Thulinius
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5281/zenodo.157078 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6274430 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/8A193E6B-9100-A21E-8D47-F9CF9D74FD5C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Thulinius |
| status |
|
Thulinius View in CoL nomen novum
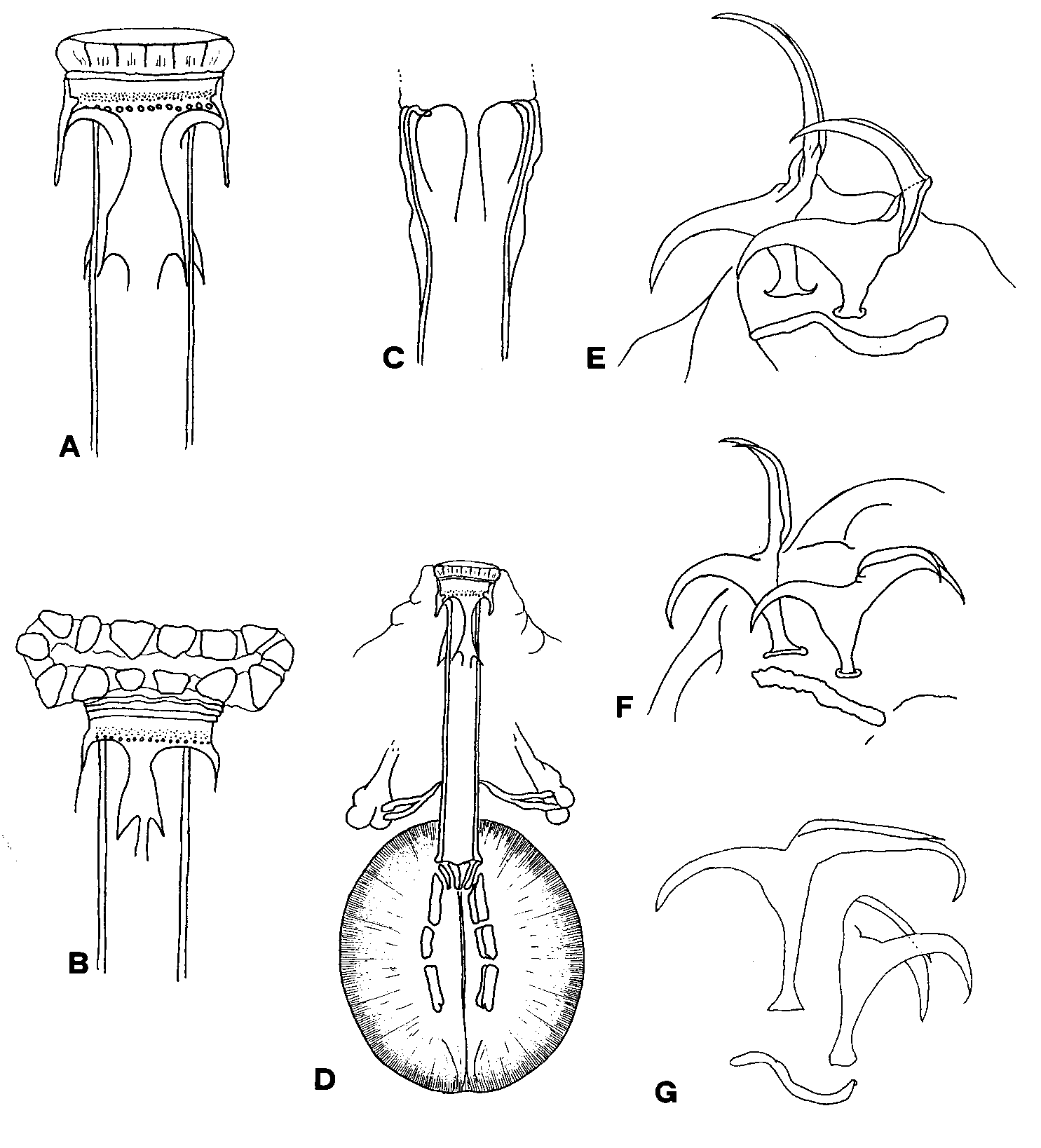
Diagnosis. Mouth opening with 12 small, partially fused peribuccal lamellae ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A) surrounded by six peribuccal lobes, sometimes subdivided into a larger number of irregular sublobes ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B); crestshaped apophyses for the insertion of the stylet muscles on the buccal tube ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 C), claws of Isohypsibius type ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 , E,F,G).
Etymology. Dedicated to Gustav Thulin, an excellent Swedish researcher.
Type species. Isohypsibius stephaniae Pilato, 1974
Composition. T. stephaniae ( Pilato, 1974) , T. ruffoi Bertolani, 1981 , T. augusti ( Murray, 1907)
Remarks. The three species are characterized by a buccal armature with a posterior band of fine teeth, followed by a line of bigger round teeth ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 A,B), instead of transverse mucrones, as in several other genera of Hypsibiidae, Macrobiotdae and Eohypsibiidae , and by rows of macroplacoids, whose curvatures resemble a Grecian urn ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 D). The species differ together mainly for the shape of the cuticular structures of the legs. Thulinius ruffoi ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 F) differs from T. stephaniae ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 G) in having thinner claws with longer tapering basal tract, lunules evident and a less prominent cuticular bar below the claws of the first three pair of legs (other than for a more slender body). Thulinius augusti differs from the other two species by the presence of a particularly long and thin basal tract of the claw, especially in the external one, from T. stephaniae also by a weaker cuticular bar below the claws of the first three pair of legs, and from T. ruffoi also by the absence of lunules. The subdivision of the lobes into sublobes ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 B) is another possible difference between T. augusti and the other two species.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |