Sphecodes schwarzi, Astafurova, Yulia V. & Proshchalykin, Maxim Yu., 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4052.1.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:5B38724D-0FC3-453C-A273-7EA87B08EA25 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5619723 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/9468AA7B-FA60-FFA6-BCCF-FAEB3AB5F96D |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Sphecodes schwarzi |
| status |
|
Key to the Sphecodes View in CoL species of the Siberia and Mongolia
Females
Note: The female of S. kozlovi Astafurova et Proshchalykin and S. schwarzi , sp. nov. is unknown. Additional characters that are not unique but are useful in the identification of some species are indicated in parentheses. *Females of this vicarious species are very difficult to distinguish morphologically; however, S. nippon is distributed in the East Palaearctic to Baikal Lake on the West, whereas S. gibbus is distributed in the West Palaeractic to Baikal Lake and Yakutsk on the East.
1. Preoccipital carina present along vertex only. F2 square, as long as wide, remaining flagellomeres distinctly longer than wide. (Head strongly transverse, 1.25 times wider than long. Scutum densely punctate, punctures separated mostly by less than a puncture diameter. Body length 8.0–11.0 mm).............................................. S. spinulosus Hagens View in CoL
- Preoccipital carina not developed or present laterally behind eye only. F2 transverse 0.5–0.7 times as long as wide, remaining flagellomeres square or slightly longer than wide........................................................... 2
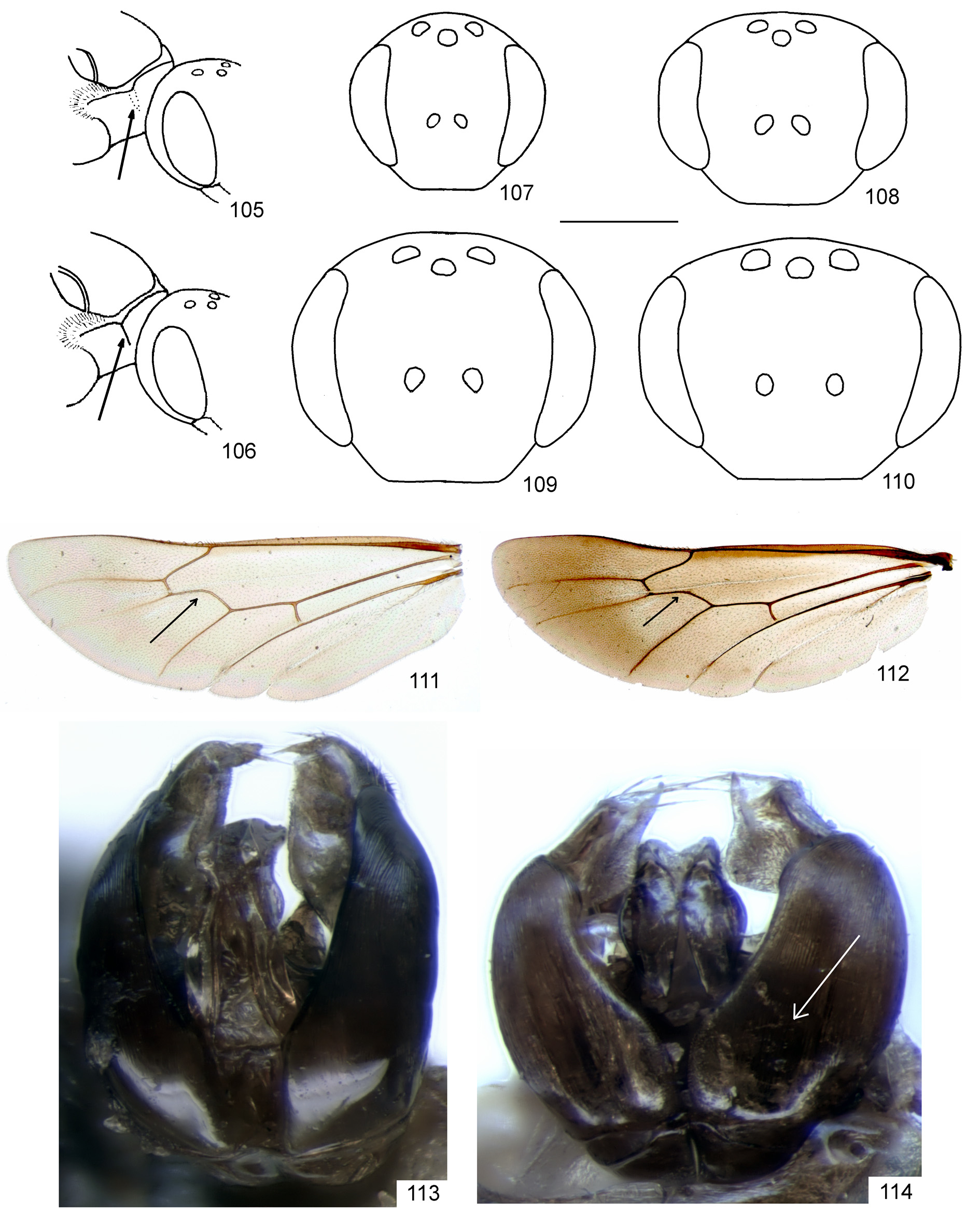
2. Hind wing with 7–14 hamuli; with basal ( M) vein weakly curved ( Fig. 112 View FIGURES 105 – 114 ). Usually large species: body length 6.0–15.0 mm................................................................................................... 3
- Hind wing with 5–6 hamuli; with basal ( M) vein strongly curved ( Fig. 111 View FIGURES 105 – 114 ). Large or small species: body length 4.5–11.0 mm.................................................................................................. 10
3(2). Vertex weakly elevated, with longitudinal sharp carina ( Fig. 101 View FIGURES 100 – 104 ). (Head strongly transverse, 1.2 times wider than long. Scutum and scutellum sparsely punctate, medially with punctures separeted by mostly 1–3 puncture diameters; Fig. 90 View FIGURES 89 – 94 . Pygid-
ium slightly narrower than hind basitarsus. Body length 6.0–8.0 mm)............................ S. cristatus Hagens View in CoL - Vertex strongly elevated, acarinate, but sometimes with weak (indistinct) longitudinal ridge......................... 4
4(3). Genal area flat. Preoccipital lateral carina developed. (Head strongly transverse, 1.3 times wider than long. Vertex short, distance from top of head to upper margin of lateral ocellus about two lateral ocellar diameters; Fig. 87 View FIGURES 77 – 88 . Scutum densely punctate and medially with punctures separated by at most 1.5–2 puncture diameters; Fig. 89 View FIGURES 89 – 94 . Pygidium slightly narrower than hind basitarsus. Body length 9.0–12.0 mm).................................................. S. scabricollis Wesmael View in CoL
- Genal area swollen. Preoccipital carina not developed....................................................... 5
5(4). Scutum densely punctate, punctures separated by less than a puncture diameter ( Fig. 91 View FIGURES 89 – 94 ). (Head strongly transverse, 1.3 times wider than long. T4 and T5 red. Pygidium slightly narrower than hind basitarsus. Body length 9.0–15.0 mm)............................................................................................. S. albilabris (Fabricius) View in CoL
- Scutum sparsely punctate, medially with punctures separated by more than a puncture diameter ( Figs. 92 View FIGURES 89 – 94 )............... 6
6(5). Vertex short, distance from top of head to upper margin of lateral ocellus about two lateral ocellar diameters ( Fig. 86 View FIGURES 77 – 88 ). Marginal zone of T4 punctate and smooth between punctures or finely tessellate without punctures. Sides of propodeum reticulaterugose.............................................................................................. 7
- Vertex longer, distance from top of head to upper margin of lateral ocellus equal to 2.5–3.0 lateral ocellar diameters ( Fig. 85 View FIGURES 77 – 88 ). Marginal zone of T4 tessellate, smooth (rarely indistinctly tessellate). Sides of propodeum strigate or reticulate-rugose.... 8.
7(6). Marginal zone of T4 impunctate, finely tessellate (Fig. 98). Scutum usually densely punctate, medially with punctures separated by not more than 1–3 puncture diameters, sometimes sparser. T1 finely punctate. Body length 7.0–10.0 mm........................................................................................... S. reticulatus Thomson View in CoL
- Marginal zone of T4 distinctly punctate, smooth between punctures (rarely indistinctly tessellate) (Fig. 99). Scutum usually sparsely punctate, medially with punctures separated by mostly 2–4 puncture diameters. T1 coarserly punctate. Body length 8.0–11.0 mm......................................................................... S. alternatus Smith View in CoL
8(6). Head rounded-rectangular on upper margin, square-shaped as seen in frontal view ( Fig. 78 View FIGURES 77 – 88 ); vertex sparsely punctate, punctures mostly separated by more than а puncture diameter. Pygidium equal or slightly narrower than hind basitarsus. T1 indistinctly punctate, with a few very fine punctures (Fig. 97). (Body length 7.0–10.0 mm)............ S. monilicornis (Kirby) View in CoL
- Head uniformly rounded on upper margin, oval in frontal view ( Fig. 84 View FIGURES 77 – 88 ); vertex densely punctate, punctures mostly separated by less than a puncture diameter. Pygidium 0.5–0.6 times narrower than hind basitarsus. T1 distinctly punctate, with fine and coarser punctures..................................................................................... 9
9(8). Mesopleura strigate or strigate-rugose, sides of propodeum strigate ( Fig. 100 View FIGURES 100 – 104 ). Marginal zone of T3 coarsely punctate. T4 red, T5 red or dark red. Body length 6.5–8.5 mm.............................................. S. rufiventris (Panzer) View in CoL
- Mesopleura reticulate-rugose, sides of propodeum strigate or reticulate-rugose. Marginal zone of T3 impunctate. T4 and T5 black, sometimes T4 laterally red. Body length 7.0–11.0 mm.................. S. nippon Meyer View in CoL / S. gibbus (Linnaeus) View in CoL *
10(1). Pygidium wider than hind basitarsus, usually dull ( Fig. 103 View FIGURES 100 – 104 ). Scutum densely punctate, punctures usually separated by less than two puncture diameters. Body length 7.0–11.0 mm...................................................... 11
- Pygidium equal or narrower than hind basitarsus, shiny ( Fig. 102 View FIGURES 100 – 104 ). Scutum usually sparsely punctate, disc medially with punctures separated by more than two puncture diameters. Body length 4.0–9.0 mm................................... 12
11(10). Head strongly transverse, 1.30–1.35 times wider than long; vertex, behind ocelli, not elevated in frontal view ( Fig. 82 View FIGURES 77 – 88 , 110 View FIGURES 105 – 114 ). Hairs on scape distinctly longer than width of scape. Pygidium 1.3–1.5 times wider than hind basitarsus. Body length 7.0–11.0 mm................................................................................. S. pellucidus Smith View in CoL
- Head weaker transverse, 1.20–1.25 times wider than long ( Fig. 83 View FIGURES 77 – 88 , 109 View FIGURES 105 – 114 ); vertex, behind ocelli, weakly elevated. Hairs on scape shorter than width of scape. Pygidium 1.2–1.4 times wider than hind basitarsus. Body length 7.0–9.0 mm.................................................................................................... S. ephippius (Linné) View in CoL
12(10). Mandible simple (without an inner tooth)................................................................. 13
- Mandible bidentate................................................................................... 14
13(12). Head weakly transverse, 1.07–1.18 times wider than long ( Fig. 79 View FIGURES 77 – 88 ). F3 transverse. Clypeus, at least in its lower half, with punctures separated by about a puncture diameter. T2–T3 usually indistinctly punctate. Body length 4.0–6.0 mm.............................................................................................. S. longulus Hagens View in CoL
- Head strongly transverse, 1.2–1.3 times wider than long ( Fig. 81 View FIGURES 77 – 88 ). F3 square. Clypeus with punctures separated by at most a puncture diameter. T2–T3 on basal half usually distinctly punctate. Body length 5.0–7.0 mm...... S. puncticeps Thomson View in CoL
14(12). Clypeus densely punctate, punctures separated by less than a puncture diameter. Pronotum, between dorsal and lateral surfaces, rounded, not angulated ( Fig. 105 View FIGURES 105 – 114 ).................................................................. 15
- Clypeus sparsely punctate, punctures separated by at least a puncture diameter. Pronotum between dorsal and lateral surfaces with sharp angle ( Fig. 106 View FIGURES 105 – 114 )............................................................................. 16
15(14). Ventral part of thorax dull, finely reticulate-rugulose ( Fig. 94 View FIGURES 89 – 94 ). Head transverse, about 1.2 times wider than long. Scutum with punctures separated by 1–3 (sometimes more) puncture diameters. Body length 5.0–7.5 mm......... S. hyalinatus Hagens View in CoL
- Ventral part of thorax shiny, coarsely reticulate-rugose ( Fig. 93 View FIGURES 89 – 94 ). Head transverse, about 1.25 times wider than long. Scutum with punctures separated by 1–4 puncture diameters. Body length 6.0–9.0 mm.................. S. ferruginatus Hagens View in CoL
16(14). Vertex long, distance from top of head to upper margin of lateral ocellus about 3–3.5 times lateral ocellar diameters. Metasomal terga relatively coarsely and densely punctate (sparser on T1) (Fig. 96). Upper half of gena with apressed, dense pubescence covering integument. (Head transverse, about 1.25 wider than long. Scutum and scutellum sparsely punctate, punctures separeted by 1–7 puncture diameters. Body length 5.0–7.0 mm)................................ S. pinguiculus Pérez View in CoL
- Vertex shorter, distance from top of head to upper margin of lateral ocellus about two lateral ocellar diameters. Metasomal terga finely and sparsely punctate or densely punctate on basal half only, T1 impunctate or with a few fine punctures (Figs. 95). Genal area with erect, sparse pubescence................................................................. 17
17(16). F3 transverse, 0.6–0.7 times as long as wide, as long as F1 ( Fig. 104 View FIGURES 100 – 104 ). Pygidium as wide as hind basitarsus. (Head transverse, 1.15 times wider than long. Labrum semicircular, 0.5 times as long as width. Scutum sparsely punctate, with punctutres separeted by 1–4 puncture diameters. Body length 4.0–6.0 mm)..................................... S. miniatus Hagens View in CoL
- F3 square, as long as wide, longer than F1 ( Figs 77, 80 View FIGURES 77 – 88 ). Pygidium narrower than hind basitarsus.................... 18
18(17). Head strongly transverse, 1.25 times wider than long ( Fig. 80 View FIGURES 77 – 88 , 108 View FIGURES 105 – 114 ). Labrum trapezoidal, 0.7 times as long as wide. Hind femur strongly enlarged on proximal half, maximum width 0.4 times its length. Scutum sparsely punctate, with fine punctures separated by 2–6 (sometimes more) puncture diameters. Pygidium 0.6–0.7 times narrower than hind basitarsus. Body length 5.0– 8.0 mm.............................................................................. S. crassus Thomson View in CoL
- Head weakly transverse, 1.1 times wider than long ( Fig. 77 View FIGURES 77 – 88 , 107 View FIGURES 105 – 114 ). Labrum semicircular, 0.5 times as long as width. Hind femur weakly enlarged on proximal half, maximum width 0.35 times its length. Scutum sparsely punctate, punctures separated by 2– 4 puncture diameters. Pygidium 0.7–0.8 times narrower than hind basitarsus. Body length 4.5–6.5 mm..................................................................................................... S. geoffrellus (Kirby) View in CoL
Males
1. Hind wing with 7–14 hamuli. Base of gonocoxite dorsally without impression ( Fig. 113 View FIGURES 105 – 114 ). Usually large species: body length 7.0–12.0 mm......................................................................................... 2
- Hind wing with 5–6 hamuli. Base of gonocoxite dorsally with impression ( Fig. 114 View FIGURES 105 – 114 ) or without it. Large or small species: body length 3.5–11.0 mm.................................................................................. 11
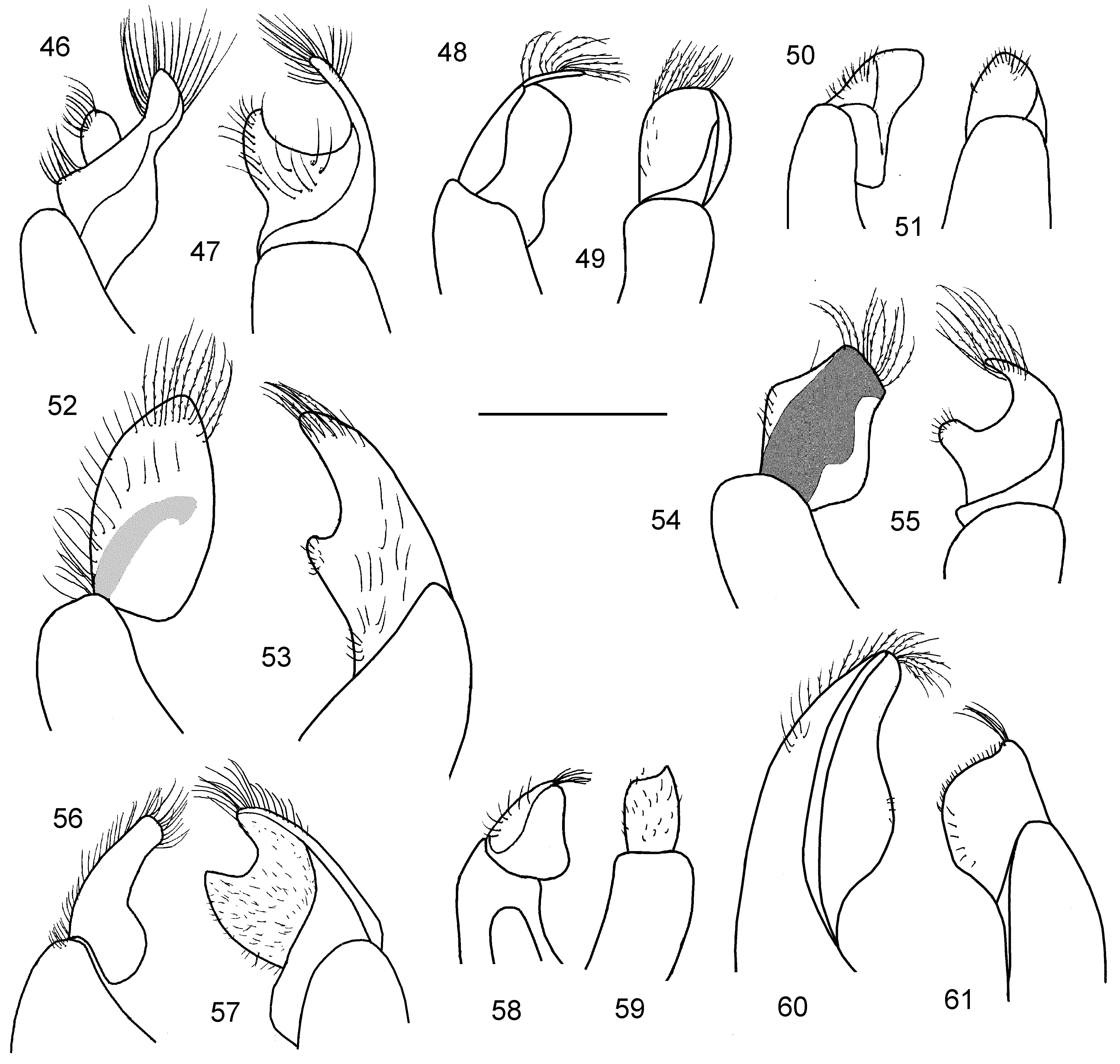
2. Preoccipital carina developed, complete. Upper side of hind tibiae with red spines ( Fig. 76 View FIGURES 72 – 76 ). (Felt-like areas on flagellomeres semicircular across basal 1/7–1/5 (at least from F4) and widely linear across rest of segment as seen in lateral view (Fig. 23), sometimes strongly developed. Hind wing with basal ( M) vein strongly curved. Scutum and scutellum densely punctate, punctutres separeted by less than a puncture diameter. Gonocoxite as in Figs 60, 61 View FIGURES 46 – 61 , 113 View FIGURES 105 – 114 . Body length 9.0–11.0 mm)............................................................................................... S. spinulosus Hagens View in CoL
- Preoccipital carina not developed or present laterally behind eye only. Upper side of hind tibiae without spines.......... 3
3. Head rounded, about as long as wide. Hind wing with basal ( M) vein strongly curved. T1 finely and sparsely (sometimes indistinctly) punctate. (Vertex strongly elevated; distance from top of head to upper margin of lateral ocellus about two lateral ocellar diameters. Felt-like areas on flagellomeres weakly developed, semicircular across basal 1/7–1/5 of flagellomere (Fig. 12). Scutum densely punctate, punctures separated by about 1–1.5 times a puncture diameter, sometimes denser. Gonocoxite as in Figs 44, 45 View FIGURES 24 – 45 . Body length 7.0–10.0 mm)................................................. S. monilicornis (Kirby) View in CoL
- Head transverse, wider than long. Hind wing with basal ( M) vein weakly curved. T1 distinctly coarsely and densely punctate.................................................................................................... 4
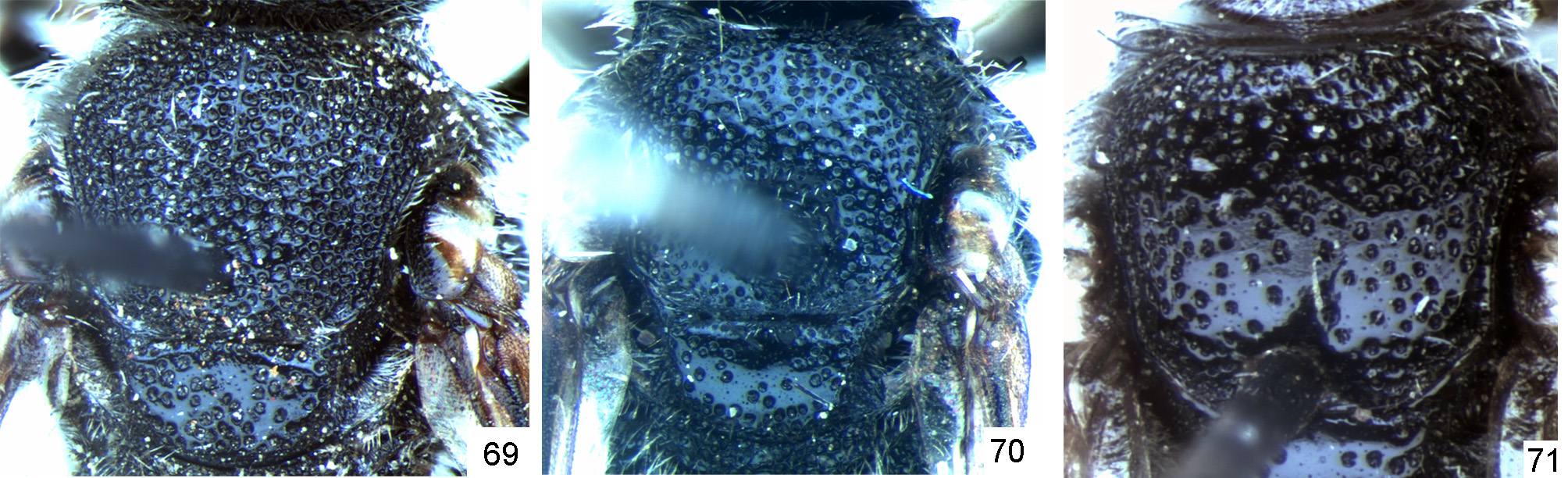
4. Scutum densely punctate, with confluent punctures (areolate) ( Fig. 69 View FIGURES 69 – 71 ).......................................... 5
- Scutum sparsely punctate, medially with punctutres separated by at least a puncture diameter ( Figs 70, 71 View FIGURES 69 – 71 )............. 6
5. Head strongly transverse, 1.2 times wider than long. Vertex long, distance from top of head to upper margin of lateral ocellus about 2.5–3.0 lateral ocellar diameters. Felt-like areas on flagellomeres (at least from F4) semicircular across basal 1/5–1/3 and linear across the rest of segment as seen in lateral view (Fig. 2). Scutellum sparsely punctate, medially with punctures separated by more than a puncture diameter and often with impunctate areas. T1 completely red. Gonostylus as in Figs 24, 25 View FIGURES 24 – 45 . Body length 9.0–12.0 mm........................................................... S. albilabris (Fabricius) View in CoL
- Head weakly transverse, 1.1 times wider than long. Vertex shorter, distance from top of head to upper margin of lateral ocellus about two lateral ocellar diameters. Felt-like areas on flagellomeres semicircular across basal 1/6–1/4, linear portion along remaining flagellomeres not developed (Fig. 20). Scutellum densely punctate, with confluent punctures. T1 black or brownish at least on basal 1/3. Gonostylus as in Figs 56, 57 View FIGURES 46 – 61 . Body length 7.0–12.0 mm................... S. scabricollis Wesmael View in CoL
6. Vertex with a longitudinal carina ( Fig. 65 View FIGURES 62 – 68 ). Marginal zone of T1 with very fine and indistinct punctures, T2 impunctate. (Feltlike areas on flagellomeres, at least from F4, semicircular across basal 1/3–1/2 (Fig. 4). Gonostylus as in Figs 26, 27 View FIGURES 24 – 45 . Body length 7.0–10.0 mm)................................................................... S. cristatus Hagens View in CoL
- Vertex without a longitudinal carina. Marginal zones of T1 and T2 with relatively coarse and distinct punctures.......... 7
7. Vertex long, distance from top of head to upper margin of lateral ocellus about three lateral ocellar diameters ( Fig. 66 View FIGURES 62 – 68 ). Feltlike areas on flagellomeres covering at least 1/3 part of flagellomere (Figs 7, 13, 19)................................ 8
- Vertex shorter, distance from top of head to upper margin of lateral ocellus about two lateral ocellar diameters ( Fig. 67 View FIGURES 62 – 68 ). Feltlike areas on flagellomeres not covering more than 1/4 part of flagellomere (Fig. 17). Gonostylus as in Figs 52, 53 View FIGURES 46 – 61 ....... 10
8. F3 short, slightly longer than wide. Lover part of mesopleura strigate or strigate-rugose. Gonostylus without an elongated apical projection ( Figs. 54, 55 View FIGURES 46 – 61 ). (Felt-like areas on flagellomeres well developed, cover larger part of flagellomer (Fig. 18, 19). Scutum coarsely and densely punctate, punctures separated by about 0.5–1.5 puncture diameters. Body length 6.0–8.0 mm).................................................................................... S. rufiventris (Panzer) View in CoL
- F3 long, about 2 times longer than wide. Mesopleura reticulate-rugose. Gonostylus with an elongated apical projection ( Fig. 46, 47 View FIGURES 46 – 61 ).............................................................................................. 9
9. Felt-like areas on flagellomeres well developed, covering large part of flagellomere as seen in lateral view (Figs. 7). Scutum coarsely punctate, density of punctures variable, usually relatively densely punctate, medially with punctures separated by at most 1–1.5 puncture diameter, sometimes sparser (up to three times a puncture diameter) ( Fig. 71 View FIGURES 69 – 71 ). Body length 7.0–14.0 mm.................................................................................... S. gibbus (Linnaeus) View in CoL
- Felt-like areas on flagellomeres weakly developed, are semicircular across basal 1/3 (Fig. 13). Scutum densely punctate, medially with punctures separated by about a puncture diameter ( Fig. 70 View FIGURES 69 – 71 ). Body length 7.0–11.0 mm......... S. nippon Meyer View in CoL
10. Marginal zone of T4 finely tessellate, without punctures ( Fig. 73 View FIGURES 72 – 76 ). Scutum densely punctate, medially with punctures separated by at most 1.5 puncture diameters. Body length 7.0–10.0 mm............................... S. reticulatus Thomson View in CoL
- Marginal zone of T4 distinctly punctate, smooth between punctures (rarely indistinctly tessellate) ( Fig. 72 View FIGURES 72 – 76 ). Scutum with punctures medially separated by at most 1.5–2 puncture diameters, rarely sparser. Body length 7.0–12.0 mm. S. alternatus Smith View in CoL
11. Base of gonocoxite dorsally without impression ( Fig. 113 View FIGURES 105 – 114 )................................................... 12
- Base of gonocoxite dorsally with impression ( Fig. 114 View FIGURES 105 – 114 )....................................................... 16
12. Vertex sparsely punctate, area between lateral ocellus and compound eye with fine punctures separated by more than а puncture diameter ( Fig. 68 View FIGURES 62 – 68 ). Head weakly transverse, 1.05–1.10 times wider than long. (Felt-like areas on flagellomeres semiovalshaped, not extending beyond middle of the flagellomere (Fig. 10). Scutum relatively sparsely punctate, medially with punctures separated by 1–3 puncture diameters. Gonostylus as in Figs 40, 41 View FIGURES 24 – 45 . Body length 3.5–6.0 mm) ...... S. longulus Hagens View in CoL
- Vertex densely punctate, area between lateral ocellus and compound eye with coarse punctures separated by about a puncture diameter. Head strongly transverse, 1.15–1.30 times wider than long............................................. 13
13. Felt-like areas on flagellomeres shallow, semi-oval (Figs 15, 16). Gonostylus triangular on apex ( Figs 50, 51 View FIGURES 46 – 61 ). Small: body length 4.5–7.0 mm. (Scutum coarsely and densely punctate, punctures separeted by 0.5–1.5 a puncture diameter. T1 impunctate or with a few fine punctures, T2 relatively coarsely and densely punctate on anterior half)..... S. puncticeps Thomson View in CoL
- Felt-like areas on flagellomeres deep, semicircular. Apex of gonostylus not triangular. Larger: body length 6.0–11.0 mm.. 14
14. Vertex with a longitudinal carina (sometimes weakly developed). Felt-like areas on flagellomeres (from F4) extending up to 1/ 3 underside of flagellomere (Fig. 9). T1 sparsely, but coarsely punctate ( Fig. 74 View FIGURES 72 – 76 ). (Gonostylus as in Figs 38, 39 View FIGURES 24 – 45 . Body length 8.0–10.0 mm)....................................................... S. kozlovi Astafurova & Proshchalykin
- Vertex without a longitudinal carina. Felt-like areas on flagellomeres (from F4) covering 1/2–4/5 underside of flagellomere (Figs 5, 14). T1 impunctate or with a few fine punctures..................................................... 15
15. Felt-like areas on last flagellomeres (from F4) usually covering more than 1/2 underside of flagellomere, often up to 4/5 (Fig. 14). Gonostylus similar to S. kozlovi (as in Figs 38, 39 View FIGURES 24 – 45 ). Body length 7.0–11.0 mm................... S. pellucidus Smith View in CoL
- Felt-like areas on last flagellomeres (from F4) usually covering about 1/2 underside of flagellomere, rarely 3/4 (Fig. 5). Gonostylus as in Figs 34, 35 View FIGURES 24 – 45 . Body length 6.0–9.0 mm........................................... S. ephippius (Linné) View in CoL
16. Face with apressed white pubescence below as well as above antennal sockets ( Figs 62, 63 View FIGURES 62 – 68 ). T1 densely punctate ( Fig. 75 View FIGURES 72 – 76 )..................................................................................................... 17
- Face with apressed white pubescence below antennal sockets only ( Fig. 64 View FIGURES 62 – 68 ). T1 impunctate or with sparse punctures (at S. miniatus View in CoL sometimes relatively densely punctate)............................................................... 18
17. Felt-like areas on flagellomeres (from F3) covering 1/2–4/5 of flagellomere (Figs 21, 22). F3 short, slightly longer than wide and shorter than F2. Gonostylus small, triangular ( Figs 58, 59 View FIGURES 46 – 61 ). Body length 5.0–5.5 mm......................................................................................... S. schwarzi Astafurova et Proshchalykin , sp. nov.
- Felt-like areas on flagellomeres (from F2) covering all underside of flagellomere. F3 longer, 1.5 longer than wide and equal to F2. Gonostylus large, rectangular ( Figs 48, 49 View FIGURES 46 – 61 ). Body length 5.0–7.5 mm........................ S. pinguiculus Pérez View in CoL
18. F2 short, 0.9–1.0 times as long as F3. Felt-like areas on flagellomeres (from F4) covering all underside of flagellomere. (Head weakly transverse, 1.05 times wider than long. Scutum with punctures separated by 0.5–2 puncture diameters. T1 and T2 smooth, with a few very fine punctures. Gonocoxite with impression, gonostylus as in Figs 32, 33 View FIGURES 24 – 45 . Body length 5.0–6.5 mm).................................................................................. S. geoffrellus (Kirby) View in CoL
- F2 longer, 1.1–1.2 as long as F3. Felt-like areas on flagellomeres shorter, covering at most 4/5 the underside of flagellomere (in S. miniatus View in CoL felt-like areas on last flagellomeres sometimes covering entire underside surface)....................... 19
19. Pronotum between dorsal and lateral surfaces rounded, not angulated ( Fig. 105 View FIGURES 105 – 114 ). Scutum densely punctate, with punctures separated by at most a puncture diameter..................................................................... 20
- Pronotum between dorsal and lateral surfaces with sharp angle ( Fig. 106 View FIGURES 105 – 114 ). Scutum sparsely punctate, punctures (at least in middle) mostly separated by more than a puncture diameter...................................................... 21
20. Felt-like areas on flagellomeres covering less than 1/3 underside of flagellomere (Fig 6). Gonostylus long, trapezoidal ( Figs 30, 31 View FIGURES 24 – 45 , 114 View FIGURES 105 – 114 ). Body length 6.0–9.0 mm.................................................. S. ferruginatus Hagens View in CoL
- Felt-like areas on flagellomeres (from F4) covering about 1/3–1/2 underside of flagellomere, rarely 3/4 on last flagellomeres (Fig. 8). Gonostylus shorter, not trapezoidal ( Figs 36, 37 View FIGURES 24 – 45 ). Body length 5.0–7.0 mm............... S. hyalinatus Hagens View in CoL
21. Felt-like areas on flagellomeres usually covering less than 1/3 underside of flagellomere (rarely 1/2) (Fig. 3). Gonostylus oval ( Figs 28, 29 View FIGURES 24 – 45 ). Body length 5.0–7.0 mm.................................................... S. crassus Thomson View in CoL
- Felt-like areas on flagellomeres cover more than 3/4 underside of flagellomere (Fig. 11), sometimes entire underside. Gonostylus trapezoidal ( Figs 42, 43 View FIGURES 24 – 45 ). Body length 4.0–6.0 mm......................................... S. miniatus Hagens View in CoL
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
SuperFamily |
Apoidea |
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |