Protohermes goodgeri, Liu, Xingyue, Hayashi, Fumio & Yang, Ding, 2013
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3620.4.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3234B0FB-5630-4080-A98B-2474C4A86C6D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6149972 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/717887AC-CB08-FFAE-FF57-FE69FC49D9BD |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Protohermes goodgeri |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Protohermes goodgeri sp. nov.
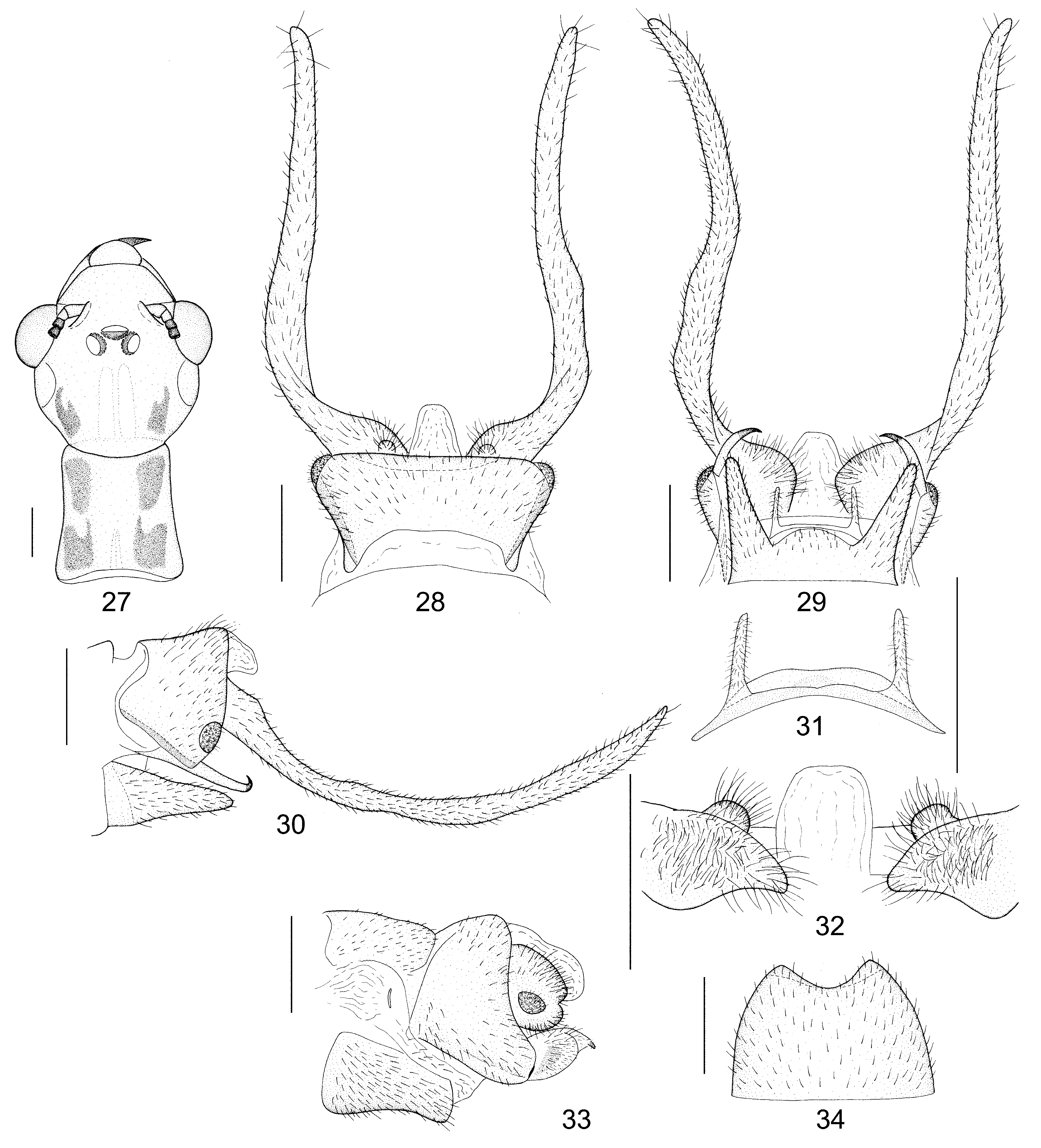
( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 4 – 6 , 27–34 View FIGURES 27 – 34 )
Diagnosis. In appearance there are one pair of black markings on posterolateral portions of vertex and two pairs of black markings on pronotum, and the forewing has a darkened transverse band, which extends posteriorly to CuA vein, between proximal and median pale markings. Genitalia of this species are characterized by the male ninth sternum with a pair of slender digitiform posterior lobes and the male ectoproct widely connected with ninth tergum by an inflated base which dorsally bears a small tubercle-shaped process.
Description. Male. Body length 25 mm; forewing length 33 mm, hindwing length 29 mm.
Head ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 4 – 6 ) yellow, vertex posterolaterally with a pair of anteriorly produced black markings; post-ocular spine absent. Compound eyes brown; ocelli yellow, medially margined black, lateral ocelli close to median ocellus. Antenna black with scape and pedicle yellow. Mouthparts yellow; mandible with distal half black; labial palpi with distal three segments brown.
Thorax ( Fig. 4 View FIGURES 4 – 6 ) yellow; pronotum with two pairs of black markings near lateral margins; meso- and metanota laterally pale brown. Thoracic pilosity white, much longer on meso- and metathorax. Legs yellow, with short dense yellowish setae; tarsal claws pale reddish brown. Wings hyaline, with several whitish markings. Forewing slightly brownish; proximally with one subtriangular marking, medially with several irregular markings usually fused with each other, and with one round marking at distal 1/3; membrane between basal and median markings darkened into a transverse band, posteriorly narrowed and extending to CuP. Hindwing almost hyaline with marginal area pale brown. Veins brown except for those in pale markings yellow. Rs 8 to 9-branched; MA bifurcate; 6–8 crossveins between R and Rs; anterior branch of MP 6-branched, posterior branch of MP 2-branched.
Abdomen yellow. Ninth tergum ( Fig. 28 View FIGURES 27 – 34 ) subtrapezoidal, with arcuately incised anterior margin and truncate posterior margin. Ninth sternum ( Fig. 29 View FIGURES 27 – 34 ) medially short, posterior margin deeply incised trapezoidal, forming a pair of attenuate posterior lobes. Ninth gonostylus ( Fig. 29 View FIGURES 27 – 34 ) slender unguiform, directed posteroventrad in lateral view, with tip slightly incurved. Ectoproct (Figs, 28–30, 32) slender band-like, extremely elongate, ~4.0 times as long as ninth tergum, proximal 1/4 directed posterolaterally, with remaining part nearly straightly directed posteriad in dorsal view and slightly curved dorsad in lateral view; base widely connected to ninth tergum, broadly inflated, dorsally with a small tubercle-shaped process. Tenth gonocoxite ( Fig. 31 View FIGURES 27 – 34 ) arched, dorsomedially strongly expanded into a broad plate; lateral lobes digitiform, straightly directed posteriad.
Female. Body length 29–30 mm; forewing length 39–42 mm, hindwing length 35–37 mm.
Eighth gonocoxite ( Figs. 33–34 View FIGURES 27 – 34 ) in lateral view, subtrapezoidal with arcuately convex posterior margin; in ventral view posterior margin medially with a deep arcuate incision. Ninth gonocoxite ( Fig. 33 View FIGURES 27 – 34 ) broad, posteriorly narrowed and ventrally incised, with a small gonostylus. Ectoproct ( Fig. 33 View FIGURES 27 – 34 ) short, with posterior margin medially incised, leaving thick, convex dorsal and slightly shorter and thinner ventral lobes in lateral view.
Type materials. Holotype 3, MALAYSIA: “ Sarawak: Mt. Dulit [3°20ʹN, 114°09ʹE], 4000 ft [= 1219 m], 14.IX.1932, Moss Forest/Oxford Univ[ersity].Exp[edition], B.M. Hobby & A.W. Moore, B.M.1933-254” (BMNH). Paratypes: MALAYSIA: Sarawak: 1Ƥ, same data as holotype (BMNH); 1Ƥ, “Mt. Dulit, 4000 ft [= 1219 m], 21.X.1932, Moss Forest/Oxford Univ[ersity].Exp[edition], B.M. Hobby & A.W. Moore, B.M.1933-254” (BMNH); 1Ƥ, “Mt. Dulit, 4000 ft [= 1219 m], 2.X.1932, Moss Forest/Oxford Univ[ersity].Exp[edition], B.M. Hobby & A.W. Moore, B.M.1933-254, F.W. RICHARDS” (BMNH).
Distribution. Malaysia ( Sarawak).
Etymology. The new species is dedicated to Mr. David T. Goodger, who is the curator for Megaloptera collection in the BMNH and kindly assisted the first author during his visit to this collection.
Remarks. The new species represents first record of this species-group in Sarawak. Protohermes goodgeri seems to be closely related to P. bellulus in having similar dorsally curving male ectoproct, but can be separated with the latter species by the male ectoproct with an inflated base, which dorsally bears a small tubercle-shaped process. In P. bellulus the male ectoproct has a simple narrow base.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |