Phyllospadix torreyi (Zapata and McMillan, 1979)
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113256 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8257557 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/A2143D69-FFED-FFD7-FFDF-FD765EADF814 |
|
treatment provided by |
Felipe |
|
scientific name |
Phyllospadix torreyi |
| status |
|
2.4. Biological potential of the P. torreyi phenolic content - evaluation of
P. torreyi View in CoL View at ENA beach cast detritus as a renewable source of bioactive compounds
Plant specialized metabolites are economically important in the field of food additives, nutraceuticals, and drugs. This is especially the case for phenolic acids and flavonoids, which possess a broad spectrum of pharmacological properties. Additionally, sulfated flavonoids have the advantage of being more water-soluble than their aglycones, which is an interesting property for therapeutic applications. Flavonoid sulfates are now recognized as potential candidates for the development of new drugs and some lead compounds are emerging mainly as anticoagulant and antiviral agents (see as examples: Martins et al., 2019; Teles et al., 2018).
The antiviral activity of luteolin 7, 3 ′ -disulfate has been demonstrated using in vivo experimental model of tick-borne encephalitis ( Krylova et al., 2011). Luteolin 7, 3 ′ -disulfate also exhibits antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemia effects, as well as antioxidant, cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, antitumoral and antiviral actions ( Styshova et al., 2017). Luteolin 7-sulfate was shown to inhibit cellular melanin synthesis ( Kwak et al., 2016; Lee et al., 2019). Luteolin-7-sulfate is also a nontoxic repellent, able to prevent bacterial settlement ( Papazian et al., 2019).
5-Methoxyluteolin exhibited a good antioxidant activity in DPPH and CUPRAC assays and a low cytotoxicity against 4T1 breast carcinoma cell line ( Rafieian-Kopaei et al., 2020). Different extracts of Plectranthus species containing 5-methoxyluteolin showed antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, diuretic, cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities with variable potency ( El-Hawary et al., 2012). Schistosomicidal activity of 5-methoxyluteolin was also reported. Schistosomiasis, which is caused by trematode flatworms of the genus Schistosoma , is one of the most significant and neglected tropical diseases in the world ( Pimenta et al., 2015).
Nepetin has been widely used for centuries to treat fever, malaria, infections and diseases associated with inflammation ( Lee et al., 2016). Nepetin also exhibited cytotoxic activity against five tumor cell lines ( Milit˜ao et al., 2004), and strongly protected primary cultured neurons against glutamate-induced oxidative stress ( Kim et al., 2002). In recent years, nepetin was reported to exhibit anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and anti-tumor cell proliferation effects (see as example Chen et al., 2020 and references therein). Strong antiproliferative activity against different cell lines was also observed with nepetin ( Talib et al., 2012). In the case of luteolin, it has been shown that the 7,3 ′ -disulfate has a lower toxic potential than the non-sulfated form and that the efficacy of its pharmacological action may therefore be increased ( Styshova et al., 2017). On this basis, the two unreported disulfates of nepetin and of 5-methoxyluteolin described here could constitute potential candidates in the search of new drugs.
A strong antiproliferative activity against different cell lines was observed for hispidulin ( Talib et al., 2012). Hispidulin also suppress angiogenesis and growth of human pancreatic cancer ( He et al., 2011) and potently inhibits human glioblastoma multiform cells ( Lin et al., 2010). Jaceosidin was identified as a strong antimutagen ( Nakasugi et al., 2000), and a putative oncogene inhibitor which might be used as a potential drug for the treatment of cervical cancers associated with the human papillomavirus ( Lee et al., 2005). As mentioned above, it could be of interest to evaluate their respective 7-monosulfate.
Rosmarinic acid is a bioactive phytochemical, which possesses remarkable pharmacological activities, including antioxidant, antisettlement, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antibacterial, antidepressant, anticarcionogenic, nematicidal, and chemopreventive properties. Rosmarinic acid also has significant antinociceptive, neuroprotective, and neuroregenerative effects ( Amoah et al., 2016; Noor et al., 2022; Styshova et al., 2017). In addition, rosmarinic acid is able to prevent bacterial settlement in marine environment ( Papazian et al., 2019).
Given the economic potential of the phenolic content of P. torreyi , it seemed worthwhile to assess the accumulated detrital stocks on beaches. The production of Torrey’ s surfgrass is very high with an average maximum biomass estimated at 586 g dw m 2 day 1 (shoot) and 486 g dw m 2 day 1 (rhizome) ( Les, 2020). Physical events and natural seasonal leaf drop result in large accumulations of detritus along the wave-exposed sandy beaches in southern California. Seagrasses are much more resistant to decomposition than are freshwater angiosperms or algae. The rate of decomposition of seagrass detritus is generally low ( < 1% of dry wt/day) compared with other sources of detritus ( Mews et al., 2006). We have previously shown in the case of Zostera spp and Cymodoceaceae members that significant concentrations of phenolic compounds remain in the detrital leaves ( Achamlale et al., 2009; Grignon-Dubois and Rezzonico, 2017).
Seagrass beds have been shown to be one of the most efficient ecosystems for carbon sequestration. However, if disturbed or degraded, they can release carbon into the environment and accelerate the rate of global climate change ( Macreadie et al., 2014). Seagrass wracks also have an important ecological value and provide important ecosystem services (see as example: Nordstrom et al., 2011). However, wrack piles can also release CO 2 and CH 4 during the decomposition process and thus become a significant source of greenhouse emissions. In addition, stranded litter can significantly reduce local tourism income and local managers are under strong public pressure to remove seagrass wracks when they accumulate along beaches and shorelines used for recreational purposes. The negative impact on the tourism industry in the affected areas results in costly beach cleanup and disposal processes. In most cases, the collected biomass is disposed of in landfills.
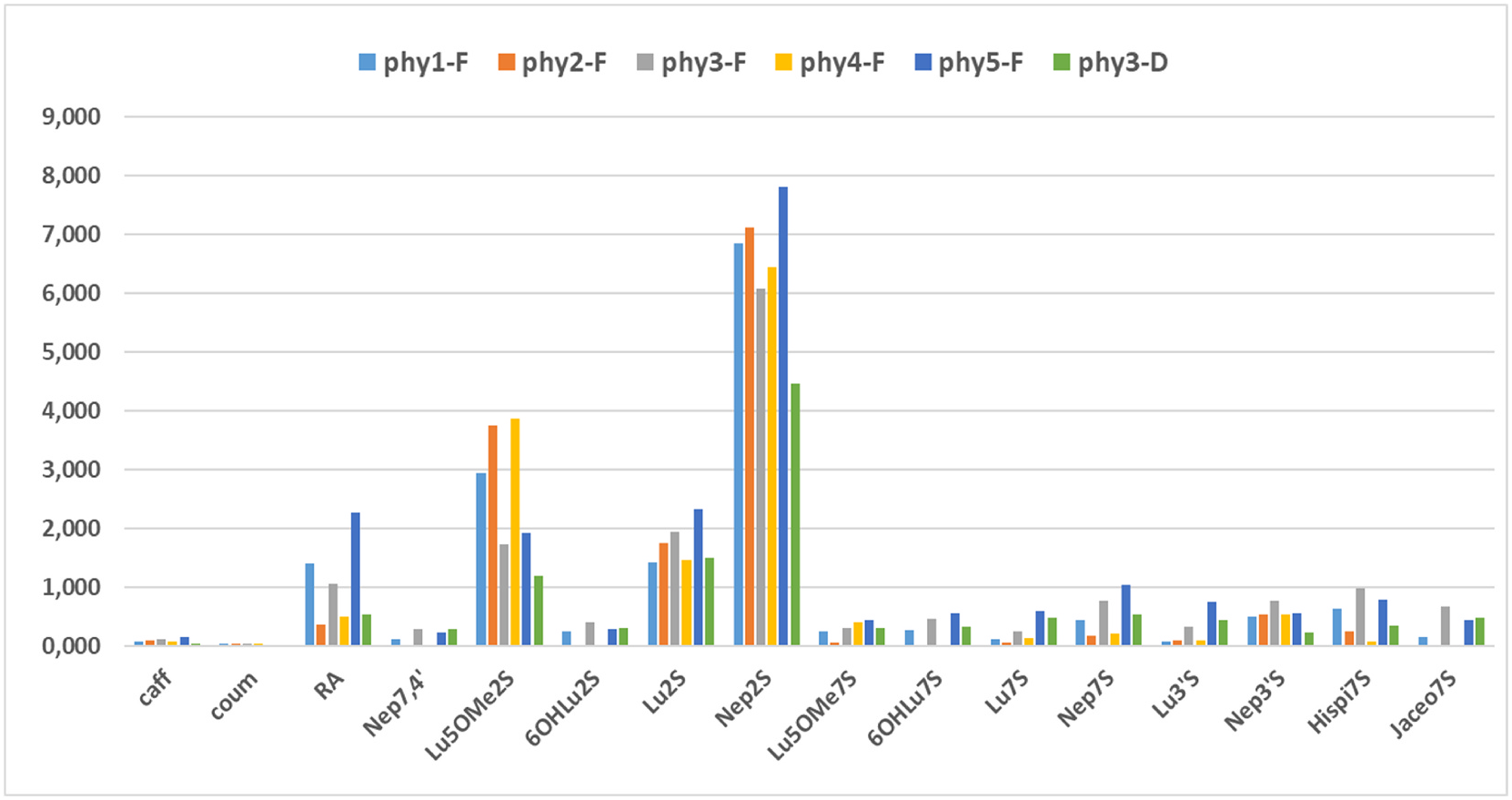
Phyllospadix wracks are resistant to decomposition ( Mews et al., 2006), and answers may come from flotsam recycling. Compared to algae, seagrasses remain largely unexploited as a raw material for the production of bioactive compounds, despite the fact that they offer enormous opportunities to find phytochemicals of commercial value. A detrital sample was collected from plant materials deposited on the shoreline, between La Jolla Underwater Park (+ 32.8528 N; 117.2614 W) and Ellen Browning Scripps memorial pier ( 32.8662 N; 117.2614 W). It was collected at the same time as the fresh sample Phy3-F, and was referenced as Phy3-D ( Table 1). An aqueous-methanolic extract (50% v/v) was prepared in the same conditions used for fresh samples and analyzed by quantitative HPLC. Its chromatographic profile was found to be similar to that of Phy3-F and the concentrations of the individual, although lower than in the fresh material, remain significant ( Table 1, Fig. 4 View Fig ). Nepetin 7, 3 ′ -disulfate remains the major product ( 7, 4.46 mg g 1), followed by luteolin 7, 3 ′ -disulfate ( 6, 1.49 mg g 1), and 5-methoxyluteolin 7, 3 ′ -disulfate ( 3, 1.19 mg g 1). The rosmarinic acid content also remains significant ( 10, 0.54 mg g 1). The significant amounts of disulfates in Phyllospadix detritus are particularly interesting given the broad spectrum of biological properties of nepetin and luteolin derivatives. These results make this abundant detrital biomass interesting for dietary and pharmaceutical applications.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |