrower than 1st antennal joint. Pronotum widened posteriorly. Lateral margin has obviously edges. Tegmina with 4 long/3 short curved oblique veins on right and 3 long/3 short on left ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 8 – 10 ). Mirror slightly shorter than wide (length ratio = 31: 27). Metanotal gland nearly triangular with few hairs on two sides which can not been seen from dorsal view ( Fig. 3 View FIGURES 1 – 7 ). External tympanum ovoid; internal tympanum slit-like with a swollen cover. Hind femur slender, not heavy. Dorsal spines on outer margin small and numerous, with 4 spurs in apical half. Dorsal spines on internal margin present only in basal half; apical half with 5 spurs which are obviously bigger than the outside ones. Supra anal plate is divided into two parts ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 1 – 7 ) as typical of the Truljalia Group I ( Gorochov, 2002).
Genitalia: Epiphallus with acute angle. Ectoparameres is very long with curved portion apical, but it becoming elliptical and flat posteriorly ( Fig. 5, 6 View FIGURES 1 – 7 , 9, 10 View FIGURES 8 – 10 ).
Female. Similar to male. Subgenital plate with deep median incision ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 1 – 7 ).
Coloration. Body nearly yellow (green when alive). Antennae alternately black and pale segments. Head with black stripe from eye to pronotum; a yellow stripe from eye to lateral margins and subccostal vein, more prominent when alive. Ventral surface with a short black lateral stripe and one black spot which are positioned beside the lateral margins. Tegmen yellow, hind wing colourless, transparent; most veins brown but yellow in the apical field.
Song. Type: Calling song. Temperature: 21 degree. Date: 2012-X-8. ( Figure 11–13 View FIGURES 11 – 13 )
Song is quite regular and slow as 0.95 C/S. Every chirp includes 9–11 pulses. Chirps last for 266.3±22.9 ms and pauses are 634.8±102.8 ms. The first several pulses in each chirp are weak. Pulse is 35.57±0.60 p/s. Main frequency is 5575±49 Hz.
Measurements (mm). Male: body 18.0–22.0, length with wings 24.0–25.0, pronotum 3.0, tegmen 19.0–20.0, hind femur 9.0; female: body 18.0, length with wings 30.0, pronotum 3.2, tegmen 23.5, hind femur 11.0, ovipositor 9.0.
Type material. Holotype 3, Taiwan, Pingdong County, Chunri Town, Dahan Mountain (N 22.4° E 120.7°), 2012-X-8. Altitude 1000m. HE Zhuqing & LIN Yixiang leg. ( IEAS)
Paratype: 131Ƥ, same data as the holotype. 13, attracted by light, other data same as the holotype ( IEAS).
Diagnosis. The genitalia of the new species is similar with T. meloda Gorochov, 1992 , but the apical part of ectoparameres is ellipse and flat as same as T. hofmanni (Saussure, 1878) .
Etymology. The new species is named after its locality, Taiwan.
| IEAS |
Institute of Entomology |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Podoscirtinae |
|
Tribe |
Podoscirtini |
|
Genus |