Stilbops auster, Watanabe, Kyohei & Maeto, Kaoru, 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.211080 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6178648 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/8079878D-FFAD-FF92-4DAD-68CCFB817712 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Stilbops auster |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Stilbops auster sp. nov.
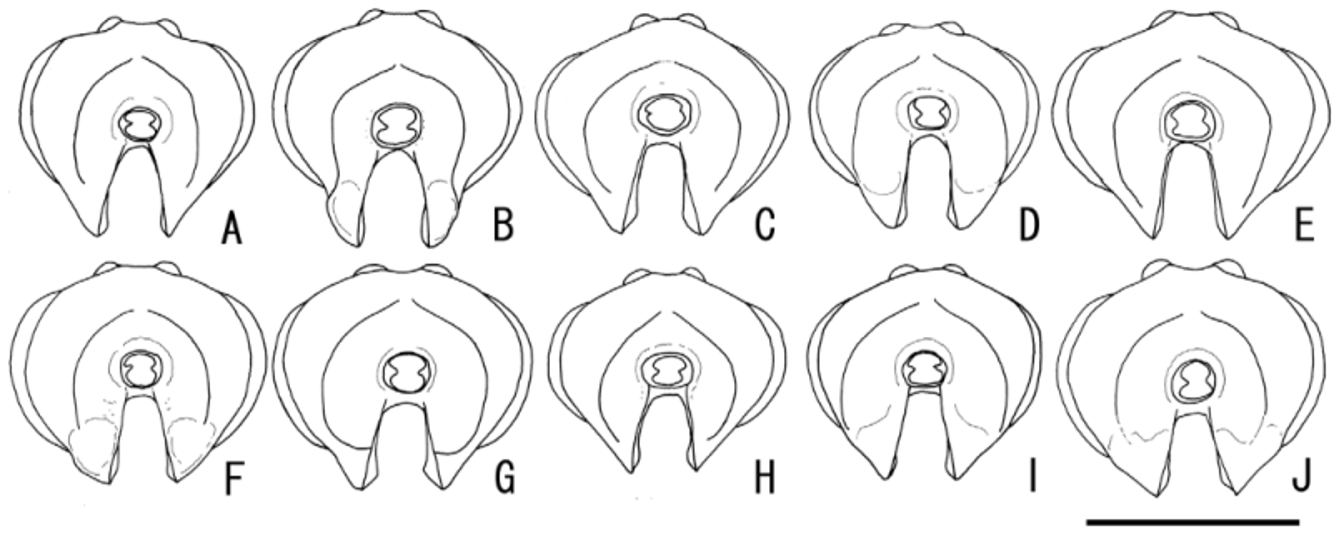
( Figs. 2 View FIGURE 2 A, K, 3 A, 4 A, 5 A, 6 A, 7 A, 8 A, 9 A, 10 A, 12 A, 13, 14 D)
Diagnosis. Anterior tentorial pit small ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A), its margin not concealed by setae; lower end of occipital carina effaced ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 A); lower part of gena without concavity in lateral view ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 A); lower margin of pronotum angulate ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A); pronotum without large smooth area on lateral area ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A); hind femur short, 4.3 times as long as deep in lateral view; lateral margin of T1 straight basally ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 A); metasomal tergites, hind femur, tibia and tarsus almost black ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 A); tegula yellow ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 A).
Description. Female (n=2). Body length 4.5–5.0 (HT: 5.0) mm; length of fore wing 3.6–4.0 (HT: 4.0) mm.
Head 0.5 times as long as wide; clypeus 0.6 times as long as wide, narrowly punctate dorsally, its margin convex in anterior view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A); anterior tentorial pit small ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 A), its margin clearly observed; face 0.6 times as long as wide, punctures on lower antennal socket elongate longitudinally; frons covered with punctures as face, lower half of it transversely striated by coalescent punctures ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 K); OOL 1.4–1.5 (HT: 1.5) times as long as OD; POL 1.5 times as long as OD; lower end of occipital carina effaced ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 A); GOI 0.4; lower part of gena without concavity in lateral view ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 A); malar space 1.0 times as long as basal width of mandible; basal portion of mandible flat. Antenna with 18 flagellomeres; flagellomere I 1.2 times as long as II and terminal flagellomere 2.5 times as long as preceding one; sensilla placodea present on flagellomere III and following all flagellomeres.
Mesosoma ( Figs. 5 View FIGURE 5 A, 6 A, 7 A, 8 A): lower margin of pronotum angulate ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A); upper end of epomia closely located with upper margin of pronotum in lateral view ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A); lateral area of pronotum entirely punctate, without smooth area ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 A); mesoscutum with weak notaulus on anterior 0.3; smooth area around episternal scrobe rather large; upper end of epicnemial carina reaching lower 0.3 of pronotum; juxtacoxal carina distinct; all carinae of propodeum present, lateral section of anterior transverse carina and lateromedian longitudinal carina along area dentipara weak, anterior part of lateromedian longitudinal carinae coalescent ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 A); all areas of propodeum punctate ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 A), punctures on areas superomedia and postero shallower.
Fore wing: Cu-a distant from Rs&M by 0.8–1.0 times length of Cu-a (HT: 1.0); ICI 0.8. Hind wing: NI 5.0; one basal hamulus, 5 or 6 (HT: 6) distal hamuli.
Legs: hind femur 4.3 times as long as deep in lateral view; hind tibia 7.2 times as long as deep in lateral view; hind tarsomere ratio I; II; III; IV; V = 3.0; 1.4; 1.0; 0.6; 1.0.
Metasoma: TI 1.2 times as long as maximum width, with distinct median dorsal carina on anterior 0.3, without distal depression, and lateral margin straight basally ( Fig. 10 View FIGURE 10 A); TII and TIII with pair of slight round convexities; lower half of subgenital plate weakly punctate. Ovipositor weakly upcurved in posterior half; ovipositor sheath 0.5 times as long as hind tibia.
Coloration ( Figs. 6 View FIGURE 6 A, 7 A, 9 A, 12 A): black, except for: antenna with pedicel and apical part of flagellum brown, scape and remainder of flagellum blackish-brown; yellow palpi; yellow tegula; apical part of fore coxa apex of mid and hind coxae yellow; trochanters and trochantelli yellow; fore and mid femora, tibiae and tarsi brown; apical part of hind femur blackish-brown; hind tibia and tarsus blackish-brown; stigma, wing veins blackishbrown; metasomal sternites yellow except for brown sclerotized areas; brown apex of ovipositor sheath; blackishbrown ovipositor.
Male. Unknown.
Type series. Holotype: female [Ryukyu Isls.] Kagoshima Pref., Tokunoshima Isl., Tokunoshima town, Kedoku, about 140 m, N27°48’51" E128°55’11", 20. v. 2008, K. Watanabe leg. ( NIAES). Paratype: JAPAN: [Ryukyu Isls.] 1Ƥ, Kagoshima Pref., Tokunoshima Isl., Amagi town, Mt. Yamatogusuku-yama, 180–200 m, N27°50’22" E128°56’47", 20. v. 2008, K. Watanabe leg. (TUA).
Distribution. Japan (Ryukyus: Tokunoshima Island) ( Fig. 13 View FIGURE 13 ).
Etymology. The specific name is from the Latin “ auster ” (south wind), referring to the warm habitat in Tokunoshima Island.
Remarks. This species closely resembles kunashiricus Kasparyan in the lateral margin of T1 straight basally, the normal-sized anterior tentorial pit and the relatively dense body punctuation. It can be distinguished from the latter by the simple gena ( kunashiricus with genal concavity) and the black metasoma ( kunashiricus at least partly red). This species was collected in the shade of wet natural forests ( Fig. 14 View FIGURE 14 D).
| NIAES |
National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |