Geranomyia piagola, Podenas, Sigitas, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4121.5.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:5DE272A5-EDFF-468E-82F5-DC5D92880011 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6068945 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7201A67A-FFBA-FFBB-31A4-97B65D59FC64 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Geranomyia piagola |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Geranomyia piagola View in CoL n. sp.
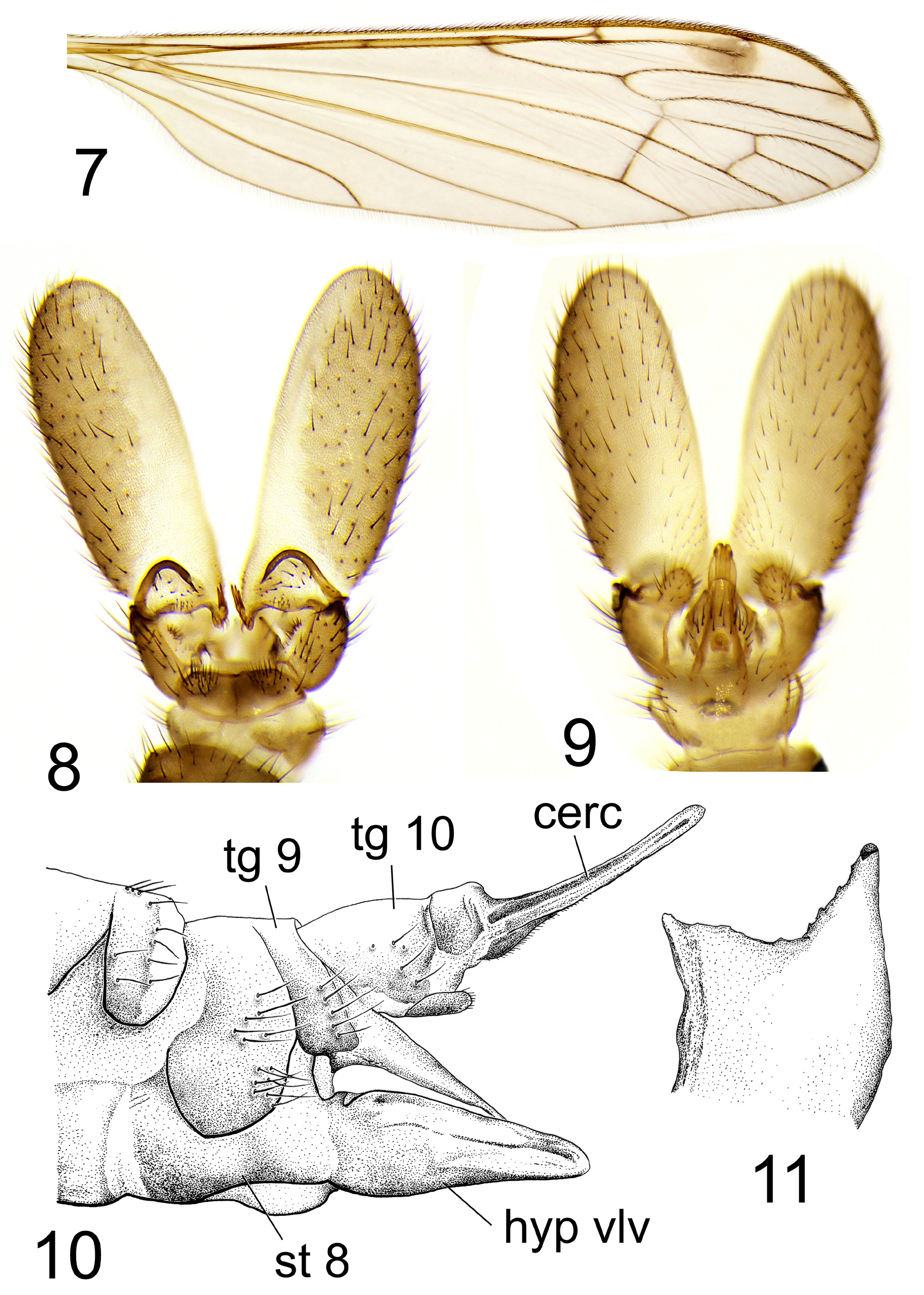
Figures 7–11 View FIGURES 7 – 11
Etymology. The species is named after the place name of Piagol valley ( Fig. 17 View FIGURES 16 – 17 ), where it was collected.
Material examined. Type specimens. Holotype male, paratypes 1 male and 1 female.
Holotype, male (pinned, wing slide-mounted, genitalia in microvial filled with glycerol and pinned together). SOUTH KOREA, Jeollanam-do, Gurye-gun, Toji-myeon, Naeseo-ri, Jirisan National Park, Piagol valley, N35.26590, E127.58096, alt. 446 m, 2014.08.24, coll. S. Podenas.
Paratypes: female (in ethanol), S. Korea, Jeollanam-do, Gurye-gun, Toji-myeon, Naedong-ri, N35.26580, E127.58128, alt. 378 m, 2013.05.12, S. Podenas, net ( NIBR); male (in ethanol), S. Korea, Jeollanam-do, Guryegun, Toji-myeon, Naeseo-ri, N35.27177, E127.57146, alt. 490 m, 2015.06.29, S. Podenas, net.
Diagnosis. Distinguished from other species in the genus by distinct dark longitudinal stripe on pleura and details of male genitalia, especially strongly extended inner gonostylus, bearing small rostral prolongation armed with two-three short spines situated on same tubercle.
Description ( Figs. 7–11 View FIGURES 7 – 11 ). Adult, male (N =2). General body coloration brown. Body length 5.9–6.2 mm. Wing length 6.5–7.2 mm. Head: black, sparsely dusted with gray pruinosity, covered with scarce semi-erect black setae. Vertex very narrow. Eyes large, dorsally separated by very narrow vertex, ventrally reaching each other. Length of antenna 1.0– 1.2 mm. Scape cylindrical, black, dorsally bearing few short erect dark setae. Pedicel rounded, same color as scape, dorsally bearing few short erect dark setae. Both basal segments sparsely dusted with gray. Flagellum 12-segmented. Three basal flagellomeres black, remaining segments brown, turning lighter towards apex. Basal flagellomere approximately as long as pedicel, distinctly narrower; remaining flagellomeres oval, slightly decreasing in length, apical flagellomere approximately 1.5 times as long as preceding segment. Verticils short, approximately as long as respective segments. Short whitish pubescence denser on ventral side of segments. Rostrum dark brown dorsally, lighter ventrally, reaching to second flagellar segment. Mouth parts same color as rostrum, covered with short adherent brownish setae. Rostrum together with mouth parts 2.3 mm long. Palpus dark brown, three-segmented. Basal segment very short, second segment oval, wider, longer than first segment, apical segment very small, rounded with few distinct erect setae. Thorax: generally yellowish brown. Cervical sclerite blackened. Pronotum frontally dark brown, posteriorly brownish yellow. Ground color of mesonotal prescutum light brown. Median prescutal stripe brown, distinct, lateral stripes indistinct, slightly darker than surrounding area. Frontal margin of prescutum yellowish. Pseudosutural fovea yellowish. Scutal lobes brown frontally, dark brown posteriorly. Scutellum dark brown frontally, posteriorly and laterally brown. Mediotergite uniformly dark brown. Pleuron yellowish brown dorsally, pale yellowish ventrally with distinct wide dark brown longitudinal stripe. Wing ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 7 – 11 ) brownish, subcostal cell yellowish. Stigma distinct, brown, egg-shaped. Small brownish spots surrounding tip of R3, both branches of Sc, base of Rs and supernumerary cross-vein in cell sc. Very weak darkenings surround cord and distal end of discal cell. Most veins brown, veins at wing base pale. Venation: Sc1 long, ending slightly before end of Rs, Sc2 close to Sc1 tip. Supernumerary cross-vein in cell sc approximately at two thirds distance from humeral vein to base of Rs. Radial sector slightly arched at base. Both branches of Rs slightly diverging towards wing margin. Vein r-m well developed. Discal cell comparatively wide, slightly more than twice as long as wide. Free end of M1+2 slightly shorter than its basal part forming frontal margin of discal cell. Basal deflection of CuA1 exactly at branching point of M. Both anal veins long, A1 slightly sinuous, A2 slightly arched at distal end. Anal angle medium-sized, posterior margin widely rounded. Halter 0.8–1.0 mm long, grayish, base of stem pale. Coxae yellow, frontal face of fore coxae slightly infuscated. Frontal trochanter yellow with slightly darkened distal part, second and third pair grayish. Distal margin of all trochanters narrowly blackened. Femur obscure yellow, tibiae light brown, tarsus light brown at base turning dark brown towards distal end. Femur covered with short blackish adjacent setae, similar setae on tibiae and tarsus brownish. Femur I: 4.4– 4.9 mm, II: 5.0– 5.3 mm, III: 5.0– 5.6 mm; tibiae I: 5.6–5.8 mm, II: 5.7–5.8 mm, III: 5.8–5.9 mm; tarsus I: 4.5–5.1 mm, II: 3.9 mm, III: 3.8–4.1 mm. Claw blackish with small subbasal spine. Abdomen: tergites blackish, covered with erect golden setae. Basal sternite pale, remaining sternites brownish. Male terminalia ( Figs. 8, 9 View FIGURES 7 – 11 ) with dark brown ninth tergite, gonocoxite and inner gonostylus light brown. Posterior margin of ninth tergite very shallowly emarginate, lateral parts slightly raised and covered with dense short brown setae. Gonocoxite elongate, bearing large ventro-median lobe ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 7 – 11 ). Distal part of lobe rounded, covered with long erect setae. Outer gonostylus strongly sclerotized, darkened, hook-shaped with sharply pointed distal end. Inner gonostylus very
elongate, about three times as long as gonocoxite, oval, with fronto-median angle extended into small rostral prolongation. Rostral prolongation directed towards frontal end with small subapical tubercle covered with small brown setae. Tubercle armed with two-three short straight brown spines, situated closely together along entire length. Right gonostylus of holotype with two, left with three spines. Paramere ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 7 – 11 ) wide at base, distal part extended into narrow lobe. Penis long, narrow in dorsal view, “S“-shaped in lateral view, with tip pointed downwards.
Female (N=1). Generally similar to male. Body length 5.8 mm. Wing length 7.9 mm. Ovipositor ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 7 – 11 ) with cercus and hypovalva brown. Cercus nearly parallel-sided, straight, tip rounded. Hypovalva wide, comparatively short and blunt-apexed, reaching to about middle of cercus. Vaginal apodeme very extended, distal part very narrow, apex nearly reaches tip of valve.
Habitat. Margins of medium-sized mountainous stream with springs on slopes, covered by mixed forest.
Elevation. Species was found at altitudes of about 380– 500 m.
Period of activity. Adults are flying from the middle of May through the end of August.
Distribution. Jirisan National Park, South Korea.
Discussion. Geranomyia piagola n. sp. has very distinct male genitalia, especially an extremely elongate inner gonostylus. In general, the male genitalia of G. piagola n. sp. resembles that of the Chinese species G. obesistyla ( Alexander, 1940) . Genitalia of both species differ only in the small details of the rostral prolongation of inner gonostylus, the shape of ventro-median lobe of gonocoxite, the shape of penis and the shape of the paramere. Both species could be easily separated on wing venation, wing pattern and body coloration. G. piagola n. sp. has a distinct longitudinal dark stripe along the pleura, the pleura of G. obesistyla is almost uniformly brownish testaceous. The wing of G. obesistyla has distinct brown spots on the frontal margin, the basal deflection of CuA1 is situated well before the branching point of M. The wing venation and pattern of G. piagola n. sp. is very similar to that of other Korean species G. gifuensis , but both species are easily separated based on the male genitalia, especially shape of inner gonostylus.
| NIBR |
National Institute of Biological Resources |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |