Simulium vernum
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.571608 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C097C43E-D522-46C4-9D64-76D3CD4BAD86 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4927543 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/7E4B87AF-B175-A24C-FF2B-FB6FFB67FD27 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Simulium vernum |
| status |
|
3) Simulium vernum View in CoL species-group
Simulium (Nevermannia) laichauense Takaoka & Sofian-Azirun sp. nov.
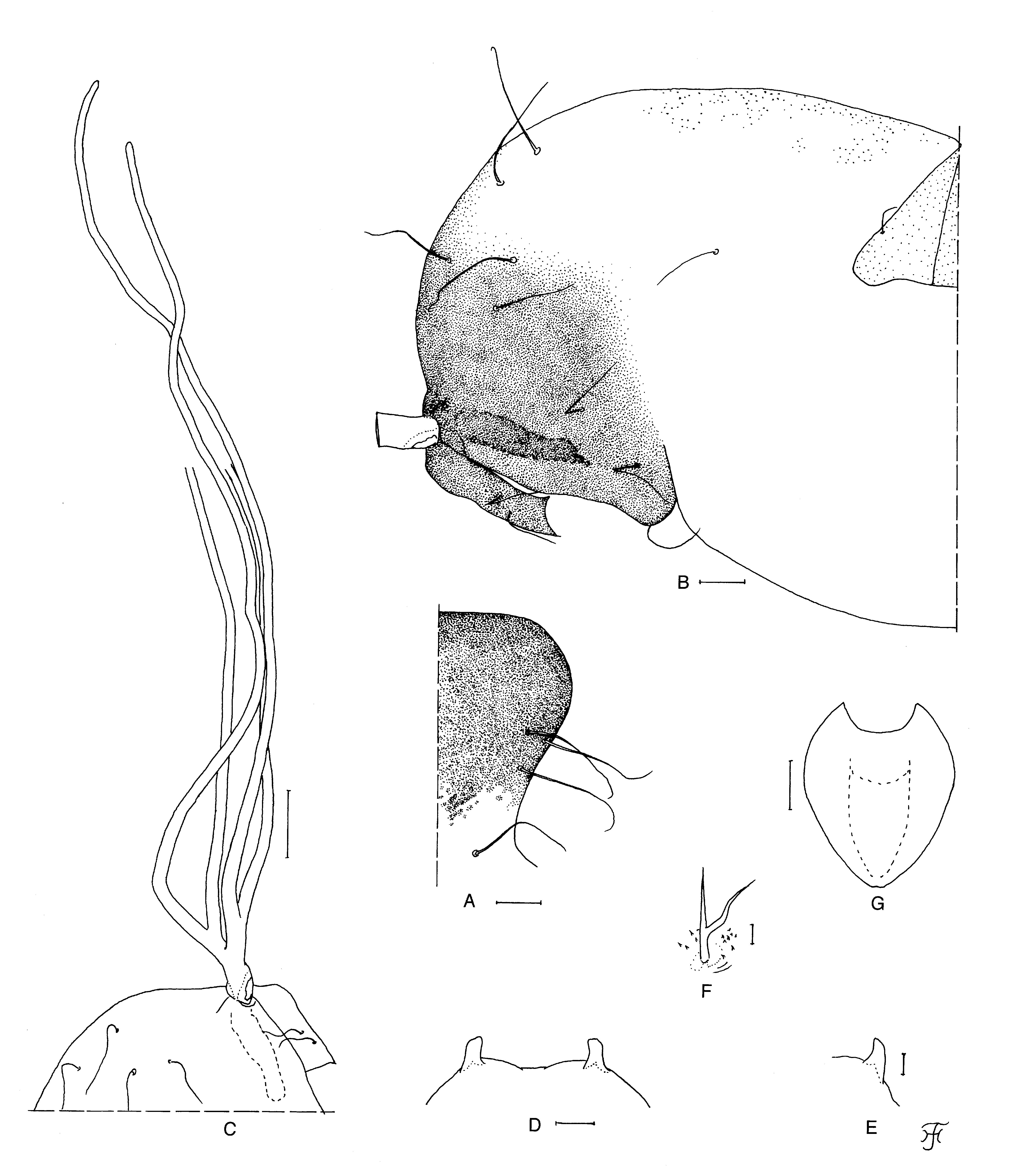
Female. Body length 2.5 mm. Head. Slightly narrower than width of thorax. Frons brownish black, moderately covered with whitish yellow (golden yellow when illuminated at certain angles) recumbent short hairs interspersed with few dark-brown long hairs along each lateral margin; frontal ratio 1.8:1.0:2.6. Frons:head ratio 1.0:5.9. Fronto-ocular area directed laterally and slightly upward, rounded apically. Clypeus dark brown, thinly whitishgray pruinose, slightly shiny when illuminated at certain angles, moderately covered with yellow short hairs interspersed with one to three dark-brown long hairs though mediolongitudinal area widely bare. Labrum 0.7 times as long as clypeus. Antenna composed of scape, pedicel and nine flagellomeres, entirely brownish black; first flagellomere 1.6 times as long as second one. Maxillary palp composed of five segments, medium brown except segments 1 and 2 ochreous and segment 3 dark brown, proportional lengths of third, fourth, and fifth segments 1.0:0.8:1.5; third segment ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 A) somewhat enlarged; sensory vesicle ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 A) enlarged, ellipsoidal, 0.5 times as long as third segment, and with large opening apically. Maxillary lacinia with 15 inner and 17 or 18 outer teeth. Mandible with 35 inner and 17 or 18 outer teeth. Cibarium ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 B) with enlarged cornuae; no processes near anterodorsal surface. Thorax. Scutum black except anterolateral calli dark brown, thinly whitish-gray pruinose and slightly shiny when illuminated at certain angles, densely covered with whitish yellow (golden yellow when illuminated at certain angles) recumbent short hairs. Scutellum dark brown, covered with whitish-yellow short hairs and dark-brown long hairs. Postnotum brownish black, whitish-gray pruinose and slightly shiny when illuminated at certain angles, and bare. Pleural membrane bare. Katepisternum longer than deep, brownish black, whitish-gray pruinose and slightly shiny when illuminated at certain angles, and bare. Legs. Medium to dark brown except basal extreme of hind tibia and narrow portion of pedisulcus of second tarsomere pale. Fore basitarsus somewhat dilated, 8.7 times as long as its greatest width. Hind basitarsus ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 C) slender, nearly parallel-sided, 7.8 times as long as wide, and 0.7 and 0.6 times as wide as tibia and femur, respectively; calcipala ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 C) well developed, slightly longer than basal width, and 0.5 times as wide as greatest width of basitarsus; pedisulcus ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 C) well developed; claw ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 D) with large basal tooth 0.5 times length of claw. Wing. Length 2.9 mm. Costa with dark-brown spinules and hairs except basal patch of hairs yellowish white. Subcosta with dark-brown hairs except apical one-fifth or one-fourth bare. Hair tuft on base of radius dark brown. Basal portion of radius fully haired. R1 with dark-brown spinules and hairs. R2 with dark-brown hairs only. Basal cell and basal median cell absent. Halter . White except basal stem darkened. Abdomen. Basal scale ochreous to light brown, with fringe of yellowish-white long hairs; dorsal surface of abdomen medium brown except rest of tergal plate of segment 2 ochreous, and moderately covered with whitish-yellow short hairs as well as dark-brown short to medium-long hairs; tergites 6–8 shiny when illuminated at certain angles; ventral surface of segments 2–7 light ochreous, and segment 8 medium brown; segment 7 with weakly defined large sternal plate medially. Terminalia . Sternite 8 ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 E) bare medially, and with 10–14 short to long hairs on each side. Ovipositor valve ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 E) triangular, rounded posteromedially, thin, membranous, densely covered with microsetae interspersed with four to six fine short setae (though one seta on each side medium-long); inner margins moderately sclerotized, narrowly darkened, slightly sinuous, and moderately separated from each other. Genital fork ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 F) of usual inverted-Y form, stem slender and moderately sclerotized; arms each with broad lateral plate having strongly sclerotized lateral margin. Paraproct in ventral view ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 G) ovoidal, with strongly sclerotized anterior surface, covered with 10 mediumlong and long hairs on ventral and lateral surfaces, with shallow depression along anteromedial margin, with four or seven sensilla on anteromedial transparent surface; paraproct in lateral view ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 H) slightly produced ventrally beyond ventral margin of cercus. Cercus in ventral view ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 G) narrow, with widely concave inner surface; cercus in lateral view ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 H) rounded posteriorly, 0.6 times as long as wide, and with numerous medium-long to long hairs. Spermatheca ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 I) small, ovoidal, 1.2 times as long as its greatest width, well sclerotized except area at juncture with duct, with reticulate surface pattern; internal setae absent; main duct and both accessory ducts subequal in diameter to one another.
Pupa. Body length (excluding gill filaments) 3.4 mm. Head. Integument including antennal sheath yellow except frons dark brown ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 A), and bare; frons with three unbranched long trichomes with straight apices ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 A) arising close together with one another on each side; face with one unbranched long trichome with straight apex ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 A) on each side. Thorax. Integument yellow except anterolateral portion widely dark brown, and bare except posterodorsal surface sparsely covered with small tubercles ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 B); thorax with three long anterodorsal trichomes with coiled or straight apices, two long anterolateral trichomes with straight apices (one slightly shorter than other), one medium-long mediolateral trichome with straight apex, and three ventrolateral trichomes with straight apices (two long, one medium-long) ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 B), on each side; all trichomes unbranched. Gill ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 C) with four slender thread-like filaments, arranged in dorsal and ventral pairs, each with short stalk arising from short common basal stalk with moderate basal fenestra at base; common basal stalk 0.54 times length of interspiracular trunk; stalks of dorsal and ventral pair subequal in length and thickness to each other, 0.4–0.5 times length of common basal stalk; common basal stalk directed forward and somewhat outward, stalk of dorsal pair directed upward and forward, with upper filament directed upward and forward, then curved downward, and lower filament directed forward; stalk of ventral pair directed somewhat outward and forward, with outer and inner filaments directed forward; upper filament of dorsal pair and outer filament of ventral pair on each side subequal in length (2.6 mm) to each other, lower filament of dorsal pair and inner filament of ventral pair on each side broken losing apical half, thus not measurable; upper filament of dorsal pair as thick as or very slightly thicker than outer filament of ventral pair; lower filament of dorsal pair and inner filament of ventral pair subequal in thickness to each other, and 0.9 times as thick as counter filament of each pair when compared basally; upper filament of dorsal pair and outer filament of ventral pair slightly tapered toward apices, each with relatively thick apical portion (0.6 times as thick as basal portion); all filaments medium brown, with annular ridges and furrows forming reticulate patterns on surface of basal half, and densely covered with minute tubercles on outer surface. Abdomen. Dorsally, segments 1 and 2 dark gray and with minute spine-like tubercles, basal half of segment 3 grayish, and other segments unpigmented except basal portions of spine-combs on segments 6–9 yellowish and posterior half of segment 9 light grayish; segment 1 with one medium-long hair-like seta on each side; segment 2 with one medium-long hair-like seta and five spinous short setae on each side; segments 3 and 4 each with four dark stout hooked spines and one short spinous seta along posterior margin on each side; segments 2–4 each with one minute seta near anterior margin on each side; segments 5–9 each with comb-like groups of minute spines in transverse rows on each side; segments 6–9 each with spine-combs in transverse row on each side (though those on segment 9 much smaller in size than those on other segments); segment 9 with pair of short blunt terminal hooks ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 D, E). Ventrally, all segments unpigmented except segment 9 yellowish gray; segment 4 with one bifid hook and few unbranched short setae on each side; segment 5 with two bifid hooks and few unbranched short setae on each side; segments 6 and 7 each with one bifid or trifid inner hook and one bifid outer hook and few unbranched short setae on each side; segments 4–8 each with comb-like groups of minute spines; all hooks on segments 4–8 each with several minute spines near its base ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 F). Cocoon ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 G). Wall-pocket-shaped, moderately woven, anterior margin thickly woven, and extended ventrolaterally, without projection; floor woven on posterior two-thirds; individual threads visible; 3.8 mm long by 3.1 mm wide.
Male and Mature larva. Unknown.
Type material. HOLOTYPE: Female (with its associated pupal exuviae and cocoon) in 80% ethanol, labeled in a vial as [ UMSRP: Vietnam 0 32, Holotype, Simulium (N.) laichauense , Female , coll. Vietnam, 20-XII-2014, Takaoka et al.], reared from a pupa collected from a river (width 6 m, depth 0.6 m, bottom rocky, water temperature 11.0˚C, exposed to the sun, elevation 1,728 m, 22˚22’22.719”N/103˚45’24.852”E) fast-flowing near a forest, Lai Chau, Sapa , Lao Cai Province, northern Vietnam, 20-XII-2014, by H. Takaoka, M. Sofian-Azirun, Z. Ya’cob, C.D. Chen & K.W. Lau.
Biological notes. The pupa of this new species was collected from a grass leaf trailing in the current. Associated species were S. (N.) tayense sp. nov. and S. (S.) giayense sp. nov.
Distribution. Vietnam (Lao Cai).
Etymology. The species name laichauense refers to the locality name, Lai Chau, where this new species was collected.
Remarks. This new species is assigned to the S. vernum species-group of the subgenus Nevermannia , defined by Crosskey (1969), judging from the female terminalia ( Fig. 28 View FIGURE 28 E–H) and pupal gill with four long slender filaments ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 C). The pupa of this new species is remarkable in having a darkened frons and anterolateral surface of the thorax ( Fig. 29 View FIGURE 29 A, B), by which it is distinguished from other members of the S. vernum speciesgroup.
Simulium (Nevermannia) tayense Takaoka & Ya’cob sp. nov.
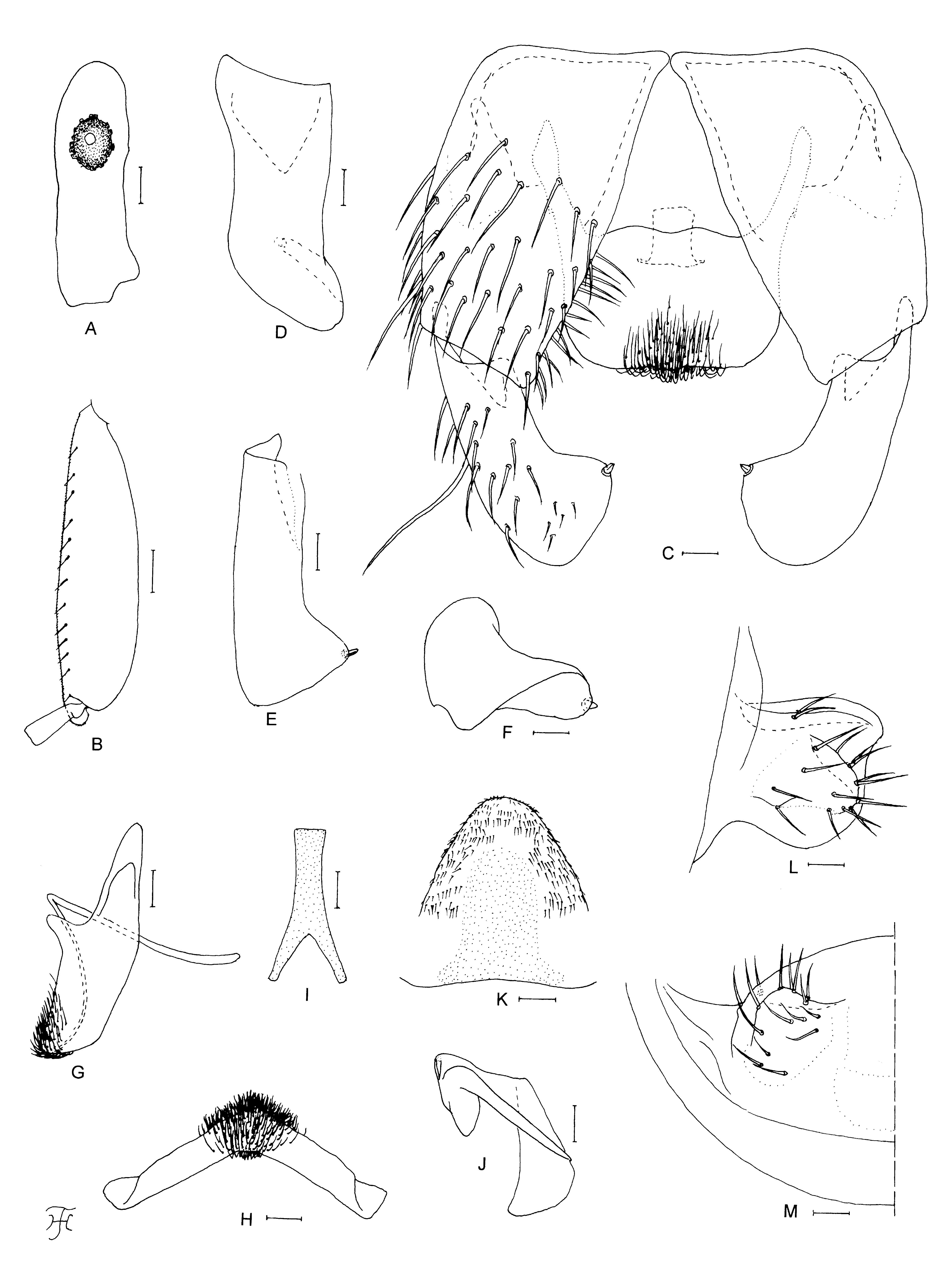
Female. Body length 2.8 mm. Head. Slightly narrower than width of thorax. Frons brownish black, gray pruinose, not shiny, densely covered with whitish-yellow scale-like recumbent short hairs interspersed with few dark longer hairs along each lateral margin; frontal ratio 1.7:1.0:2.4; frons:head ratio 1.0:4.9. Fronto-ocular area well developed, narrow, directed dorsolaterally. Clypeus dark brown, gray pruinose, moderately covered with whitishyellow hairs interspersed with few dark longer hairs on each side, though upper and lower portions bare. Labrum 0.9 times as long as clypeus. Antenna composed of scape, pedicel and nine flagellomeres, brownish black except scape and pedicel medium brown. Maxillary palp composed of five segments, light to medium brown except anterior surface of segments 1 and 2 yellowish and third segment dark brown, proportional lengths of third, fourth, and fifth segments 1.0:0.8:1.5; third segment ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 A) swollen; sensory vesicle ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 A) elongate (0.6–0.7 times as long as third segment), with medium-sized opening. Maxillary lacinia with 13 or 14 inner and 15 or 16 outer teeth. Mandible with 32–34 inner and 14 or 15 outer teeth. Cibarium ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 B) without any processes. Thorax. Scutum brownish black except anterolateral calli medium brown, densely covered with yellow scale-like recumbent hairs interspersed with several dark-brown long upright hairs on prescutellar area. Scutellum medium brown, moderately covered with yellow short hairs mixed with several dark-brown long upright hairs. Postnotum dark brown, and bare. Pleural membrane bare. Katepisternum dark brown to brownish black, longer than deep, whitish-gray pruinose, slightly shiny when illuminated at certain angles, and bare. Legs. Foreleg: coxa and trochanter light brown; femur dark yellow to light brown except apical cap dark brown; tibia dark brown, with median large portion on outer surface light brown; tarsus dark brown, with moderate dorsal hair crest; basitarsus moderately dilated, 8.2 times as long as its greatest width. Midleg: as in foreleg except coxa medium brown on anterolateral surface and dark brown on posterolateral surface, and trochanter medium brown. Hind leg: coxa and trochanter medium brown; femur dark yellow to light brown with apical cap medium brown; tibia medium to dark brown except medial large portion on outer surface light to medium brown; tarsus dark brown except basitarsus light to medium brown (though base dark brown) and basal half of second tarsomere light brown; basitarsus ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 C) narrow, nearly parallel-sided, 7.1 times as long as wide, and 0.8 and 0.7 times as wide as greatest widths of tibia and femur, respectively; calcipala ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 C) nearly as long as width at base, and 0.5 times as wide as greatest width of basitarsus; pedisulcus ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 C) shallow; claw ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 D) with large basal tooth 0.48 times as long as claw. Wing. Length 3.0 mm. Costa with dark-brown spinules and light-brown hairs though intermixed with yellowish hairs basally. Subcosta with light-brown hairs except apical one-fourth bare. Hair tuft on base of radius dark brown. Basal portion of radius fully haired; R1 with dark spinules and hairs; R2 with hairs only. Basal cell absent. Halter . White except basal stem darkened. Abdomen. Basal scale light brown, with fringe of whitishyellow hairs. Dorsal surface of abdomen dark brown except segment 2 light brown, and tergites 7–9 medium brown, moderately covered with dark short to long hairs intermixed with yellow short hairs; tergites of segments 2 and 7–9 wide and shiny when illuminated at certain angles, tergites 3–6 relatively narrow and dull. Ventral surface of abdomen mostly ochreous to medium brown except segment 2 whitish; sternal plate on segment 7 developed medially. Terminalia . Sternite 8 ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 E) bare medially, with 11 medium-long to long yellow hairs together with few slender short yellow hairs on each side. Ovipositor valve ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 E) triangular (though medioposterior corner rounded), thin, membranous, moderately covered with microsetae interspersed with four short slender yellow hairs; inner margins slightly concave medially, somewhat sclerotized, and somewhat separated from each other. Genital fork ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 F) of usual inverted-Y form, with slender stem; arms of moderate width medially; lateral plate of each arm strongly sclerotized along dorsolateral margin, and with thin lobe directed medioposteriorly. Paraproct in ventral view ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 G) nearly quadrate with triangular projection directed medially, with six sensilla on unpigmented anteromedial surface; paraproct in lateral view ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 H) somewhat produced ventrally, 0.7 times as long as wide, with 12 or 13 medium-long to long hairs on ventral and lateral surfaces. Cercus in lateral view ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 H) short, with truncate posterior margin, 0.7 times as long as wide; cercus in end view much curved outward. Spermatheca ( Fig. 30 View FIGURE 30 I) ovoidal, 1.2 times as long as its greatest width, well sclerotized except duct and small area near juncture with duct unsclerotized, and with hexagonal patterns (though not well defined) on surface; internal setae absent; both accessory ducts slender, subequal in diameter to major one.
Male. Body length 3.2 mm. Head. Wider than thorax. Upper eye medium brown, with large facets in 17 vertical columns and 19 horizontal rows. Face dark brown, whitish-gray pruinose. Clypeus brownish black, whitish-gray pruinose, moderately covered with golden-yellow medium-long hairs (mostly directed upward). Antenna composed of scape, pedicel and nine flagellomeres, dark brown except extreme base of first flagellomere light brown; first flagellomere elongate, 1.9 times as long as second one. Maxillary palp composed of five segments, light brown except segments 1 and 2 yellow; proportional lengths of third, fourth, and fifth segments 1.0:0.9:1.8; third segment ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 A) not swollen; sensory vesicle ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 A) ellipsoidal, small, 0.2 times as long as third segment, and with small opening. Thorax. Scutum black, densely covered with golden-yellow recumbent short hairs interspersed with several medium-brown upright long hairs on prescutellar area; other features as in female. Legs. Color nearly as in female except fore trochanter medium brown except inner surface yellow, hind trochanter yellowish except anterior surface medium brown, hind femur yellowish on inner surface. Fore basitarsus slightly dilated, 10.4 times as long as its greatest width. Hind basitarsus ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 B) enlarged, spindle-shaped, 3.8 times as long as wide, and 1.1 and 1.2 times as wide as greatest widths of hind tibia and femur, respectively; calcipala ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 B) slightly shorter than basal width, and 0.3 times as wide as greatest width of basitarsus. Pedisulcus ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 B) well developed. Wing. Length 2.9 mm; other features as in female except subcosta with few hairs. Halter . White except basal stem darkened. Abdomen. Basal scale dark brown, with fringe of dark long hairs. Dorsal surface of abdomen medium brown except little less than basal half of segment 2 ochreous, moderately covered with yellow short hairs intermixed with dark brown short to medium-long hairs; segments 7 and 8 each with pair of slightly shiny lateral patches when illuminated at certain angles; ventral surface of segment 2 white, those of segments 3–6 ochreous except sternites medium brown, and those of other segments medium brown. Genitalia. Coxite in ventral view ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 C) nearly rectangular, twice as long as its greatest width. Style in ventral view ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 C) bent inward, nearly parallel-sided, with truncated apex having apical spine; style in ventrolateral view ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 D) shorter than coxite (0.8 times as long as coxite), straight up to apical one-third, then curved inwardly, widest at base, nearly parallel-sided up to apical one-third, then gradually narrowed toward apex and with rounded apex; style in medial view ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 E) boot-shaped, with triangular apical lobe directed dorsomedially; style in caudal view ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 F) widely depressed on posterodorsal surface of medially-directed apical lobe. Ventral plate in ventral view ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 C) with subquadrate body, 0.7 times as long as wide, with anterior margin undulate with median concavity, both sides nearly straight though posterolateral corners rounded, and posterior margin with two small and shallow concavities submedially; body of ventral plate darkened along anterior margin, and nearly bare except posteromedian portion of ventral surface densely covered with microsetae; basal arms of moderate length, well sclerotized, divergent from base as shown in Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 C; ventral plate in lateral view ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 G) with body slightly narrowed posteriorly; ventral plate in caudal view ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 H) with body appearing as shallow inverted-V shape, having similar width, posteroventral margin roughly undulate, and densely covered with microsetae medially on posterior surface. Median sclerite ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 C, G, I) club-shaped, narrow, with forked apex, and with base located in front of anterior margin of ventral plate. Parameres ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 J) large, each with small apical appendix bearing one distinct long and stout hook and one small short hook at its base. Aedeagal membrane ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 K) moderately setose, dorsal plate well defined, broadly produced ventrally with round apex. Abdominal segment 10 ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 L, M) with one distinct hair on ventral surface and one distinct hair on lateral surface near each posterolateral margin. Cercus ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 L, M) small, rounded, with 14 hairs.
Pupa. Body length 2.8–3.3 mm. Head. Integument light ochreous, bare; antennal sheath without any protuberances; frons with three pairs of unbranched long trichomes with coiled apices ( Fig. 32 View FIGURE 32 A), and face with pair of unbranched long trichomes with coiled apices ( Fig. 32 View FIGURE 32 B). Thorax. Integument light ochreous, bare except dorsal and dorsolateral surfaces of posterior half sparsely covered with small round tubercles (though small area near posterior margin almost bare); thorax with three long dorsomedial trichomes with coiled or straight apices (anterior and middle ones ( Fig. 32 View FIGURE 32 C) slightly longer than posterior one), two long anterolateral trichomes with coiled apices (anterior trichome somewhat shorter than posterior one) ( Fig. 32 View FIGURE 32 D), one medium-long with coiled or straight apex ( Fig. 32 View FIGURE 32 E), and three ventrolateral trichomes with straight apices (one medium-long, two short) ( Fig. 32 View FIGURE 32 F), on each side; all trichomes unbranched. Gill ( Fig. 32 View FIGURE 32 G) composed of four slender thread-like filaments, arranged in pairs, with medium-long common basal stalk having somewhat swollen transparent basal fenestra ventrally at base; common basal stalk 0.7–1.4 times length of interspiracular trunk; stalk of dorsal pair slightly shorter and thicker than that of ventral pair, and 0.2–0.6 times length of common basal stalk; stalk of ventral pair 0.3–0.7 times length of common basal stalk; stalk of dorsal pair 1.1–1.3 and 0.7–0.8 times as thick as stalk of ventral pair and common basal stalk, respectively; all filaments slightly different in length and thickness from one another, though filaments of ventral pair subequal in length and thickness; upper filament of dorsal pair longest, with its length including its own stalk and common basal stalk 4.0– 4.8 mm, ventral filament of dorsal pair second longest with its length 3.3–4.5 mm, two filaments of ventral pair shortest, with their length 3.0– 4.3 mm; relative thickness of filaments from dorsal to ventral when their basal portion measured 1.0:0.8:0.7:0.7; cuticle of all filaments grayish brown except common basal stalk much lighter, with well-defined annular ridges and furrows, and densely covered with minute tubercles. Abdomen. Dorsally, segment 1 entirely dark grayish, segment 2 dark grayish on anterior three-fourths, segment 3 dark grayish on basal half and segment 4 dark grayish on anterior onethird, and segments 1 and 2 weakly tuberculate; segment 1 with one long slender hair-like seta and one to three minute setae submedially on each side ( Fig. 32 View FIGURE 32 H); segment 2 with one short slender hair-like seta and five short somewhat spinous setae submedially along posterior margin ( Fig. 32 View FIGURE 32 I) and one minute seta (similar to those on segment 1) submedially near anterior margin on each side; segments 3 and 4 each with four hooked spines and one short somewhat spinous seta along posterior margin and one minute seta submedially near anterior margin on each side; segments 5–8 each with spine-combs in transverse row and comb-like groups of minute spines along anterior margin and two short setae near posterior margin (except segment 5 with four or five setae) on each side; all setae unbranched; segment 9 with pair of cone-like terminal hooks ( Fig. 32 View FIGURE 32 J) and comb-like groups of minute spines. Ventrally, segment 4 with one short seta and few minute setae on each side; segment 5 with pair of bifid hooks submedially and two short setae on each side; segments 6 and 7 each with pair of bifid inner and unbranched outer hooks somewhat spaced from each other and one short setae on each side; segments 3–8 each with comb-like groups of minute spines. Each side of segment 9 without grapnel-shaped hooklets. Cocoon ( Fig. 32 View FIGURE 32 K). Wallpocket-shaped, light yellowish, thinly woven except anterior margin thickly woven, widely extended ventrolaterally, appearing round when viewed dorsally; anterior margin with medium to long dorsal projection (1.0– 1.2 mm long) usually slightly curved downward; posterior half with floor roughly or moderately woven; individual threads partially visible; 3.4–4.0 mm long by 3.0– 4.6 mm wide.
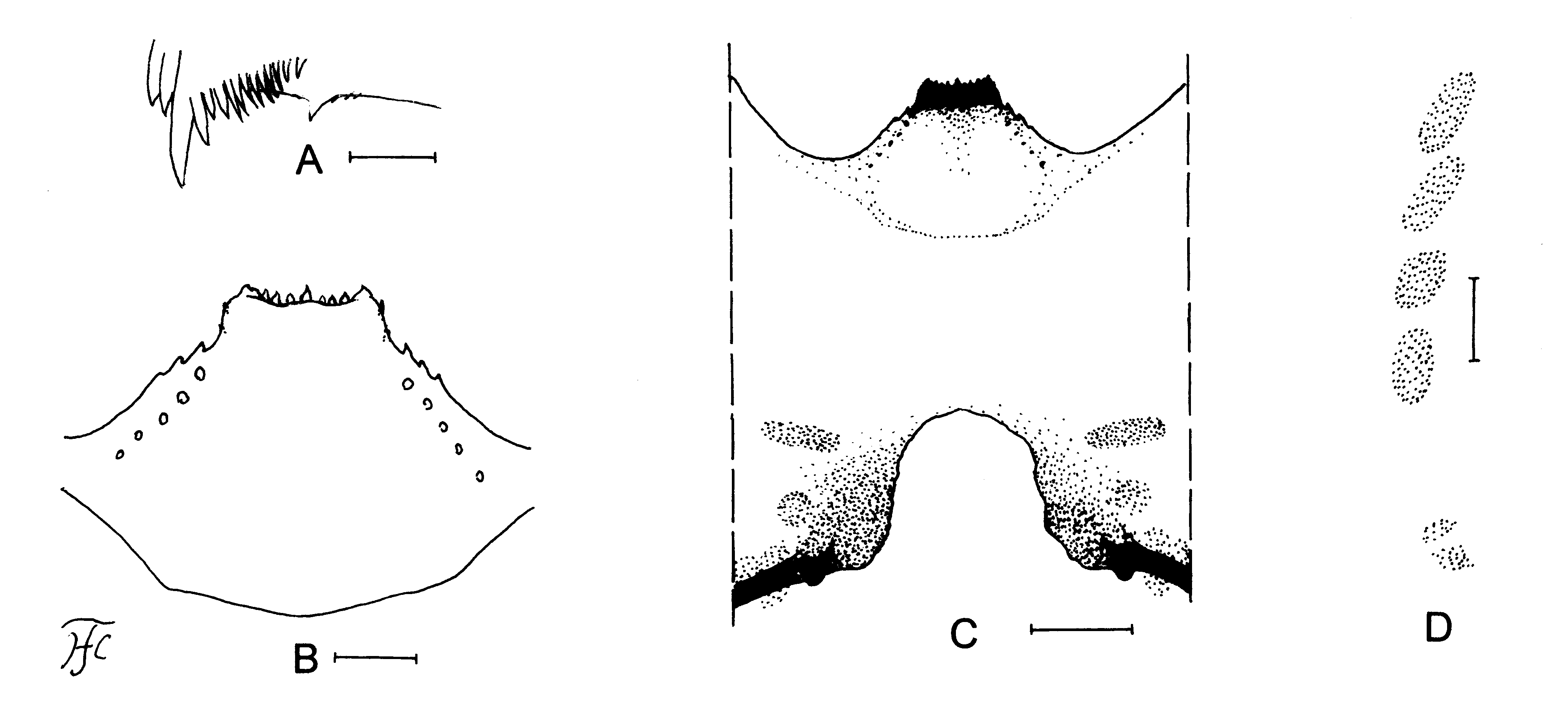
Mature larva. Body length 6.4 mm. Body light ochreous. Head. Cephalic apotome whitish yellow, though narrow area along posterior margin darkened, and moderately covered with unpigmented short setae; head spots moderately positive except anterior spot of mediolongitudinal spots and anterior spots of mediolateral spots in one larva and anterior spots of posterolateral spots in two larvae much lighter. Lateral surface of head capsule whitish yellow except eye-spot region whitish; eyebrow distinct; two relatively large spots and two or three smaller spots in front of posterior margin moderately positive; one small round spot below eye-spot region faintly positive. Ventral surface of head capsule whitish yellow to yellow except darkened area near posterior margin on each side of postgenal cleft; horizontal elongate spot and round spot on each side of postgenal cleft moderately positive. Antenna composed of three articles and apical sensillum, somewhat longer than stem of labral fan; proportional lengths of first, second, and third articles 1.0:1.0:0.7. Labral fan with 35 primary rays. Mandible ( Fig. 33 View FIGURE 33 A) with three comb-teeth, of which first is longest and second is as long as or little shorter than third; mandibular serration composed of two teeth (one medium-sized and one small); major tooth at obtuse angle against mandible on apical side; supernumerary serrations present though consisting of one minute slender tooth or two). Hypostoma ( Fig. 33 View FIGURE 33 B) with row of nine apical teeth; median and each corner tooth prominent, subequal in length to one another and much longer than three intermediate teeth on each side; lateral margin serrate anterirorly; four or five hypostomal bristles per side lying nearly parallel to lateral margin. Postgenal cleft ( Fig. 33 View FIGURE 33 C) short, rounded apically, 0.94 times length of postgenal bridge. Cervical sclerite composed of two medium-brown small oblong pieces, not fused to occiput, widely separated medially from each other. Thorax and Abdomen. Thoracic cuticle bare. Abdominal cuticle almost bare except few posterior segments sparsely or moderately covered with unpigmented short setae, and last segment moderately covered with unpigmented short setae on each side of anal sclerite including ventral papillae. Rectal scales present. Rectal organ compound, with finger-like secondary lobules (number of secondary lobules uncountable due to retracted rectal organ). Anal sclerite of usual X-form, with anterior arms 0.9 times as long as posterior ones, broadly sclerotized at base; accessory sclerite ( Fig. 33 View FIGURE 33 D) composed of four to six sclerotized spots on each side. Last abdominal segment with pair of large conical ventral papillae. Posterior circlet with 78–85 rows of up to 13–15 hooklets per row.
Type material. HOLOTYPE: Male (with its associated pupal exuviae and cocoon) in 80% ethanol, labeled in a vial as [ UMSRP: Vietnam 0 33, Holotype, Simulium (N.) tayense , Male, coll. Vietnam, 20-XII-2014, Takaoka et al.], reared a from pupa, collected from a stream (width 50 cm, depth 10 cm, bottom rocky, water temperature 11.0˚C, exposed to the sun, elevation 1,750 m, 22˚21’43.110”N/103˚47’19.221”E) slowly flowing from a secondary forest, Sapa , Lao Cai, northern Vietnam , 20-XII-2014, by H. Takaoka, M. Sofian-Azirun, Z. Ya’cob, C.D. Chen & K.W. Lau. PARATYPES: One pupal exuviae and one mature larva, same data and date as those of the holotype in 80% ethanol, labeled in each vial as [ UMSRP: Vietnam 0 33, Paratype, Simulium (N.) tayense , coll. Vietnam, 20-XII-2014, Takaoka et al.]; two females (with their associated pupal exuviae and cocoons) in 80% ethanol, labeled in each vial as [ UMSRP: Vietnam 0 33, Paratype, Simulium (N.) tayense , Female, coll. Vietnam, 20-XII-2014, Takaoka et al.], collected from a river (width 6 m, depth 60 cm, bottom rocky, exposed to the sun, elevation 1,728 m, 22˚22’22.719”N/103˚45’24.852” E) fast-flowing in a forest, Sapa , Lao Cai, northern Vietnam , 20-XII-2014, by H. Takaoka, M. Sofian-Azirun, Z. Ya’cob, C.D. Chen & K.W. Lau.
Biological notes. The pupae and larvae of this new species were collected from plastic sheets and dead grass leaves in the current. Associated species were S. (M.) nigrofilum sp. nov., S. (N.) laichauense sp. nov., S. (S.) laocaiense sp. nov., S. (S.) rosliramlii sp. nov., S. (S.) sapaense sp. nov. and S. (S.) turgidum sp. nov.
Distribution. Vietnam (Lao Cai).
Etymology. The species name tayense refers to the land in which the Tay tribe lives.
Remarks. Simulium (N.) tayense sp. nov. is placed in the S. vernum species-group of the subgenus Nevermannia , based on the shape of the male genitalia ( Fig. 31 View FIGURE 31 C–M). This new species is characterized by the presence of an accessory sclerite on each side of the last larval abdominal segment ( Fig. 33 View FIGURE 33 D). Beside this new species, the following seven species are known to bear accessory sclerites among species of the S. vernum speciesgroup: S. (N.) aberrans Delfinado from the Philippines ( Takaoka 1983), S. (N.) caudisclerum Takaoka & Davies from Peninsular Malaysia ( Takaoka and Davies 1995), S. (N.) chomthongense Takaoka, Srisuka & Choochote and S. (N.) khunklangense Takaoka & Srisuka , both from Thailand ( Takaoka et al. 2012c, 2013), S. (N.) ludingense Chen, Zhang & Huang from Sichuan, China ( Chen et al. 2005), S. (N.) yushangense Takaoka from Taiwan (Takaoka 1979), and S. (N.) zhangjiajiense Chen, Zhang & Bi from Hunan, China (Chen et al. 2004). However, this new species is easily distinguished from these seven species by the following characteristics: from S. (N.) aberrans , S. (N.) ludingense and S. (N.) khunklangense by the cocoon with an elongate anterodorsal projection (the cocoon is simple, without a projection in the former two species and the cocoon has a short bulge in S. (N.) khunklangense ), and from four other species by the greater number (19) of horizontal rows of male upper-eye facets (13 in S. (N.) zhangjiajiense , 15 in S. (N.) caudisclerum , 17 in S. (N.) yushangense , 17 or 18 in S. (N.) chomthongense ). The number (19) of horizontal rows in the male upper-eye facets of this new species is close to that (17 or 18) of S. (N.) chomthongense but both species are separated from each other by the ratio of the postgenal cleft against the postgenal bridge (0.9 in this new species versus 0.7–0.8 in S. (N.) chomthongense ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |