Stenothemus leishanensis Y. Yang et X. Yang
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3847.2.2 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:EE4EC566-9A4A-4A47-BEBB-320F0CE4A58A |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5188491 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/8E1FE82A-0814-FFB4-6BCC-520FDB3BFE06 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Stenothemus leishanensis Y. Yang et X. Yang |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Stenothemus leishanensis Y. Yang et X. Yang , sp. nov.
Figs. 7 View FIGURES 5 ‒ 8 , 19, 36‒38, 44
Type material. Holotype ♂ ( MHBU): CHINA: Guizhou: Leigong Shan , Forestry center, 13.‒14.IX.2005, leg. J.L. Wang & C. Gao . Paratypes: 10 ♂♂, 7 ♀♀ ( MHBU): same data as holotype ; 2 ♀♀ ( MHBU): same data, 14.IX.2005 [above transliterated from Chinese labels]; 4 ♂♂, 3 ♀♀ ( IZAS): Leishan, Lianhuaping, 1500m, 15.IX.2005, leg. Y. Liu ; 1 ♀ ( IZAS): same data, 16.IX.2005.
Distribution. China (Guizhou).
Description. Male ( Fig. 7 View FIGURES 5 ‒ 8 ). Head black, reddish brown on middle line of vertex, mouthparts light brown, more or less darkened at maxillary and labial palpi, dark brown at apices of mandibles, antennae black, light yellow at apex of each antennomere, pronotum light yellow, with a large dark brown marking on disc, scutellum light yellow, elytra light yellow and mottled with irregular dark brown markings, legs light yellow, black at bases of coxae and tibiae and apices of femora and tarsomeres, more or less darkened at outer sides of femora and outer and dorsal sides of tibiae, prosternum light yellow, meso- and metasterna and abdominal ventrites black brown, light yellow at posterior margins of abdominal ventrites and the whole terminal ventrite. Body densely covered with light brown pubescence, mixed with slightly long, semirecumbent light brown pubescence and erect black brown setae on elytra.
Head subquadrate, temples straight and slightly converging posteriorly, dorsum distinctly convex in central part, surface semilustrous, densely and finely punctate, each side with a smooth and rectangular impression behind antennal socket; eyes strongly protruding, head width across eyes almost as wide as pronotum; terminal maxillary palpomeres long-triangular, widest at basal one-third, with apical parts of inner margins arcuate and sharp, acute at apices; antennae extending to elytral midlength, antennomere II about twice as long as wide at apices, III about one-third longer than II, IV longest, from V to XI gradually shortened, XI pointed at apex.
Pronotum nearly as long as wide, widest nearly in middle, anterior margin arcuate, lateral margins sinuate, posterior margin arcuate and narrowly bordered, anterior angles rounded, posterior angles nearly sharp and protruding, disc distinctly convex on posterolateral parts, surface semilustrous, finely and sparsely punctate.
Elytral length about 5 times length of pronotum, 3 times as long as humeral width, with lateral margins slightly diverging posteriorly, surface semilustrous, rugulose-lacunose and finely punctate.
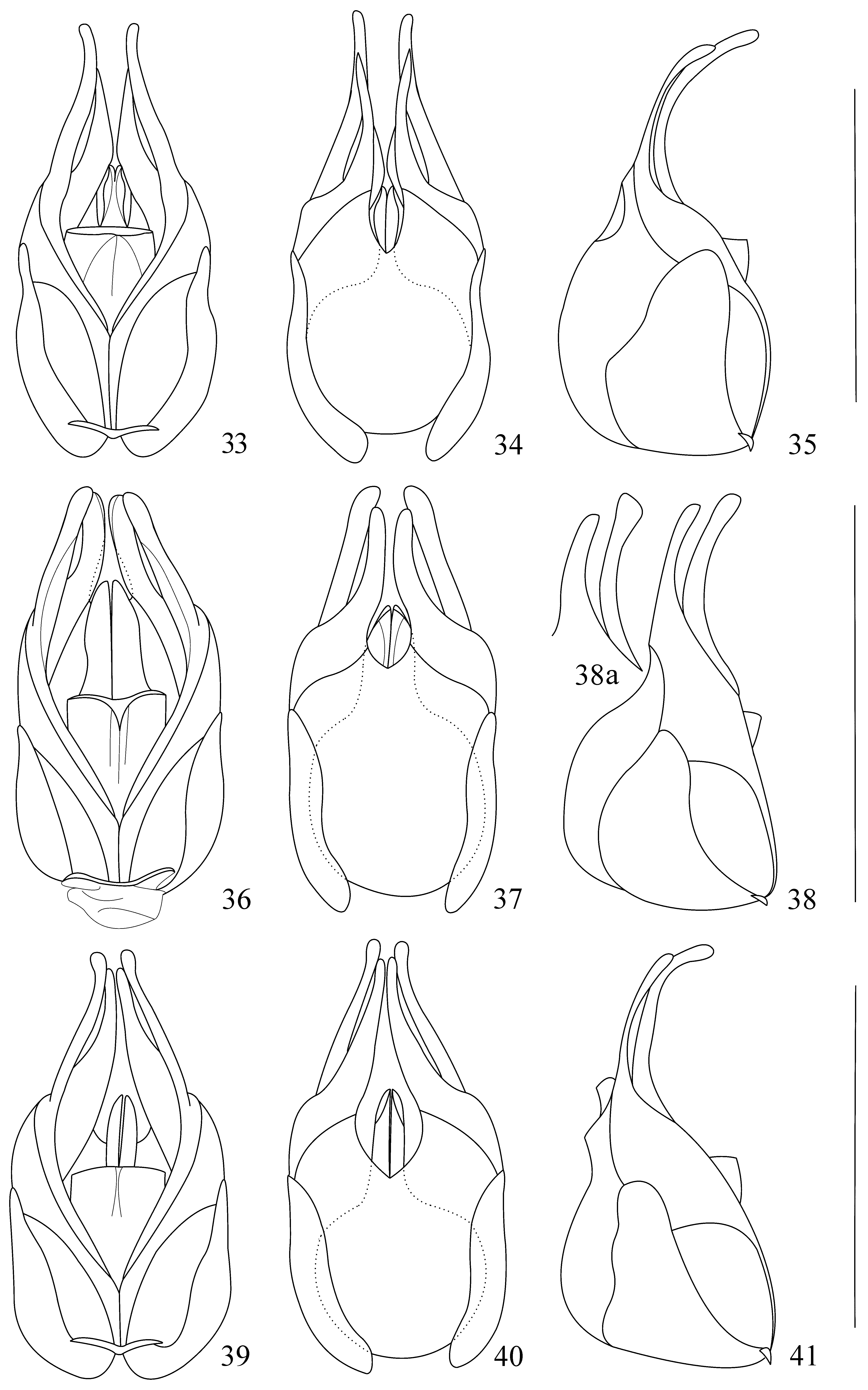
Aedeagus ( Figs. 36‒38 View FIGURES 33 ‒ 41 ): ventral process of each paramere bent ventrally about 30 degrees, with the bent portion at apical part distinctly shorter than the basal portion, flattened and subtriangularly dilated at apex in dorsolateral view ( Fig. 38 View FIGURES 33 ‒ 41 a), dorsal plate slightly shorter than ventral process, abruptly narrowed apically, rounded at apex; laterophyse rounded at apex.
Female. Similar to male, but head slightly convex on dorsum, head width across eyes distinctly narrower than pronotum, antennae shorter and extending to basal one-third length of elytra, pronotum distinctly wider than long, about 1.26 times as wide as long, moderately convex on posterolateral parts of disc, elytra with lateral margins distinctly diverging posteriorly, abdominal sternite VIII (Fig. 19) evenly narrowed posteriorly, triangularly convex at posterior half of middle sclerotized part, with lateral margins strongly sclerotized, posterior margin roundly emarginated in middle, lateroapical angles rounded, the lobe slightly sclerotized and triangular.
Body length: 6.0‒8.0 mm; width: 1.4‒1.8 mm.
Diagnosis. This species can be distinguished from others by the aedeagus: ventral process of each paramere slightly bent ventrally, flattened and subtriangularly dilated at apex in dorsolateral view, dorsal plate slightly shorter than ventral process.
Etymology. Derived from the name of its type locality, Leishan County, Guizhou Province, China.
| IZAS |
Institut Zoologii Akademii Nauk Ukraini - Institute of Zoology of the Academy of Sciences of Ukraine |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |