Clunio ponticus Michailova, 1980
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.5324/cjcr.v0i33.3332 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7996108 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A2061A24-0F62-FFAE-B5EB-FB37EF9E2A49 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Clunio ponticus Michailova, 1980 |
| status |
|
Clunio ponticus Michailova, 1980 View in CoL View at ENA
Holotype and paratypes in Institute of Biodiversity and Ecosystem research, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Sofia, Bulgaria ( Michailova 1980b) .
Material examined
Topotypes : 30 male adults, 2 female adults, 2 pharate females, 1 male pupal exuviae, 7 larva, Varna, Bulgaria. rocky seashores at Varna beach, St. Konstantin and Helena Resorts (43°13’45” N and 28° 0’30’’ E) (locus typicus), 26.VI.2019, leg. P. Michailova. Water temperature: low 10-12 °C; high 22-25 °C GoogleMaps .
Material is deposited in the authors’ collections as follows: 5 male adults ( JM) ; 23 male adults including 7 mounted on slides and 14 preserved in ethanol 95%, 2 female adults, 7 larvae ( PM) ; 1 male adult, 2 pharate females, 1 male pupal exuviae ( PHL) . 1 male adult mounted on 1 slide is deposited in the Zoologische Staatssammlung München ( ZSM) , Germany.
Diagnostic characters
Although C. ponticus is keyed near C. mediterraneus and C. boudouresquei , some atypical morphological characters found in male and female adults and pupal exuviae enable us to separate this species from its congeners. The species is also distinguished by its ecology and the stability of its biological cycle, which is not related to the lunar periodicity as for most populations of C. marinus , C. mediterraneus and C. boudouresquei . The following combination of morphological characters will separate C. ponticus from other related species:
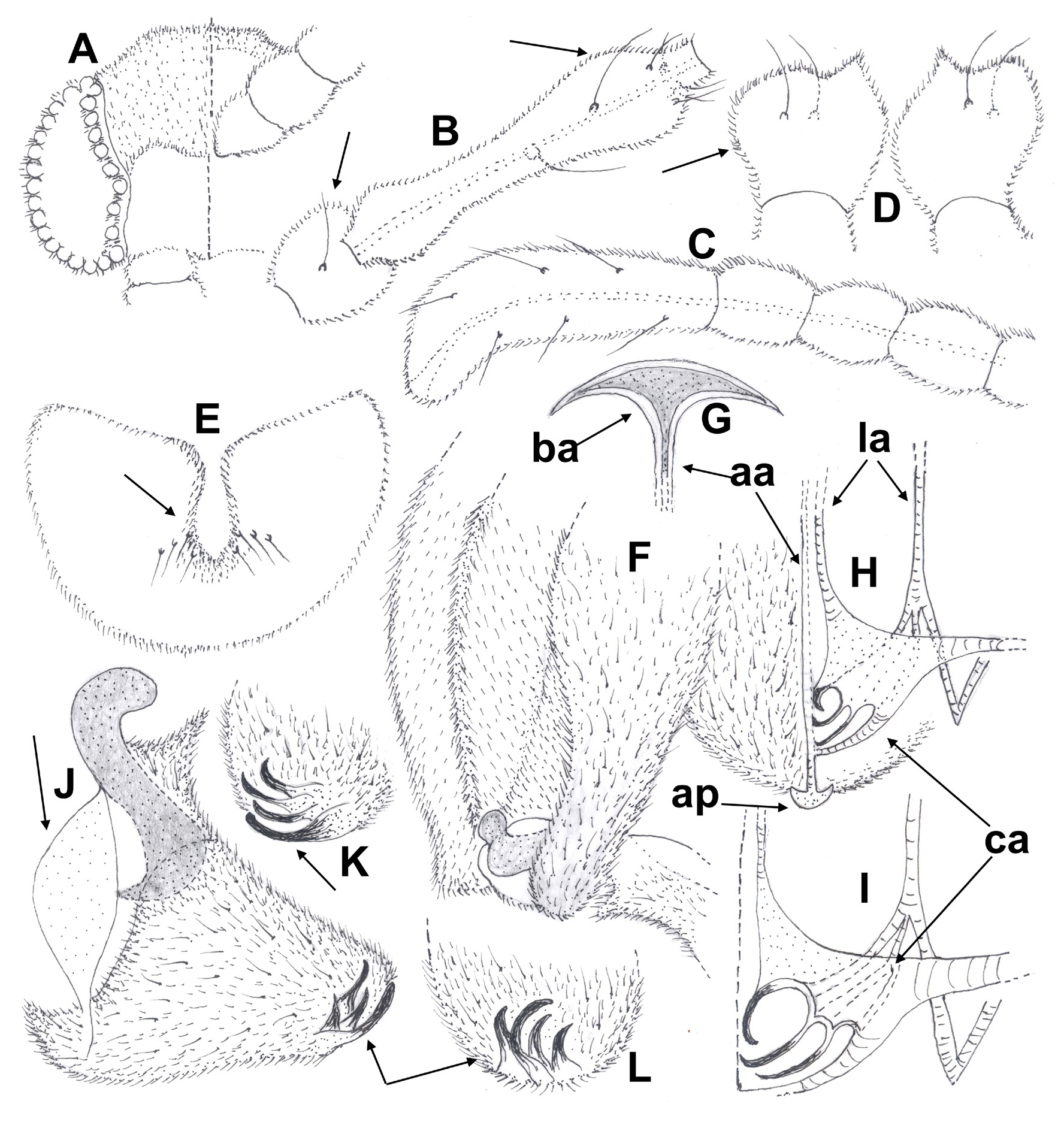
Male adult: frontal margin of head atypically straight and not projecting. Antenna 10-segmented; pedicels conical, closely inserted at their base on midline of head; segment 1 globular with 1 long seta; segment 2 linearly elongated and swollen proximally and distally, bearing 2 long setae on distal half and 5-6 shorter setae apically; last flagellomere as long as the 3 preceding segments, slightly bent apically; AR 0.40-0.43. Palp 2-segmented, palpomere 2 sub-circular with 2 long setae (1 dorsal and 1 ventral), inner apical margin pointed. Ridge of tergite VIII long, drop-shaped with 8 median setae (4 on each side of the midline). Hypopygium. Inferior volsella wider at base, narrowing distally and ending with parallel-sided margins; basal apodeme umbrella-shaped, caudal apodeme with 3 long, thin, spine-like extensions, anterior one distinctly curved downwards. Gonostylus with basal tooth crochet-shaped and conspicuous, posterior area with 4 pointed and characteristic teeth; crista dorsalis a wide lobe, long extended and occupying about 90% of the anterior side; megaseta absent.
Female adult: antenna 7-segmented. Segment 3 as long as the 2 preceding segments, last flagellomere slightly longer than the 3 preceding segments, AR about 0.45; apical segment of palp sub-circular, bearing 2 long setae (1 dorsal, 1 ventral) and several shorter setae located close to the margin; tergite VIII with a large drop-like posterior margin; gonocoxite elongated vertically and weakly prominent; tergite IX ellipsoidal to egg-shaped; gonapophysis VIII, dorsomesal lobe convex medially, apodeme lobe swollen medially and thicker distally, seminal sac ovoid; cercus bean-shaped with 2 long dorsal setae located on 1 side.
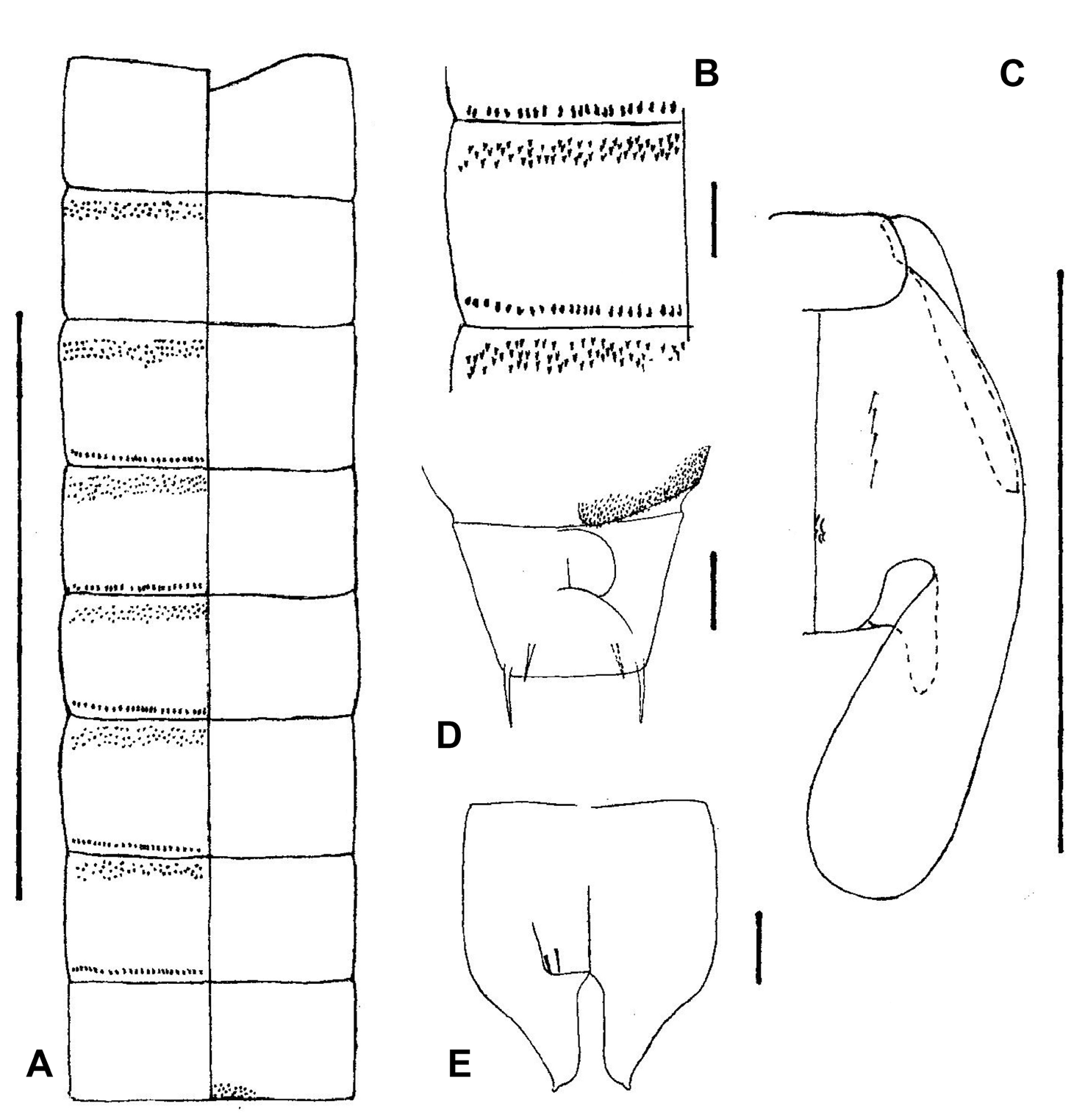
Pupal exuviae: anterior transverse rows of points present on tergite II-VII, not broken medially on any tergite; posterior transverse rows of hooks present on sternites III-VII; posterior transverse rows of hooks absent on sternites.
Fourth instar larvae: clypeus trapezoidal; setae 1 and 2 plumose, occasionally with branches; setae 3 and 4 are simple. Antenna 5-segmented; ring organ located close to pedestal; segment 2 with a lancetshaped style reaching apex of segment 4; segments 3 and 4 sub-equal. Median tooth of mentum widely domed, and smooth. Mandible with 5 teeth. Pecten epipharyngis with lanceolate setae on both sides.
Male adult
(n = 6; Figs 1-5 View Figure 1 View Figure 2 View Figure 3 View Figure 4 View Figure 5 )
Clunio sp. 1 , Moubayed-Breil & Dominici (2019)
Total length 2.70-2.90 mm. Wing length 1.35-1.40 mm, TL/WL = 2-2.10. General colouration contrasting brown to dark brown. Head and antennae dark brown; thorax contrasting light brown to brown with dark brown mesonotal stripes; wing pale translucent; legs brown to dark brown; tergites I-VII brown, tergite VIII and hypopygium distinctly contrasting light brown to dark brown.
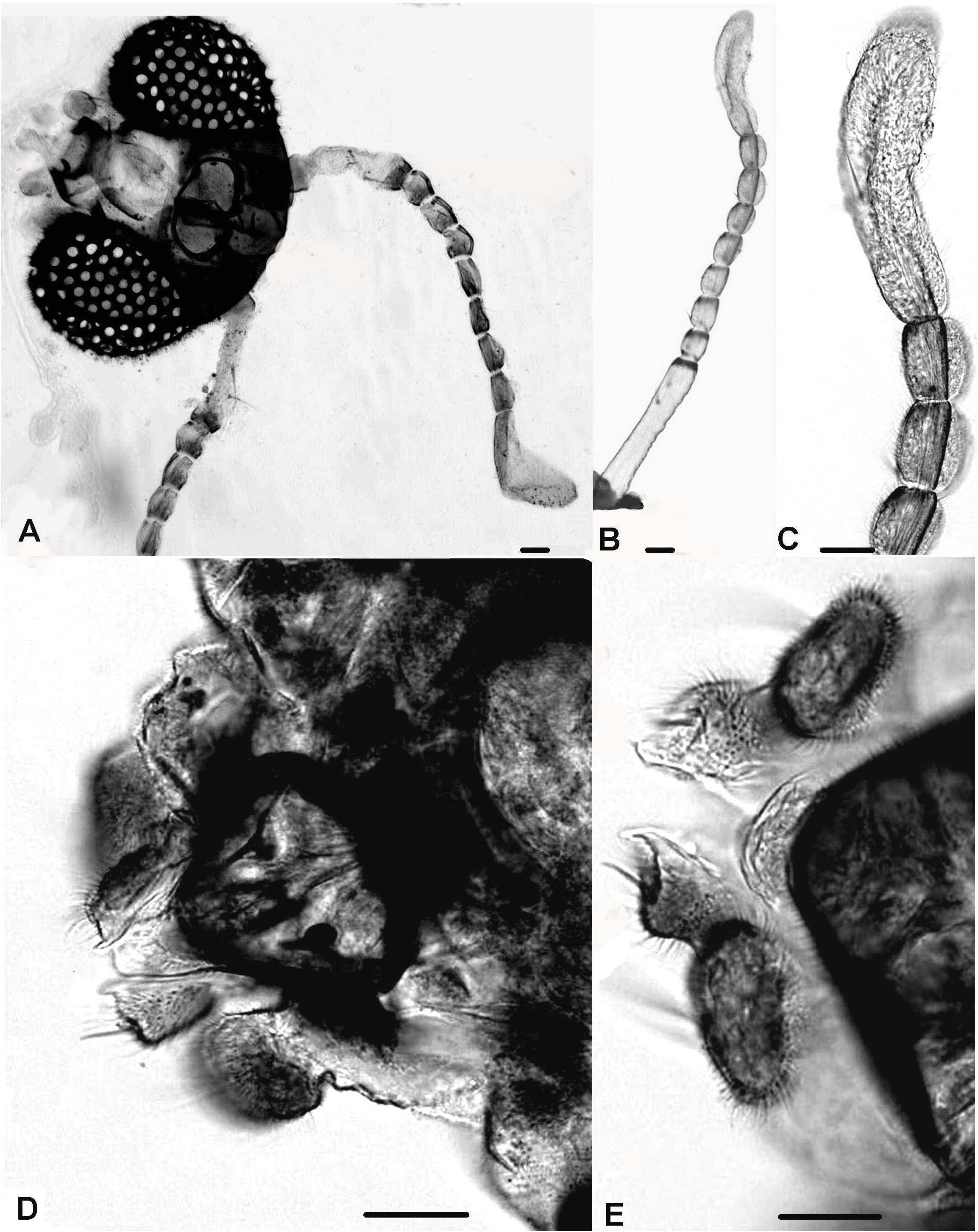
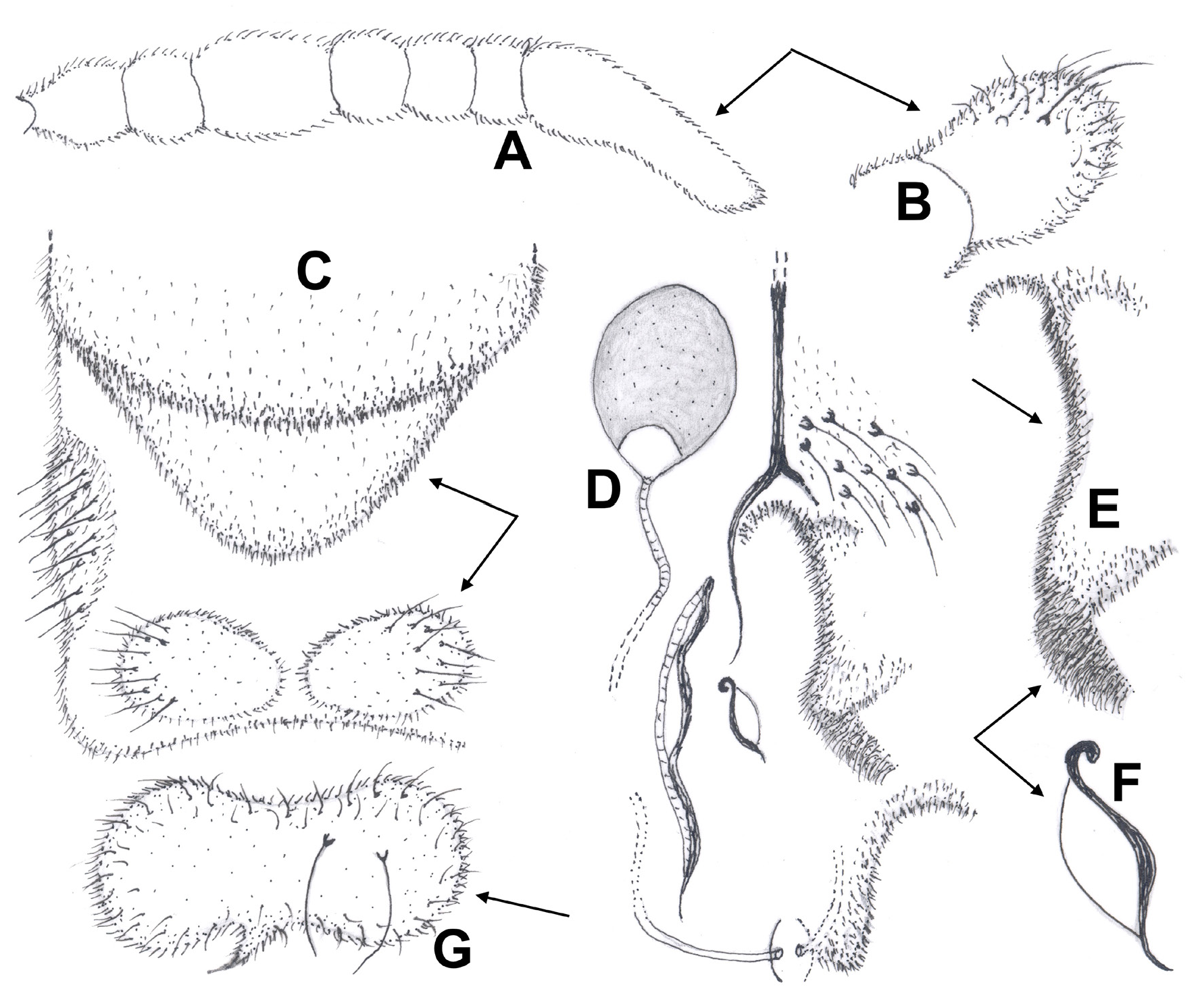
Head ( Figs 1A View Figure 1 , 2 View Figure 2 A-E). Eyes sub-circular without dorsomedian extension, densely hairy with long and short pin-like microtrichiae; microtrichiae absent from inner lateral eye margin, outer posterior margin lacking setae. Frontal area of head ( Figs 1A View Figure 1 , 2A, 2 View Figure 2 D-E) atypically with a straight anterior margin, vertex not projecting; temporals 4 consist of 2 inner and 2 outer verticals, postorbitals absent. Antenna ( Figs 1 View Figure 1 B-C, 2A-C) 10-segmented, about 575-585 µm long, bearing a few short setae located on all segments; pedicels ( Fig. 2A View Figure 2 ) conical (funnel-like) with sclerotized margins, closelyconnected at their base and inserted on the midline of head; segments 1-2 ( Figs 1B View Figure 1 , 2 View Figure 2 A-B), respectively 70 and 165-175 µm long, segment 1 globular with 1 long seta, segment 2 linearly elongated, swollen in its proximal and distal parts, thinner medially, bearing 2 long setae on distal half and 5-6 shorter setae apically; segments 7-9 globular, nearly sub-equal (20-25 µm long), bearing sensilla chaetica; ultimate flagellomere ( Figs 1C View Figure 1 , 2 View Figure 2 B-C) 140-150 µm long, about 35 µm maximum width, as long as the 3 preceding segments, thumb-like, bearing 6-7 long setae; antennal groove reaching segment 2; AR 0.40-0.43. Palp ( Figs 1D View Figure 1 , 2 View Figure 2 D-E) 2-segmented, lacking sensilla clavata; palpomere 2 similarly shaped, sub-circular, about 30 µm long, with 2 long setae (1 dorsal and 1 ventral), inner apical margin projecting and pointed apically. Clypeus semi-circular and bare.
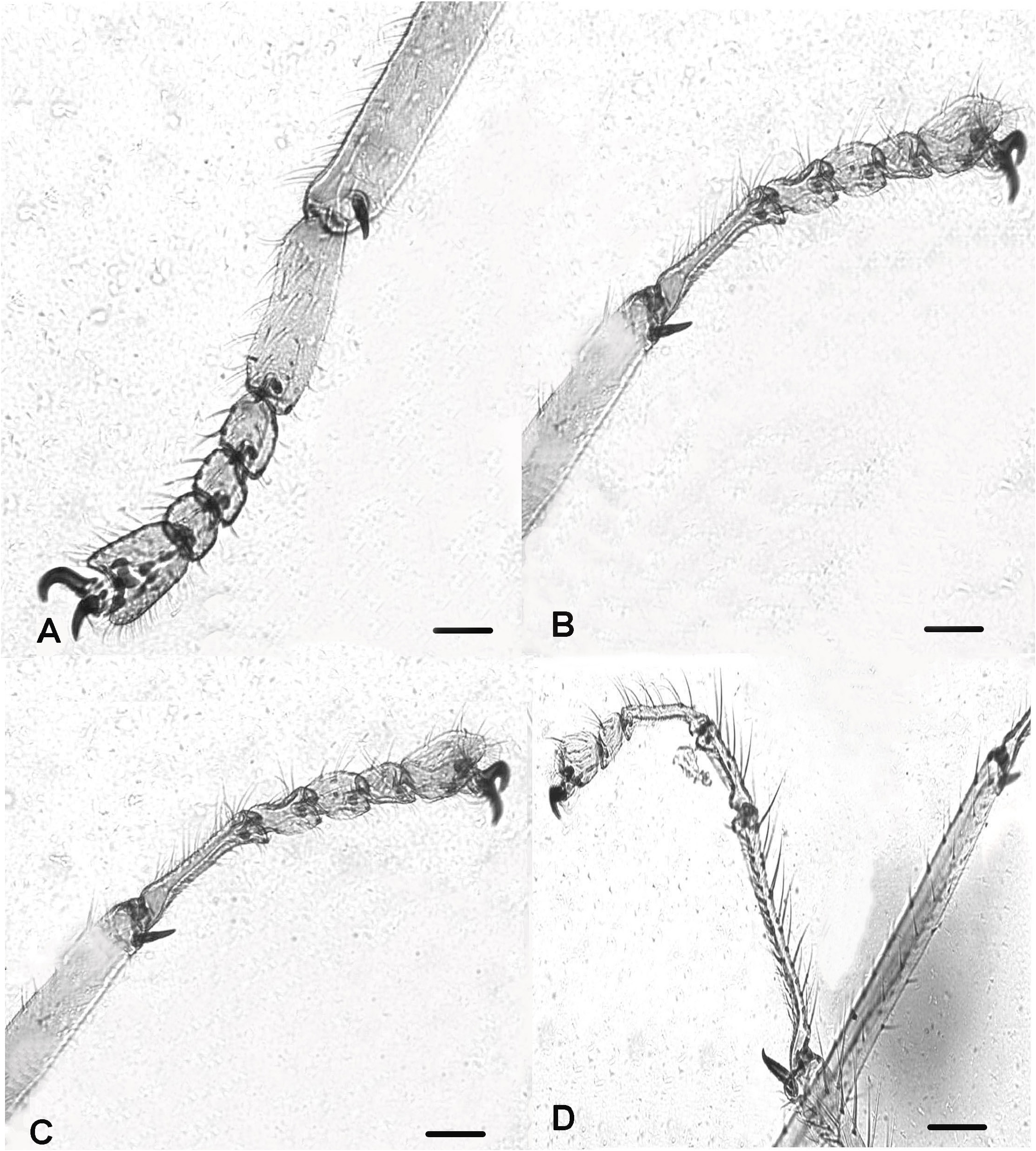
Thorax. Antepronotum well-developed, distinctly domed with joined lobes. Antepronotals absent; acrostichals 2-3 starting close to antepronotum; dorsocentrals 3 in 1 row; prealars absent; scutellum with 6 stout setae located 3 on each side of the midline. Wing. Brachiolum with 1 stout seta; number of setae on veins: R, 4-5; R 1 4-5 located distally; remaining veins and squama bare. Legs ( Figs 3 View Figure 3 A-D). Femur of PI distinctly broad basally (about 180-85 µm maximum width), femur of PII and PIII are narrower (about 50-55 µm). Tibial spurs of third leg curved apically ( Fig. 3C View Figure 3 ); length (in µm) of tibial spurs: PI, 30; PII, 45; PIII, 50 µm long. Tarsomeres ta 3 and ta 4 of PI and PII (35 and 30 µm long) shorter than tarsomere ta 5 (45 and 60), while only tarsomere ta 4 of PIII (45) is shorter than tarsomere ta 5 (70). Tarsomere ta 3 of third leg is long and thin ( Fig. 3C View Figure 3 ). Value of SV ( Table 1 View Table 1 ) of PII and PIII (8.64 and 10.64) is much higher than in PI (4.67). Sensilla chaetica present on tibia and tarsomere ta 1 of PI-PIII, those on tibiae are located apically. Length (µm) and proportions of legs as in Table 1 View Table 1 .
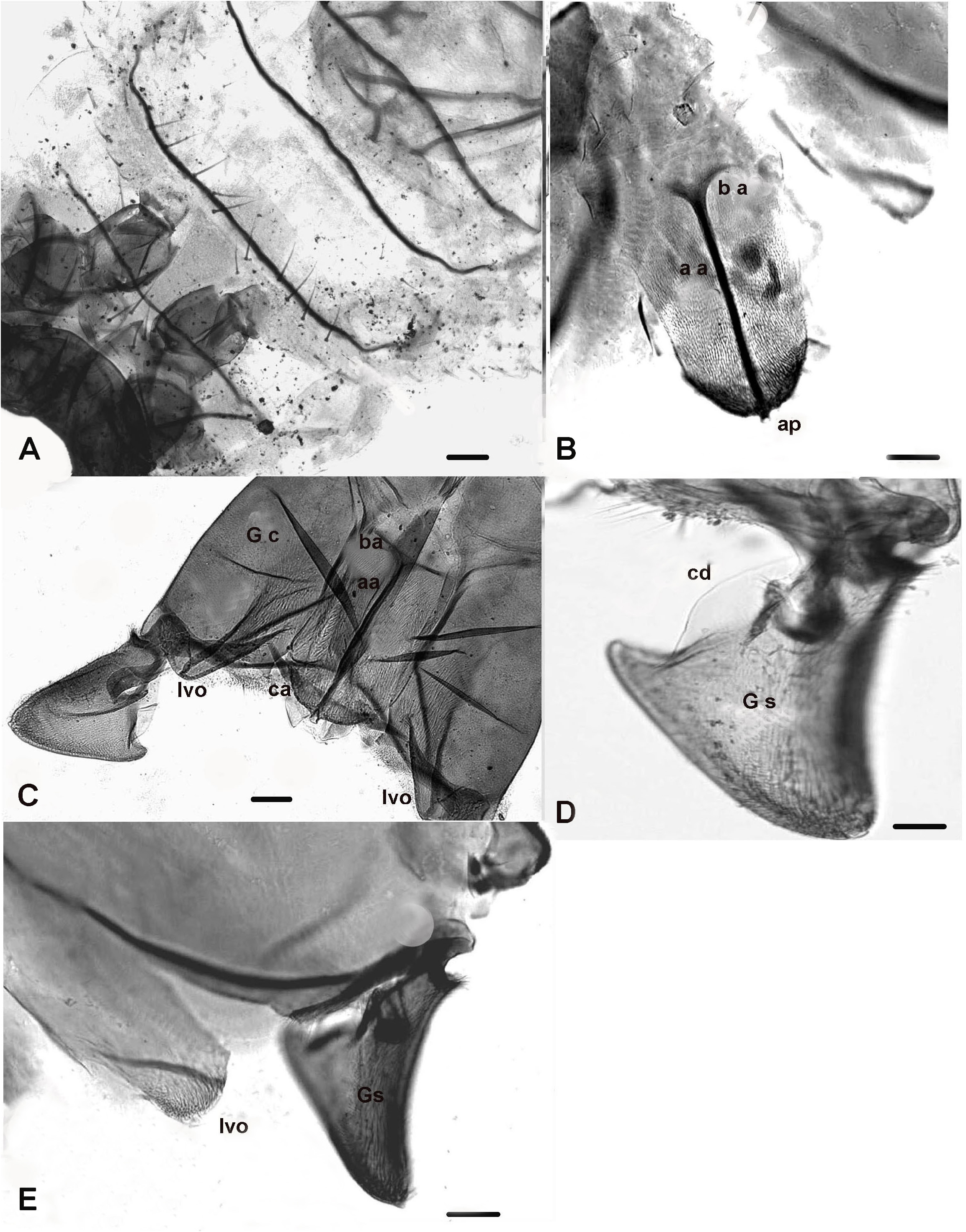
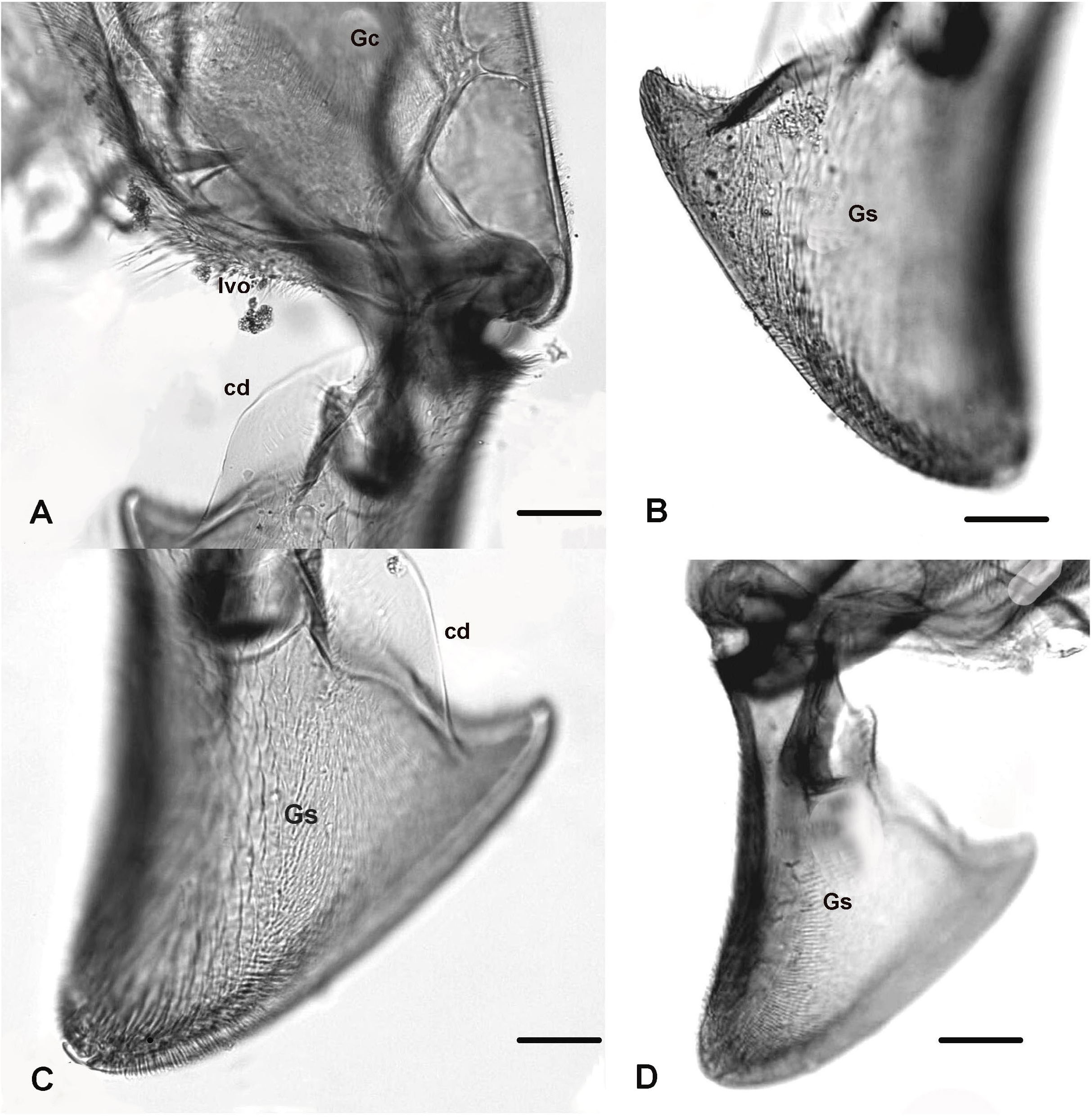
Abdomen and anal segment ( Figs 1 View Figure 1 E-L, 4A-E). Ridge of tergite VIII ( Fig. 1E View Figure 1 ) 70-75 µm long, broad drop-shaped with a slightly narrowing pointed apex; 8 setae are located medially (4 on each side of the caudal part of ridge). Hypopygium in dorsal and ventral view as in Figs 1 View Figure 1 F-L and Figs 4 View Figure 4 B-C; dorsal view ( Figs 1F View Figure 1 , 4 B View Figure 4 ), ventral view with tergite IX omitted ( Figs 1 View Figure 1 H-I, 4C). Tergite IX 265-275 µm long, 200 µm maximum width at base and 100-120 µm at apex, anal point absent; dorsal side ( Figs 1F View Figure 1 , 4B View Figure 4 ) densely covered with macrotrichia-like setae reclinate (orally directed) setae about 35-40 short setae; ventral side ( Figs 1 View Figure 1 H-I) with a semi-circular posterior lamella covered with macrotrichia. Apodemes consist of 4 distinct parts (basal, axial, lateral and caudal): basal apodeme (ba, Figs 1G View Figure 1 , 4 View Figure 4 B-C) about 200 µm maximum width, umbrella-shaped with anterior side convex; axial apodeme (aa, Figs 1 View Figure 1 G-H, 4B-C) about 235-245 µm long, ending with a bi-lobed semi-circular apical expansion; lateral apodeme (la, Figs 1H View Figure 1 , 4C View Figure 4 ) 270-280 µm long, inwardly bent distally to connect with caudal apodeme; caudal apodeme (ca, Figs 1 View Figure 1 H-I, 4C) on each lateral side with 3 long, pointed, spine-like extensions, basal one claw-like with a downwardly curved apex, the two others are upwardly projecting apically. Gonocoxite ( Figs 1F View Figure 1 , 4C, 4E View Figure 4 ) about 420-450 µm long, 160-170 µm maximum width, distal inner area with a dense group of proclinate short setae. Inferior volsella ( Figs 1F View Figure 1 , 4C View Figure 4 ) about 70 µm long in its median part and about 35 µm in its distal half, conical basally and nearly parallel-sided in its distal half, densely covered with short upwardly directed setae. Gonostylus ( Figs 1 View Figure 1 J-L, 4C-E, 5A-D) 240-250 µm long, inverted triangular, much thinner in median and distal parts, arched with rounded posterior angle, antero-lateral end projecting upwards into a pointed anterior apex; basal part with a well-sclerotized tooth, crochet-like and conspicuous, rounded at base and pointed apically; posterior part ( Figs 1 View Figure 1 K-L, 4D, 5C) with 4 pointed teeth (clearly visible when viewed laterally, as in Figs 1 View Figure 1 K-L), posterior one is much longer than the 3 others. Crista dorsalis ( Figs 2J View Figure 2 , 4D View Figure 4 , 5C View Figure 5 ) well-developed, a single wide lobe occupying about 90% of the anterior side; megaseta absent.
Female adult
(n = 3; Figs 6-8 View Figure 6 View Figure 7 View Figure 8 )
Small as in all female Clunio species. Total length 1.55-1.65 mm. General colouration less contrasting than in the male adult; head dark brown with light brown antennae; thorax brownish; legs brown with blackish claws; tergites I-VII brownish, tergite VIII and anal segment distinctly contrasting light brown to dark brown.
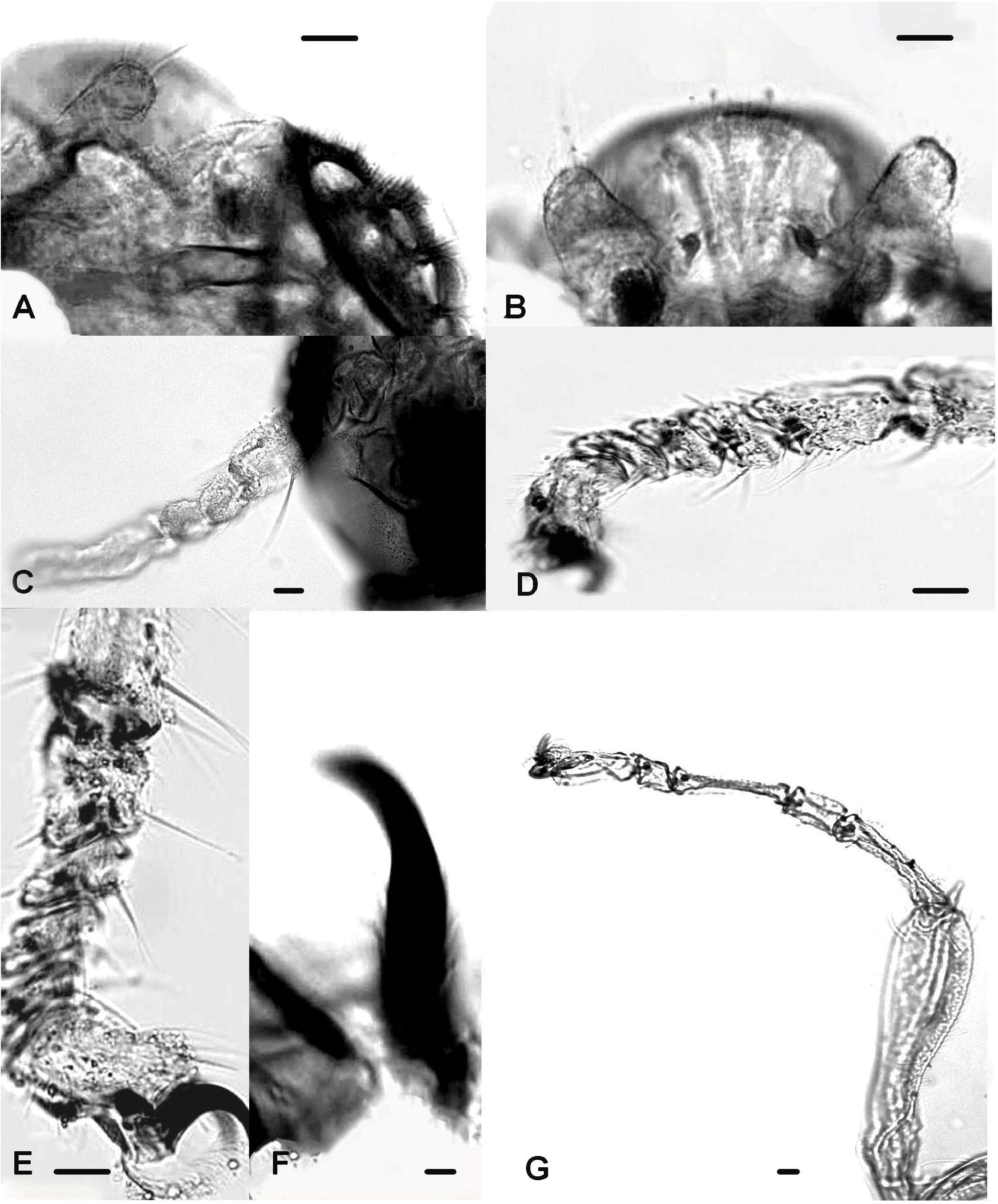
Head ( Figs 6 View Figure 6 A-B, 7A-B). Eyes densely hairy, sub-circular without dorso-median extension, microtrichiae absent from inner and lateral eye margin, outer posterior margin lacking setae. Frontal area straight ( Figs 7 View Figure 7 A-B); temporals 3, including 1 inner and 2 outer verticals. Antenna 7-segmented ( Figs 6A View Figure 6 ; 7C View Figure 7 ), about 190-200 µm long; last flagellomere 55-60 µm long, swollen proximally and nearly parallel-sided in its distal half; antennal groove reaching segment 2; AR 0.45. Palp ( Figs 6B View Figure 6 , 7 View Figure 7 A-B) 2-segmented; segment 1, indistinct; palpomere 2 about 20 µm long, sub-circular to globular, bearing 2 long fine setae.
Thorax. Chaetotaxy indistinct and difficult to observe. Legs ( Figs 7 View Figure 7 D-G). Tibia of PII and PIII nearly equal (115 and 118 µm long); tarsomeres ta 2 -ta 4 of PI and PIII equal in size. Femur of PI is much wider (85 µm) than in PII-PIII (60 and 55); tibia of PIII is wider (50 µm) than in PI and PII (40 µm each); tibial spur ( Fig. 7F View Figure 7 ) strongly curved apically. LR value of PIII (0.54) much higher than in PI and PII (0.28 and 0.25); SV value of PII (9.02) much higher than in PIII (4.32). Few sensilla chaetica present on tibia and tarsomere ta 1 of PI, PII and PIII. Length (in µm) and proportions of legs as in Table 2 View Table 2 .
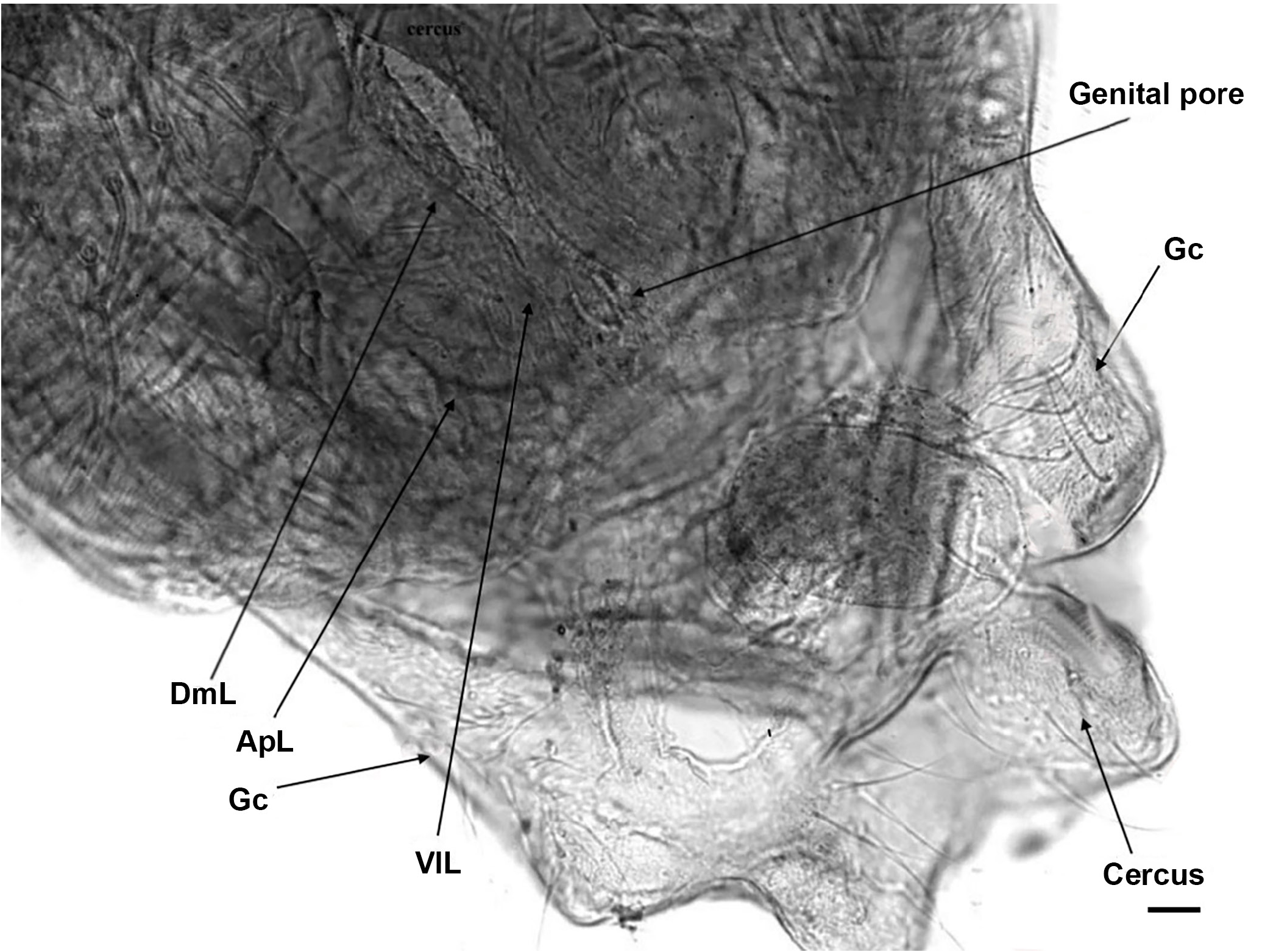
Abdomen. Anal segment ( Fig. 6C View Figure 6 , dorsal; Figs 6D View Figure 6 and 8 View Figure 8 , ventral) about 230 µm long, 210 µm maximum width at base, 110 µm wide at caudal part. Genitalia ( Figs 6 View Figure 6 E-F; 8). Notum about 140 µm long with separate long and sinuous rami, which are almost connected to the sternal axial apodeme. Sternite VIII with 20-22 setae (10-11 on each side of the notum). Gonapophysis VIII ( Figs 6 View Figure 6 D-F, 8). Dorsomesal lobe ( Figs 6 View Figure 6 D-E, 8) concave medially and projecting in both proximal and apical parts; ventrolateral lobe projecting outwards, broader basally and slightly narrowing distally; apodeme lobe ( Fig. 6D View Figure 6 , right; Fig. 6F View Figure 6 , left) distinctly swollen in its median part and thicker distally. Seminal capsules about 60 µm long, 30 µm maximum width, sub-oval, well-sclerotized except for its basal part. Spermathecal ducts with loops and separate openings. Tergite IX ( Figs 6C View Figure 6 , 8 View Figure 8 ) egg-shaped, distinctly divided, with 18-20 setae (9-10 on each side). Gonocoxite ( Figs 6C View Figure 6 , 8 View Figure 8 ) bearing 11-12 setae, weakly prominent, well-developed and widely extended vertically along the lateral margin. Cercus ( Figs 6G View Figure 6 , 8 View Figure 8 ) bean-shaped with sub-equal parts, bearing 2 long dorsal setae located on 1 side.
Pupal exuviae
(n = 3: 1 male exuviae and 2 female pharate adults)
(Male pupal exuviae, Figs 9 View Figure 9 A-E)
Exuvial length 2 mm. Colourless. Frontal apotome rectangular, the free apex truncate. Thorax smooth apart from a small patch of tubercles by suture a little behind middle ( Fig. 9C View Figure 9 ). 4 dorsocentral setae about 50 μm long; setae 1, 2 separated by 25 μm, 2, 3 by 35 μm and 3, 4 by 50 μm (in general, setae on Clunio exuviae are very small; other than the dorsocentrals, neither frontal setae nor abdominal setae have been detected in these specimens). Wing sheath 200 μm long, without nose or pearl row.
Abdominal tergites I-VII ( Figs 9 View Figure 9 A-B) with a continuous anterior transverse band of colourless points; III-VII with a posterior transverse row of small hooks extending the width of the tergite. Sternites unarmed except VIII which has a posterior transverse band of minute points, restricted to the middle half in the male ( Fig. 9A View Figure 9 ), but extending to the lateral margins in the female ( Fig. 9D View Figure 9 ). Anal tergite without lobes, truncate apically and bearing at the postero-lateral corners two strong spines ( Figs 9 View Figure 9 D-E). Female genital sheaths are restricted to a circular patch beneath the anal segment ( Fig. 9D View Figure 9 ), whereas those of the male are massive, far exceeding the anal segment both laterally and posteriorly, parallel-sided for the anterior half, thence narrowed inwards to a papillate point ( Fig. 9E View Figure 9 ).
| JM |
Jura Museum, Eichstatt |
| PM |
Pratt Museum |
| ZSM |
Bavarian State Collection of Zoology |
| R |
Departamento de Geologia, Universidad de Chile |
| PI |
Paleontological Institute |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |