Flatocerus wuyishanensis Zheng
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.1080/00222933.2017.1293749 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:334D6268-E3C1-450E-A3A2-31F9839B4EE6 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/8D5C306F-FFFF-2314-FF79-FB85FCACC34D |
|
treatment provided by |
Carolina |
|
scientific name |
Flatocerus wuyishanensis Zheng |
| status |
|
Redescription of Flatocerus wuyishanensis Zheng View in CoL based on our collections
( Figures 2 View Figure 2 (a–c) and 3(a–f))
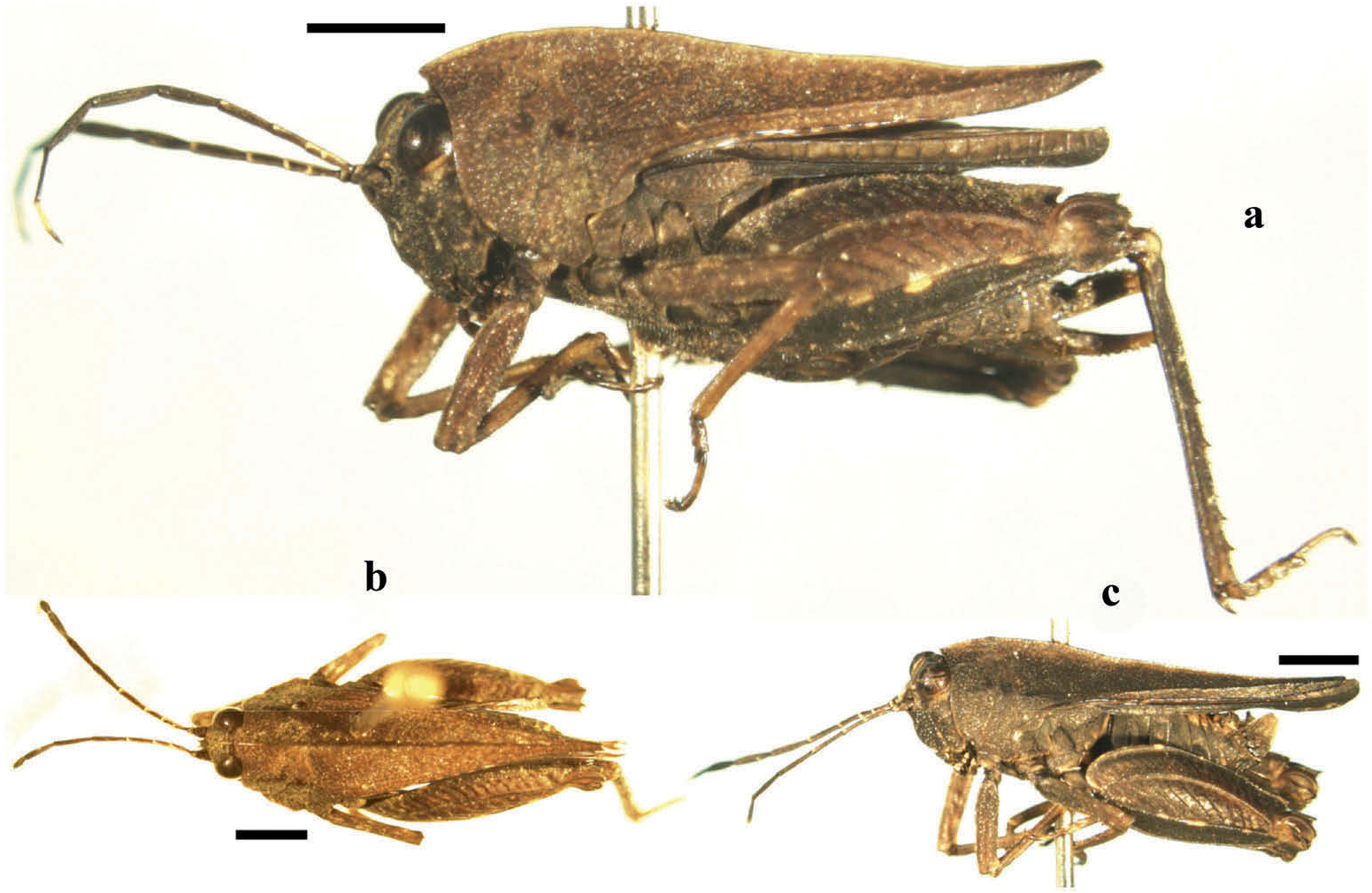
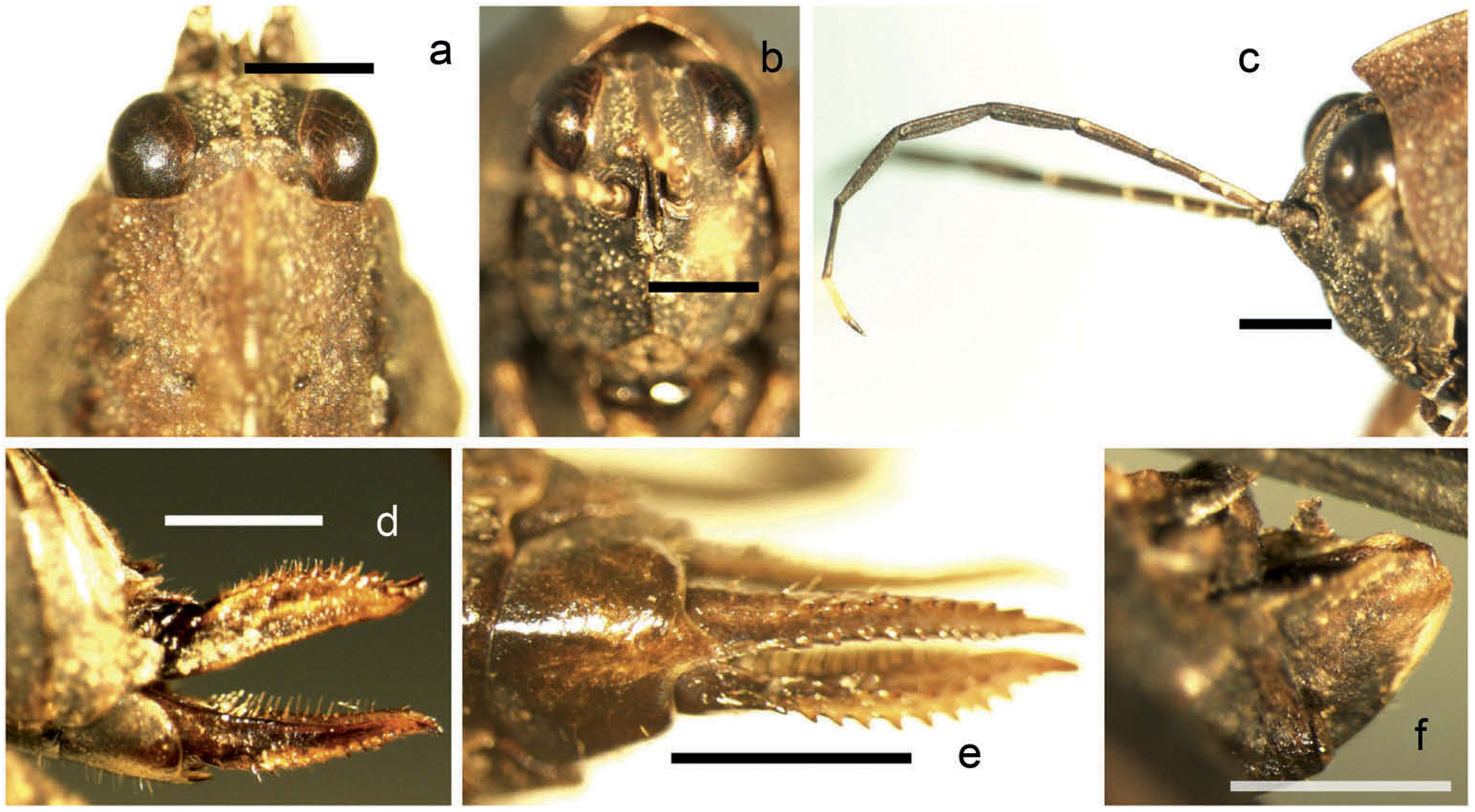
Female. Body size small, body surface smooth, covered with numerous punctations ( Figure 2 View Figure 2 (a)). Vertex nearly at the same level, contracted forward, 1.2 times as wide as an eye, extremely short, only reaching to middle of inner margins of eyes, anterior margin straight, medial carina entire, lateral carinae slightly folded up and not reaching up to top of eyes; paired fossulae shallow, behind them vertex irregularly elevated; in lateral view vertex together with frontal costa widely and obtusely angled, between antennal grooves extremely triangularly protruding forward; fascial carinae diverged slightly above lateral ocelli, then parallel downwards; longitudinal furrow deep, distinctly narrower than diameter of scapus of antenna. Upper margin of antennal grooves at the same level of low margin of eyes, antennae 13-segmented, segments from third to sixth slightly compressed, from seventh to tenth distinctly compressed, apical three segments not compressed and the last two very short. Eyes exserted, in lateral view globose, in dorsal view with triangular inner margins and in frontal view ovate and inclined; lateral ocelli situated at lower quarter of inner margin of eyes ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 (a–c)).
Pronotum roof-like ( Figure 2 View Figure 2 (a)), anterior margin prominent forwards, acute angled in lateral view and obtusely angled in dorsal view ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 (a,c)); median carina high and lamellate, in lateral view upper margin of pronotum slightly arcuate in anterior half, the posterior part nearly straight ( Figure 2 View Figure 2 (a)); prozonal carinae short, barely visible, a little contracted inward; humeral angle widely arcuate, indistinct, between shoulders interhumeral carinae long, oblique inward, also barely visible; hind process reaches or slightly surpasses apex of hind femora, tapered backwards, apex truncated; posterior angle of lateral lobe of pronotum extending obliquely backwards, apex decidedly truncated ( Figure 2 View Figure 2 (a)), posterior margin of each lateral lobe with two concavities. Visible part of tegmen ovate, wings reach or slightly surpass apex of hind process and slightly narrower than mid femur ( Figure 2 View Figure 2 (a)). Upper and lower margins of fore and mid femora straight and serrate, mid femur slightly wider than tegmen; hind femur 2.6 times as long as wide, posterior halves of upper and lower margin distinctly serrate; antegenicular denticle not isolated, acute angled, genicular denticle also acute; outer/inner side of hind tibia with 4–7/5–7 (male 6/8) spines, margins serrate; first segment of hind tarsi nearly as long as third (a little longer), three pulvilli equal and all apexes obtuse. Ovipositor long and narrow, 4.2 times as long as wide, upper margin of upper valva and lower margin of lower valva serrate, but base of upper valva smooth ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 (d)). Posterior margin of subgenital plate nearly truncated, in the middle with an acute triangular projection, which is slightly folded inward ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 (e)).
Body dark brown; antennae black, colour of apices from third to sixth segment light, 11th segment white, 12th and 13th segments brown ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 (c)); hind wings black; lower outer side of hind femur black, upper margin and ventro-external carina maculated with numerous white spots; hind tibia black ( Figure 2 View Figure 2 (a)).
Male. Slightly smaller than female. Eyes exserted higher than female; hind process of pronotum distinctly surpasses apex of hind femora (longer than female), hind wings distinctly surpass apex of hind process (longer than female) ( Figure 2 View Figure 2 (c)); apex of antegenicular denticle slightly right angled; subgenital plate compressed and very short, in lateral view apex nearly truncated but with a small triangular projection, apex of upper side directed downward ( Figure 3 View Figure 3 (f)). Other structures and coloration same as female.
Measurements. Length of body (mm): ♂ 8.9, ♀ 10.8–12.0; length of pronotum: ♂ 10.2, ♀ 9.5–10.0; length of hind femur: ♂ 6.0, ♀ 6.0–6.5; length of antenna: ♂ 7.0, ♀ 7.0.
Material examined. 2♂ 2♀, China, Guizhou, Jiangkou, Fanjingshan Mountain ( Figure 1 View Figure 1 ), 27.872450 N, 108.784858 E, about 300 m altitude, 30 July 2016, collected by Lingsheng Zha GoogleMaps . GoogleMaps
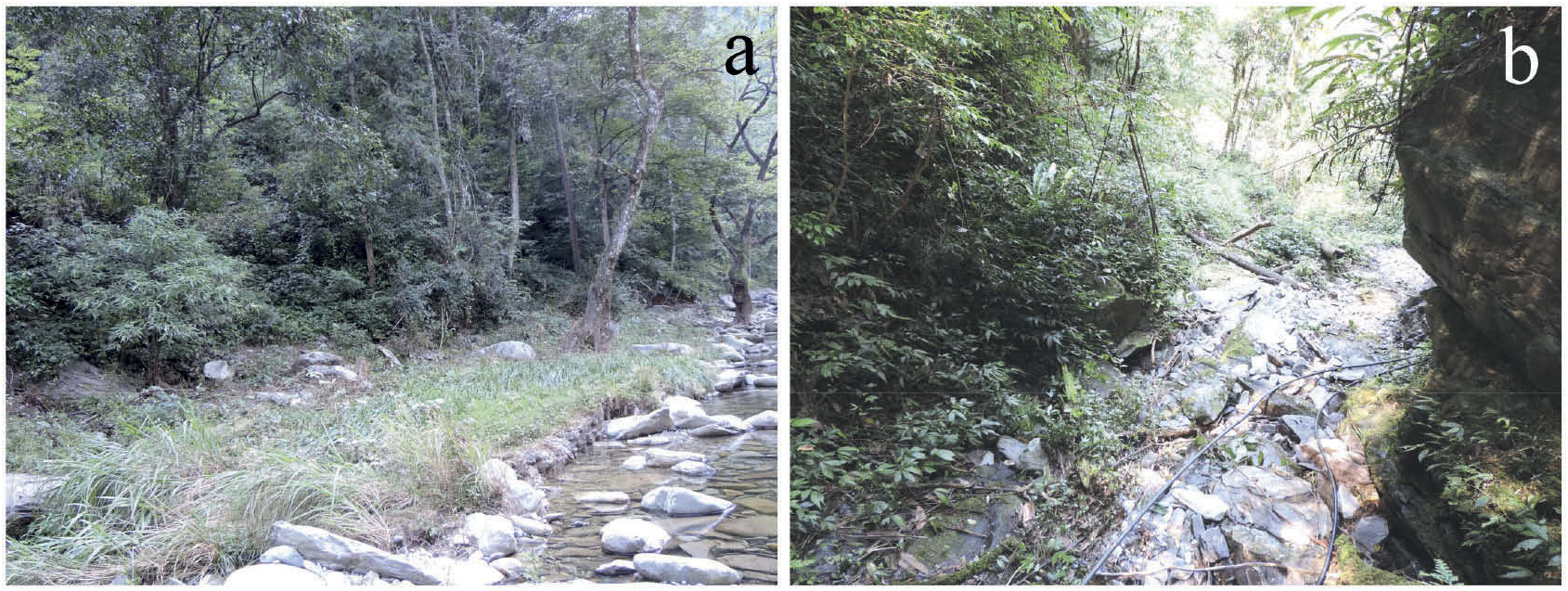
Ecology and habits. Individuals of F. wuyishanensis were collected among sparse shrubs of sandy soil near streams ( Figure 4 View Figure 4 ). They like shady areas rather than being exposed under the sun. They move quickly and will jump into shrubs when disturbed. They may mainly feed on humus.
Note. Fanjingshan Mountain covers partial areas of three counties (Jiangkou, Songtao and Yinjiang), instead of Jiangkou County only ( Figure 1 View Figure 1 ).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |