Camptotheca SLAS
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2020.112626 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8302366 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/8D608791-DF67-1365-FFCD-2C4AFABDB246 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Camptotheca SLAS |
| status |
|
2.5. In vitro reconstitution of Camptotheca SLAS View in CoL View at ENA activities
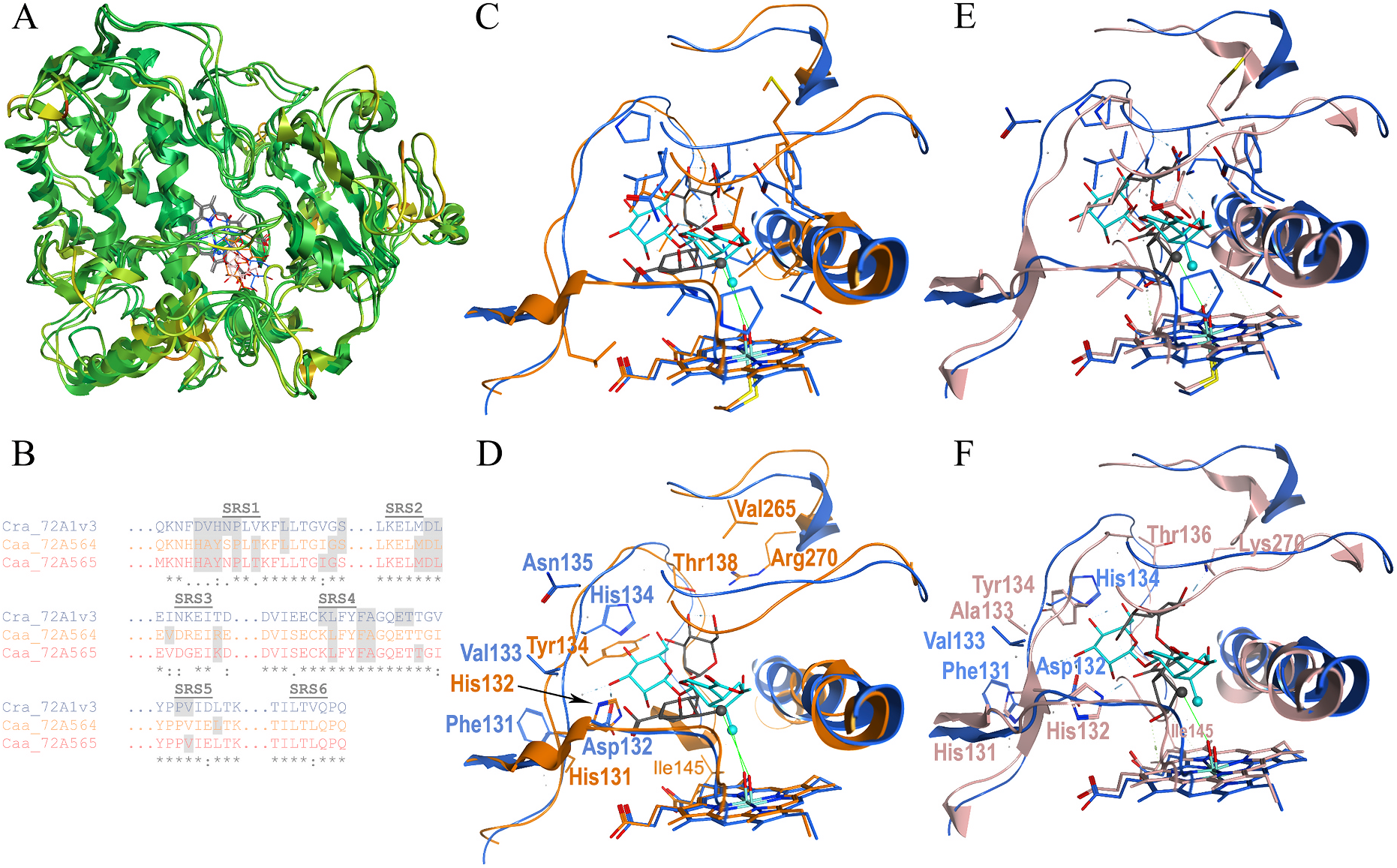
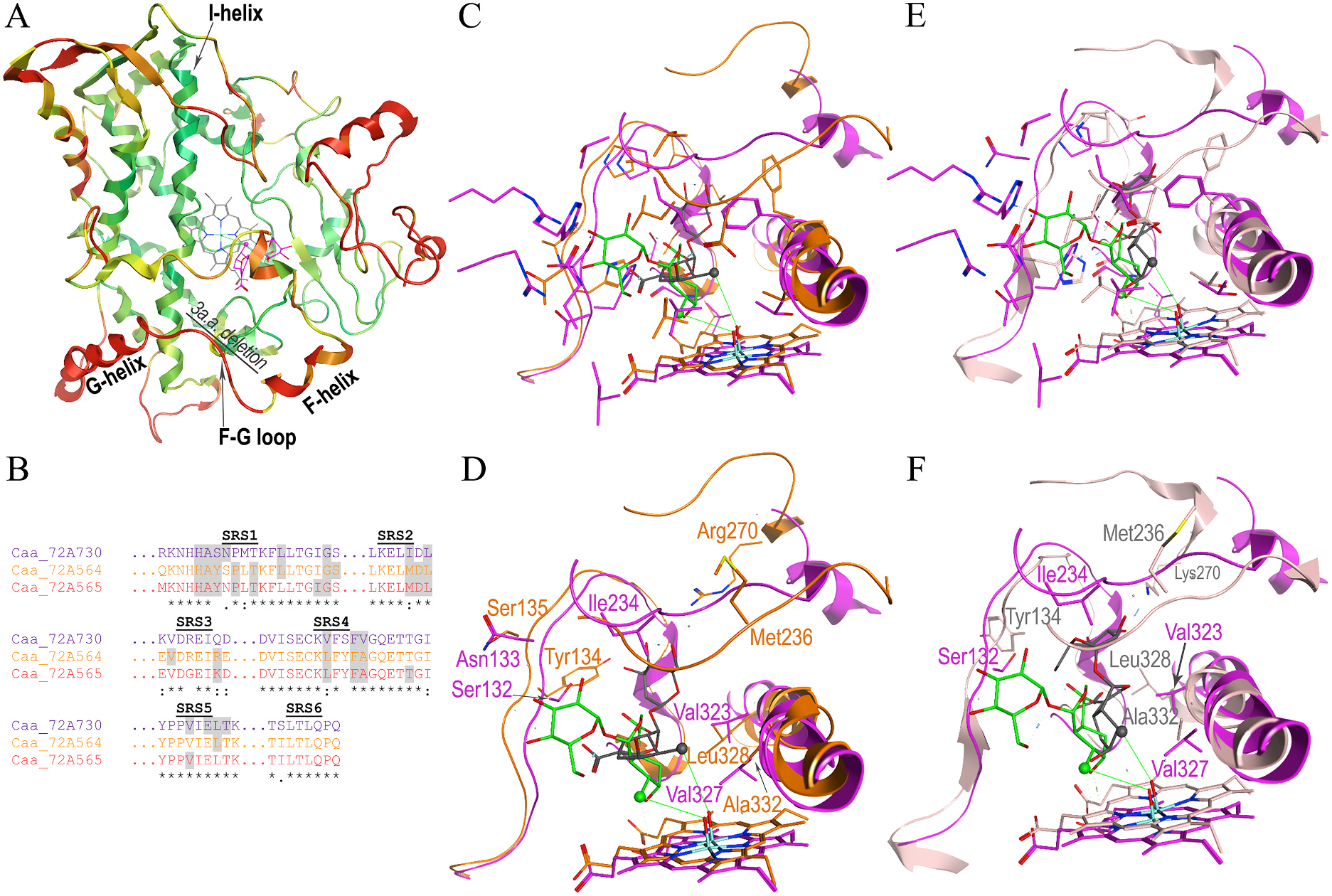
For subsequent in vitro reconstitution assays, the His 6 -tagged Camptotheca CYP 72A564, CYP72A565 and CYP72A730 and Catharanthus CYP 72A1v3 ORFs were cloned into the IPTG-inducible pCW bacterial expression vector and their full-length proteins were purified from E. coli as outlined in the experimental procedures. His 6 -tagged full-length membrane-bound forms of Camptotheca CPR 1 (His 6 CPR1full) and CPR2 (His 6 CPR2full) as well as truncated soluble forms of these electron transfer proteins (His 6 CPR1Δ48, His 6 CPR2Δ68) were cloned into the IPTG-inducible pET28 bacterial expression vector and purified from E. coli. Reduced carbon monoxide difference spectra ( Omura and Sato, 1967) used to quantify P450 levels indicated that all three Camptotheca His 6 -tagged CYP72A proteins were mixtures of properly folded protein (peak around 450 nm) with some free heme from misfolded protein (peak around 420 nm) ( Fig. S7 View Fig ). The calculated P450 concentrations for these Camptotheca preparations were in the micromolar range (15.9 μM for CYP72A564, 31.9 μM for CYP72A565, 3.34 μM for CYP72A730). Cytochrome c reduction assays ( Guengerich et al., 2009) used to quantify CPR activities indicated that the full-length and truncated His 6 --tagged CPR1 proteins efficiently reduced cytochrome c whereas the full-length and truncated His 6 -tagged CPR2 proteins inefficiently reduced cytochrome c at equivalent protein levels ( Fig. S8 View Fig ).
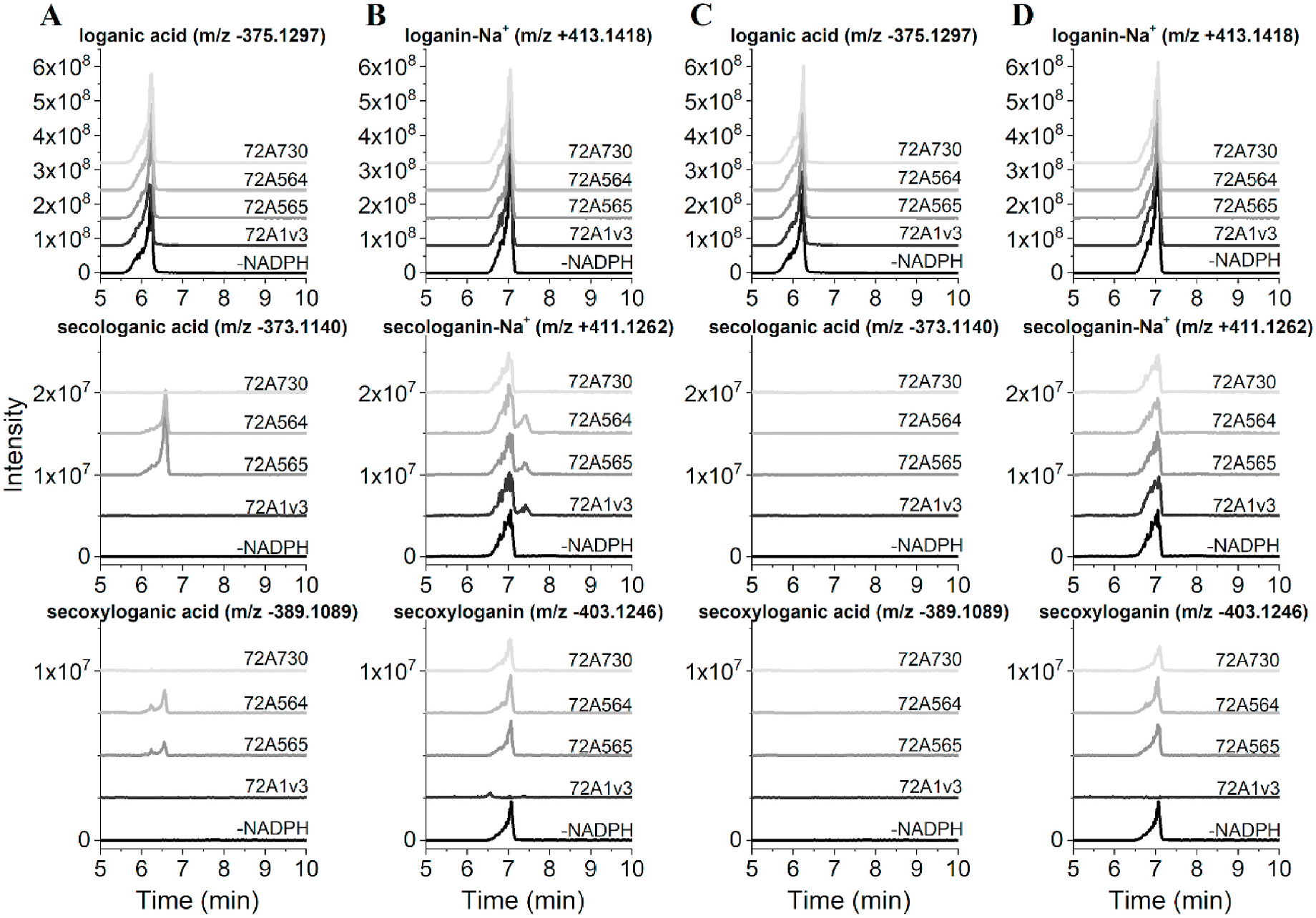
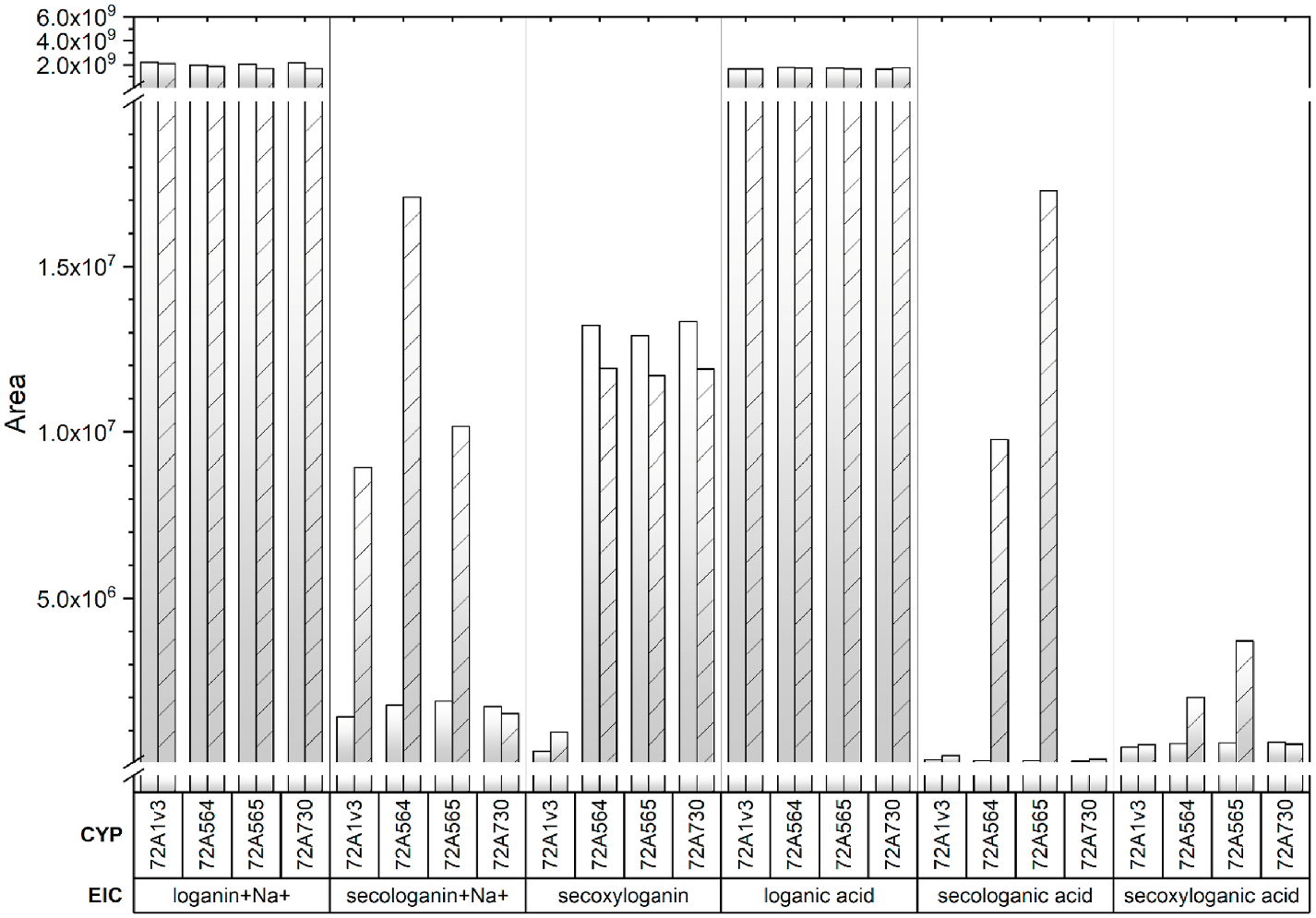
Reconstitution of the purified His 6 -tagged CYP72A564 and CYP72A565 proteins with His 6 CPR1full and DLPC showed that both of these Camptotheca P450s metabolize loganic acid and loganin in the presence of NADPH ( Fig. 4A and B View Fig , 5 View Fig ). For both proteins, products from loganic acid include significant amounts of secologanic acid and smaller amounts of secoxyloganic acid—an overoxidation of the aldehyde to a carboxylic acid. Both proteins also produced secologanin from loganin. Similar reconstitutions of these two Camptotheca P450s with His 6 CPR2full showed no detectable conversion of loganic acid or loganin ( Fig. 4C and D View Fig ); reconstitutions with His 6 CPR1Δ48 and His 6 CPR2Δ68 showed no conversion of loganin or loganic acid (data not shown). Reconstitutions of the more divergent CYP72A730 with His 6 CPR1full showed no conversion of loganic acid or loganin ( Fig. 4A and B View Fig , 5 View Fig ). Reconstitutions with full-length Catharanthu s CYP72A1v3 showed conversion of loganin to secologanin but not conversion of loganic acid ( Fig. 4A and B View Fig , 5 View Fig ).
Lacking access to the 7-deoxyloganic acid needed to assess the 7-hydroxylation activity of these CYPs reported by Yang et al. (2019), we assayed the structurally-related geniposide listed as an alternate substrate. Although we observed product formation consistent with geniposide hydroxylation for CYP72A1, CYP72A564, and CYP72A565 reconstituted with Camptotheca His 6 CPR1full, no such activity was observed for CYP72A730 (Supplemental Fig. S13).
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |