Paraportanus marica, Felix, Márcio & Mejdalani, Gabriel, 2016
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4196.3.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:64971FDA-C8D8-465E-B4F8-1735A2C7F7FA |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6078810 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/3EC67A96-2076-4779-B7A8-5BBE75508A4F |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:3EC67A96-2076-4779-B7A8-5BBE75508A4F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Paraportanus marica |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Paraportanus marica View in CoL sp. nov.
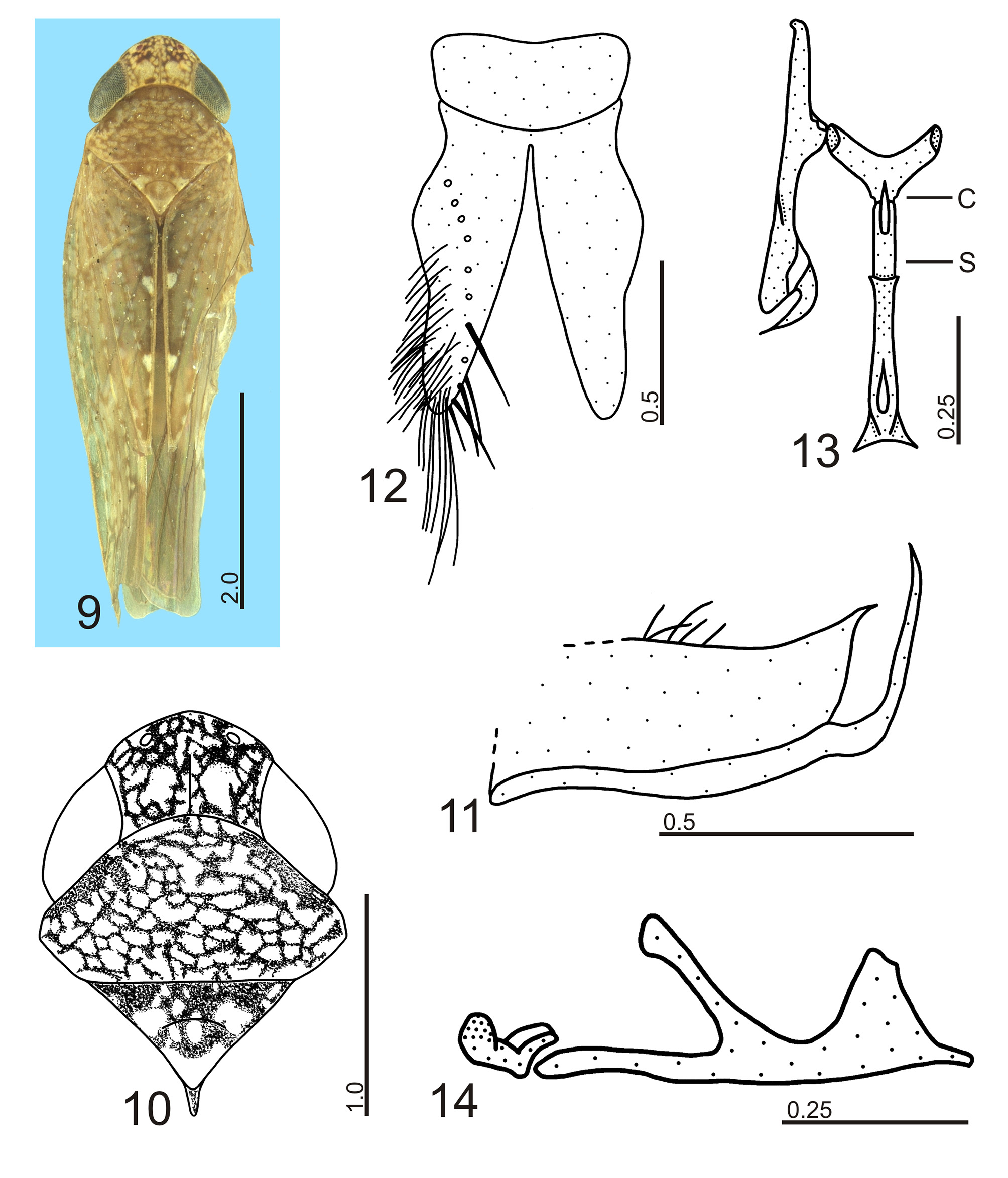
( Figs 9–14 View FIGURES 9 – 14 )
Diagnosis. Pygofer ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) acutely produced posterodorsally; aedeagus ( Figs 13, 14 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) with pair of short ventroapical processes, laterally divergent.
Measurements (mm). Male holotype: body length 5.43; crown length 0.48; transocular width 1.33; interocular width 0.59; maximum pronotal width 1.38; forewing length 4.55.
Description. Head ( Figs 9, 10 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) with median length of crown slightly more than 8/10 interocular width and slightly less than 4/10 transocular width. Pronotum ( Figs 9, 10 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) with width slightly greater than transocular width. Forewings with three closed anteapical cells; median cell longer than inner and outer ones. Hind legs with femoral setal formula 2:2:1; length of basal tarsomere similar to combined length of two succeeding tarsomeres.
Male genitalia. Pygofer ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ), in lateral view, well produced posteriorly; posterior margin obliquely truncate with short dorsal projection; ventral margin with long, slender acute process turned posterodorsally, extending slightly beyond projection; dorsomedian portion of pygofer with group of long macrosetae; irregular longitudinal row of minute macrosetae on median portion of disc. Valve ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) broad, subrectangular, posterior margin broadly convex. Subgenital plates ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) long, extending posteriorly slightly beyond pygofer apex; narrowed on apical half; apex rounded; ventral longitudinal row of long macrosetae; outer lateral and apical areas with long slender macrosetae densely arranged and some small macrosetae. Style ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) long and narrow, extending posteriorly much beyond connective apex; apical portion broad in lateral view; preapical lobe well produced; apex long and acute, curved outwards, with minute subapical tooth. Connective ( Figs 13, 14 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) Y-shaped in ventral view; arms moderately long; stalk short, with median keel. Aedeagus ( Figs 13, 14 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) long and narrow; dorsal apodeme conspicuous, slender; apical portion of shaft broadened; ventroapical margin produced, with pair of short divergent processes.
Color. Dorsum ( Figs 9, 10 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) mostly brown with numerous pale yellow to ivory dots and small marks. Crown ( Figs 9, 10 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) brown mottled with pale yellow to ivory elliptical areas; two pairs of ivory elliptical spots, anterior one touching outer margin of ocelli, posterior one near posterior coronal margin. Ocelli red. Eyes brown. Pronotum ( Figs 9, 10 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) pale brown mottled with pale yellow elliptical marks; pair of irregular small ivory maculae posterior to eyes. Mesonotum ( Figs 9, 10 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) mostly ivory with pair of irregular anterolateral brown areas. Forewings ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) translucent; veins mostly dotted with pale brown and white small areas; clavus with small ivory basal mark and two transcommissural ivory maculae bordered by brown, located on apex of claval veins; corium with basal veins of apical cells bordered by pale brown, apex fumose. Face with ground color yellow to brownish-yellow; frons dorsally continuing dotted pattern of crown; frontogenal sutures bordered by brown along a short area ventrally to antennal pits; upper portion of genae with yellow macula behind eyes; apical portion of labium pale brown. Thoracic sclerites mostly pale yellow laterally and ventrally. Legs pale yellow with brown areas.
Female unknown.
Type material. Brazil. Holotype: male, “ Restinga de \ Maricá—RJ \ 19-VII-1985 \ (Arm. Luminosa) [ light trap]” ( DZRJ).
Etymology. The specific epithet, marica , refers to the type locality, Restinga de Maricá , a sandy coastal plain in Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil.
Remarks. Paraportanus marica has the male genital structures very similar to those of Paraportanus eburatus ( Kramer, 1964) , P. elegans ( Kramer, 1961) and P. longicornis (Osborn, 1923) . The pygofer of these species is posterodorsally produced and ventrally there is a long, acute slender process that is dorsally directed ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ; Kramer 1964: fig. 8; Kramer 1961: fig. 12; Linnavuori 1959: fig. 18 D). However, the new species has an acute projection dorsally ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) instead of a rounded short lobe. The aedeagi of P. eburatus , P. elegans and P. longicornis are similar to that of the new species. They are long and broadened apically, with a pair of short processes ventrally ( Figs 13, 14 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ; Kramer 1964: fig. 7; Kramer 1961: fig. 9; Linnavuori 1959: fig. 18 B). In P.
elegans and P. longicornis the processes are lamellar, while in P. m a r i c a and P. eburatus they are slender. However, the new species has the aedeagal processes shorter and laterally divergent ( Figs 13, 14 View FIGURES 9 – 14 ) when compared with those of P. eburatus .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Aphrodinae |
|
Genus |