Smacigastes Ivanenko & Defaye
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.183742 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6231328 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/89008784-FFCC-FF96-EAE3-8F10FC2BFBCA |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Smacigastes Ivanenko & Defaye |
| status |
|
Genus Smacigastes Ivanenko & Defaye
Type species Smacigastes barti sp. nov.
Type material
Holotype dissected Ψ, 19 slides (nr. SMF 31411) Paratype 1: dissected ɗ, 13 slides (nr. SMF 31412) Paratype 2: Ψ (nr. SMF 31413)
Paratype 3: ɗ (nr. SMF 31414)
Paratype 4: Ψ (nr. SMF 31415)
Paratype 5: ɗ (nr. SMF 31416)
Paratype 6: Ψ (nr. SMF 31417)
Paratype 7: ɗ (nr. SMF 31418)
Paratype 8: dissected copepodite stage V, 3 slides (nr. SMF 31419) Paratype 9: Ψ (nr. OLML 2007/199)
Paratype 10: ɗ (nr. OLML 2007/200)
Paratype 11:Ψ (nr. OLML 2007/201)
Paratype 12: ɗ (nr. OLML 2007/202)
Paratype 13: copepodite stage V (nr. OLML 2007/203)
Type locality
East Pacific Rise (EPR); 9°50.447´N, 104°17.493´W; 2500 m depth. The site Tica is located on the EPR between the Clipperton and Sequeiros transform faults. The site was colonized by the giant tubeworm Riftia pachyptila in 1997 ( Fornari et al. 2004). Type material was collected from artificial substrates (PVC hoses) deployed in 2002, and recovered one year later (see Govenar & Fisher 2007).
Etymology
The species is named in honor of Breea Govenar who designed the artificial devices from which specimens were collected ( BART: Breea´s Artificial Riftia Tubes ).
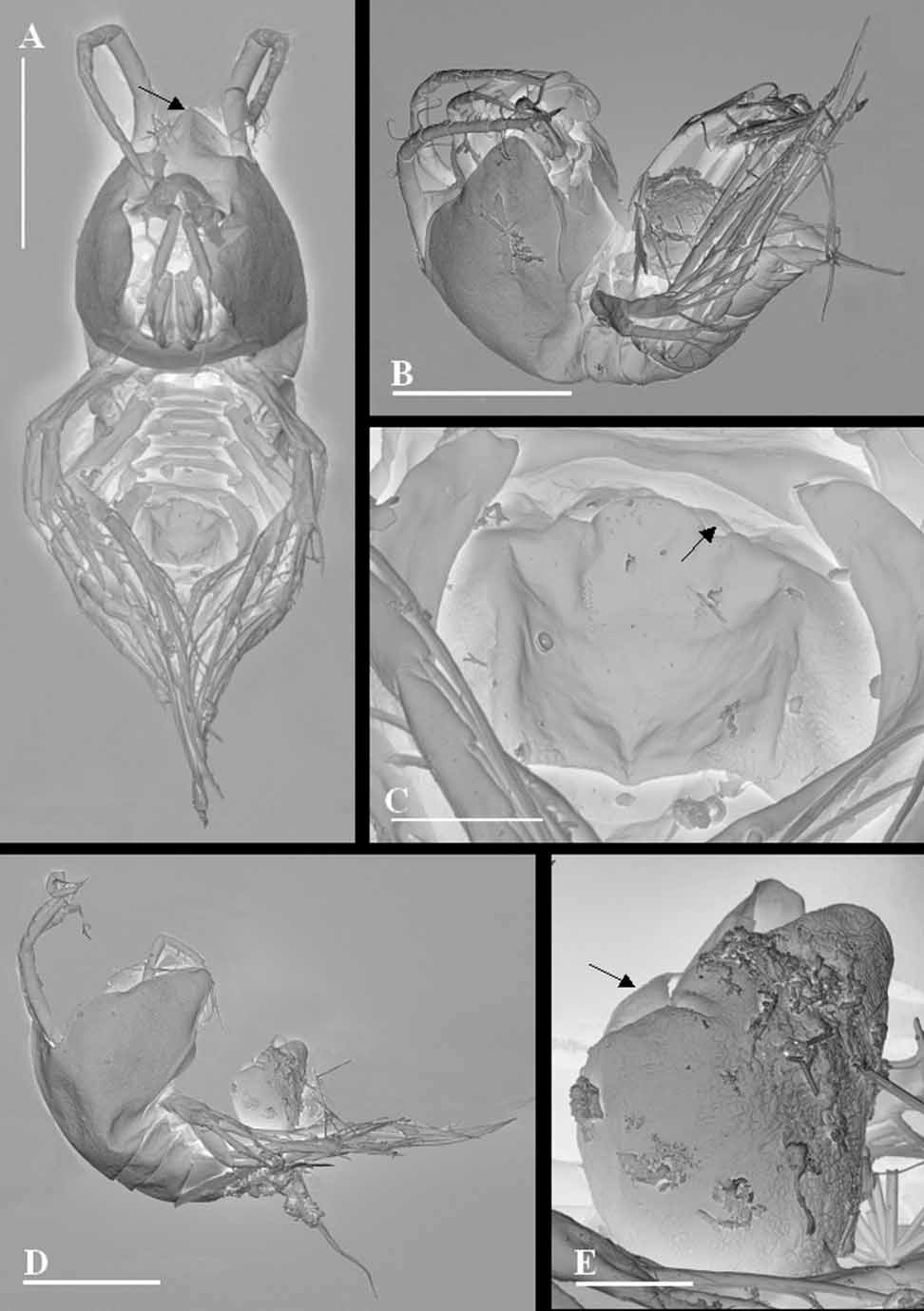
Female
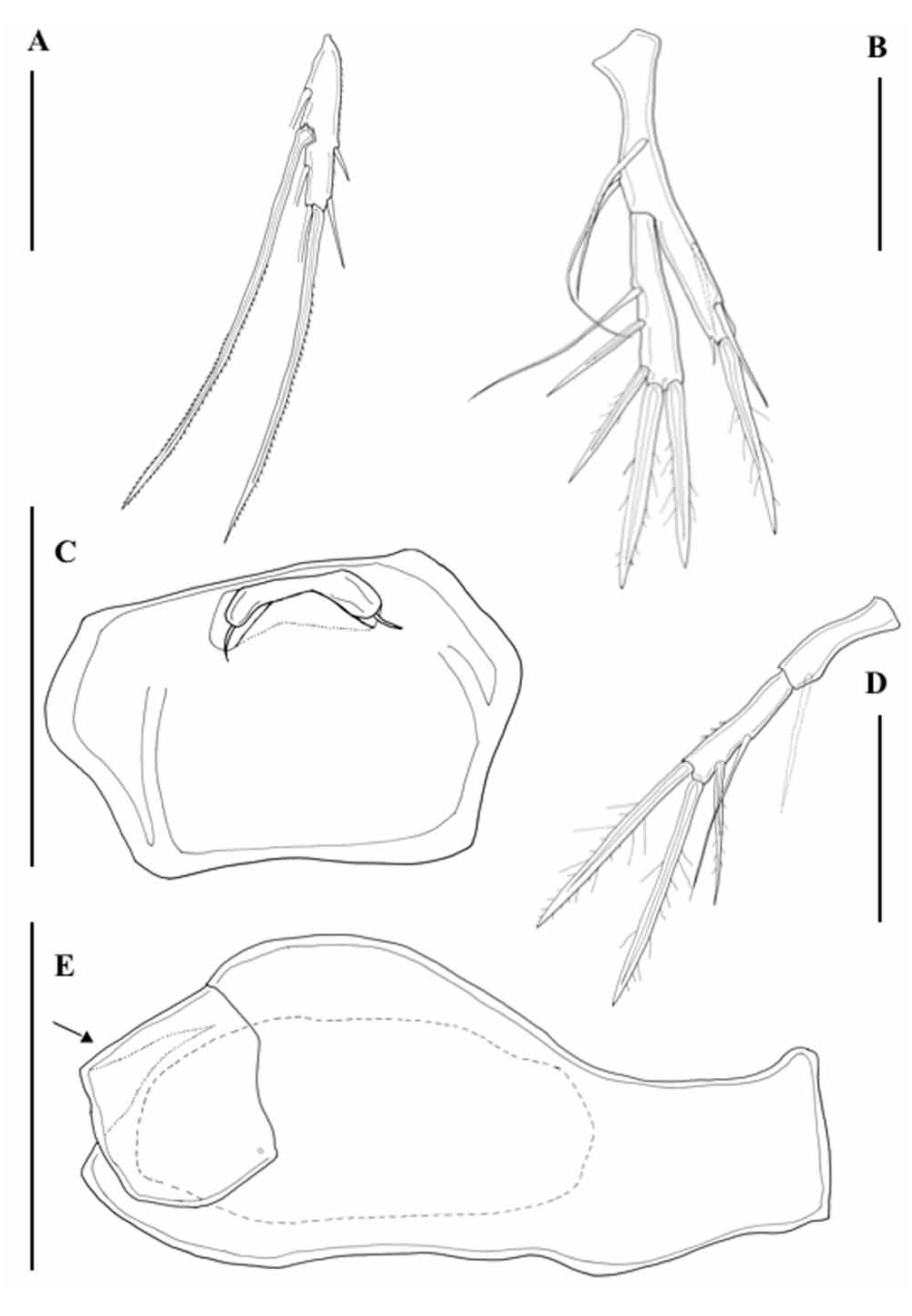
Body ( Fig.1 View FIGURE 1 a, 1b, 2a) laterally compressed, weakly chitinized, with short sensilla and few pores. Total length of female holotype (rostrum to posterior margin of telson) 420 µm, greatest width 180 µm. Rostrum rounded and prominent ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 a). Prosome 4segmented (cephalothorax and 3 somites bearing legs 2 to 4) (Fig. 2a). Urosome (Fig. 2b) 5segmented: first urosomite with leg 5, genitaldouble somite with ventral depression and one gonoporus covered by flap of the minute leg 6 ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 c, 5b, 5c), and 2 postgenital somites plus telson with furca. Furca 3 times as long as wide, with 7 setae of different length (Fig. 2c).
Antennule (Fig. 2d) 7segmented; formula of setation: 1, 10, 9, 3+aesthetasc, 6, 4, 6+aesthetasc.
Antenna (Fig. 2e) with small coxa and elongate basis with 1 seta and a field of cuticular spinules. Exopod 2segmented, proximal segment with 1 inner setae, distal segment with 3 apical setae; endopod 2segmented, proximal segment with 1 median seta, distal segment with 4 inner setae, 6 terminal setae and a hyaline frill subdistally on outer margin.
Labrum (Fig. 2a) projecting over shield of cephalothorax in lateral view.
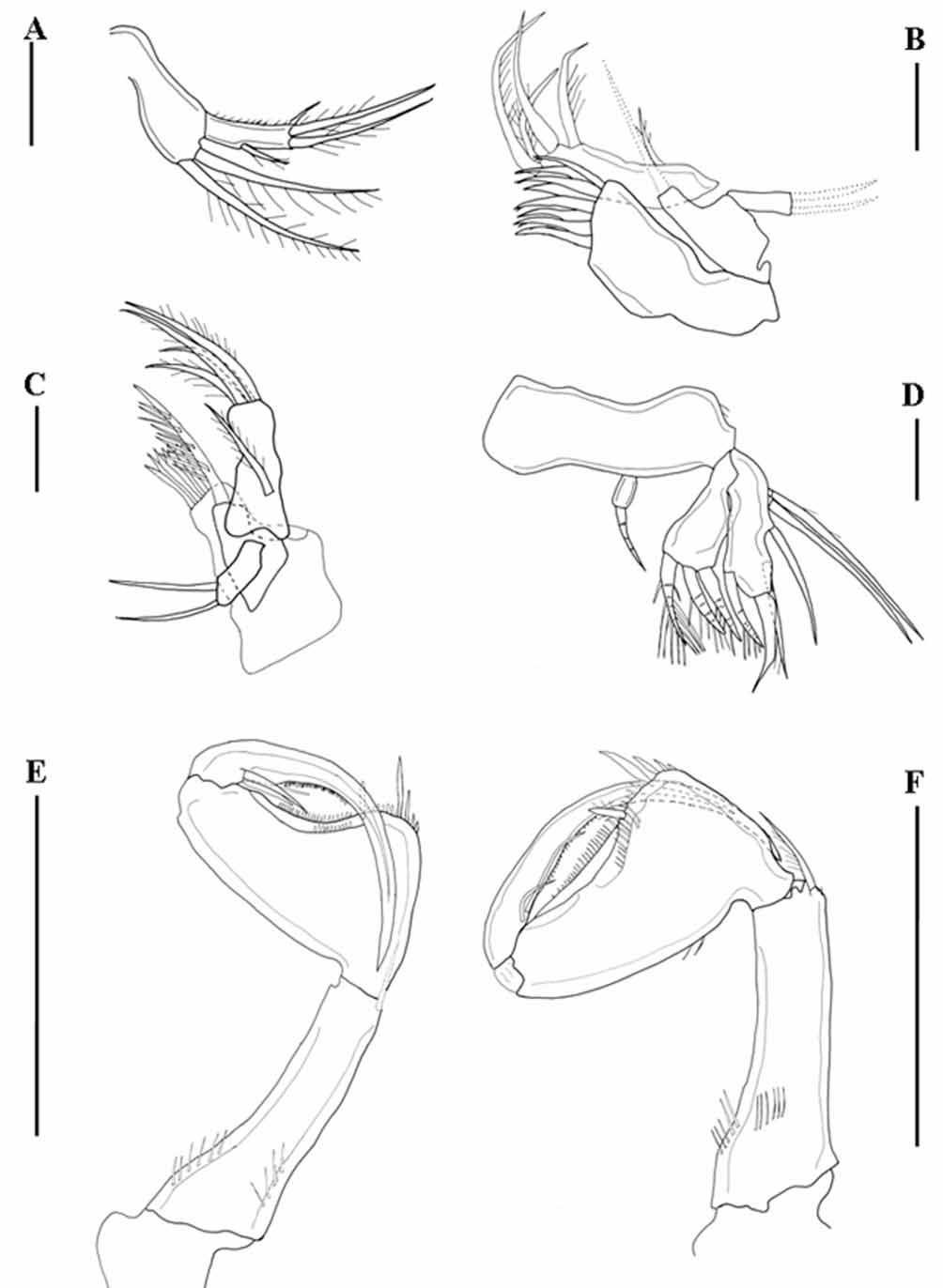
Mandible ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 a) with gnathobase (not shown); palp 2segmented, with 2 distal setae on basis and 1segmented endopod bearing 1 outer and 3 terminal setae.
Maxillule ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 b, c) with praecoxal arthrite bearing 8 spines; coxal endite with 1 seta; exopod with 2 setae; basis elongate with 1 median and 4 terminal setae.
Maxilla ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 d) syncoxa with two endites, proximal endite with 1, distal endite with 3 spines. Allobasis with 3 lateral setae, two subdistal and one apical spine.
Maxilliped ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 e, f) 3segmented, subchelate; syncoxa elongated with 1 distal seta; basis with 2 rows of spinules; endopod 1segmented, produced into a strong claw, with 2 proximal setae and an inner row of short spinules.
Swimming legs 1–4 biramous; armature formula as in Table 1.
FIGURE 2. Smacigastes barti sp. nov. Ψ holotype LM drawings: A, habitus, lateral (labrum indicated by arrow); B, urosome, ventral; C, furca, ventral; D, antennule (a seta on 2nd segment broke and is indicated by a circle); E, antenna (frill indicated by arrow). Scale bars A 100 µm; B–E 50 µm.
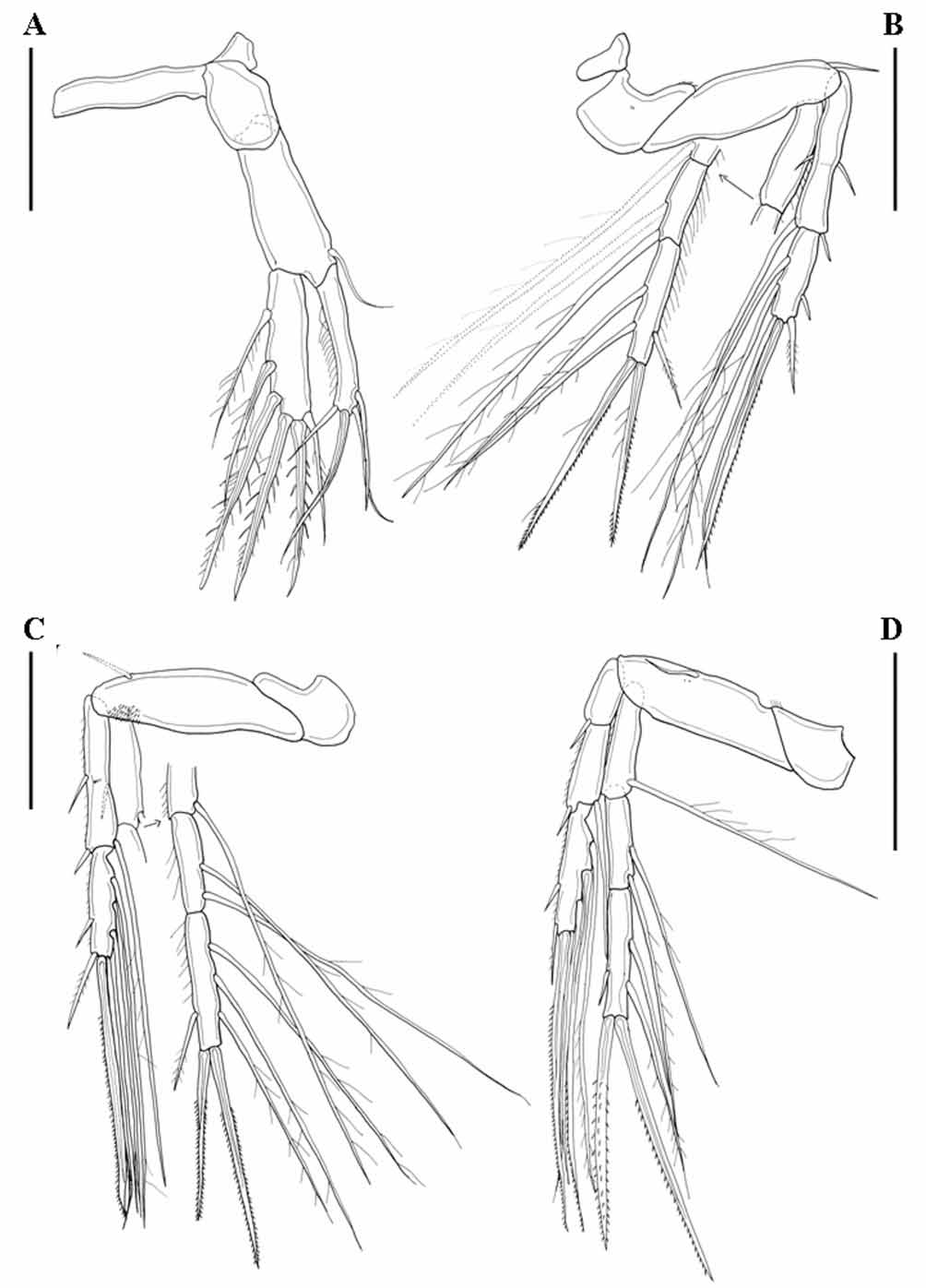
Leg 1 ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 a) with 1segmented rami.
Leg 2 and leg 3 ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 b, 4c) with 3segmented endopods and 2segmented exopods; proximal segments of exopods elongated, derived by fusion of former proximal and middle segments.
Leg 4 ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 d) with 3segmented rami. Distal exopod segment with an inner seta slightly modified into a spine ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 a).
Leg 5 ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 b) with baseoendopod and exopod; baseoendopod with 1 basal outer seta, 3 inner setae, 1 terminal spine, and 1 small terminal outer seta; exopod with 3 outer elements (proximal setalike; middle and distal ones spinelike), and 2 terminal spines.
Leg 6 a small flap with 1 minute seta ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 c).
Single egg sac with three eggs, located ventrally between fifth legs ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 b, 1c, 2a).
Male differs from female in the following:
Length of paratype 1 ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 d, 6a) 325 µm; greatest width 150 µm. Genitaldouble somite ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 e, 5e) produced ventrally into a large, elongated prominence bearing a distally asymmetrical genital flap representing leg 6.
Antennule ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 b) 10segmented; setation formula as follows: 1, 10, 6+aesthetasc, 1, 7+aesthetasc, 1, 2, 1, 4, 7+aesthetasc.
Leg 5 ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 d) 2segmented; basis with 1 outer seta, exopod with 1 outer proximal seta, 1 outer subdistal spine, and 2 terminal spines.
Leg 6 ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 e, 5e) a membranous genital flap on the left side.
One spermatophore stored inside the genitaldouble somite ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 e).
Copepodite stage V
Leg 2 ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 c) and Leg 3 ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 d) consist of 3segmented exopods (in contrast to adult) and 2segmented endopods (shortly before division into the adult 3segmented endopod).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |