Malthopsis formosa, Ho & Koeda, 2019
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4702.1.12 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:BE56EC81-D523-4C7D-AD89-9260DB619C58 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/D972E029-5385-4B7F-9C32-182A86D9A02C |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:D972E029-5385-4B7F-9C32-182A86D9A02C |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Malthopsis formosa |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Malthopsis formosa sp. nov.
New English name: Taiwanese triangular batfish
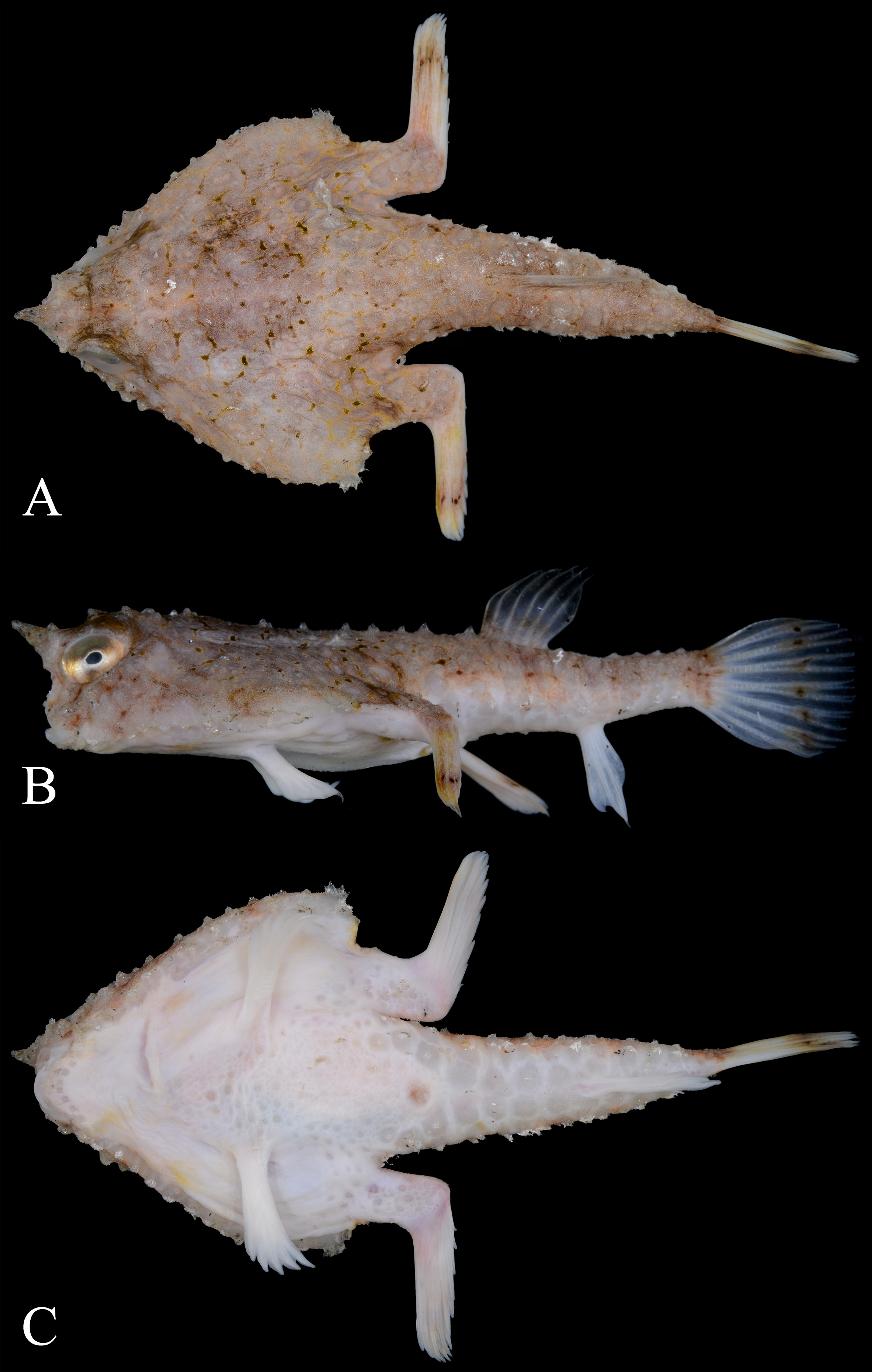
Figures 1–4 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 ; Table 1 View TABLE 1
Malthopsis tiarella View in CoL (not of Jordan, 1902): Ho & Shao 2008:308, fig. 14 (in part; figure provided is present species). Ho & Shao, 2010b:fig. 6 (same figure of preceding one).
Holotype. NMMB-P27866 ( 50.8 mm SL), off Dong-gang , Pingtung, southwestern Taiwan, northern South China Sea (collected at a landing area), bottom trawl, 14 Dec. 2017, coll. K. Koeda.
Paratypes. Eight specimens, 39.1–48.0 mm SL . NMMB-P22009 (1, 44.2), 31 Dec. 2013 ; NMMB-P25410 (1, 39.1), 6 Nov. 2015 ; NMMB-P26656 (1. 48.0), 1 Oct. 2017 ; NMMB-P27777 (1, 47.3), 15 Nov. 2017 ; NMMB- P28475 (1, 44.4), 8 Nov. 2013 ; all collected from off Dong-gang near the type locality by H.-C Ho . NMMB-P23809 (1, 40.8), 21 Jan. 2015 ; NMMB-P26435 (1, 46.4, stained), 18 Jun. 2017 ; NMMB-P28476 (1, 39.4), 21 Jan. 2015 ; all collected from off Ke-tzu-liao, Kaohsiung, southwestern Taiwan by H.-C. Ho .
Diagnosis. A species of Malthopsis with numerous small prickle-like bucklers on ventral surface, and distinguished from other congeners in having the following combination of characters: dorsal-fin rays 5; pectoral-fin rays 11–12; rostral spine directed forward horizontally; principal bucklers on dorsal surface relatively low, few in number and scattered in arrangement; body densely covered by small prickle-like bucklers; head length 27.1–29.1% SL; posterior tip of appressed anal fin not reaching caudal-fin base.
Description. Morphometric and meristic data are provided in Table 1 View TABLE 1 .
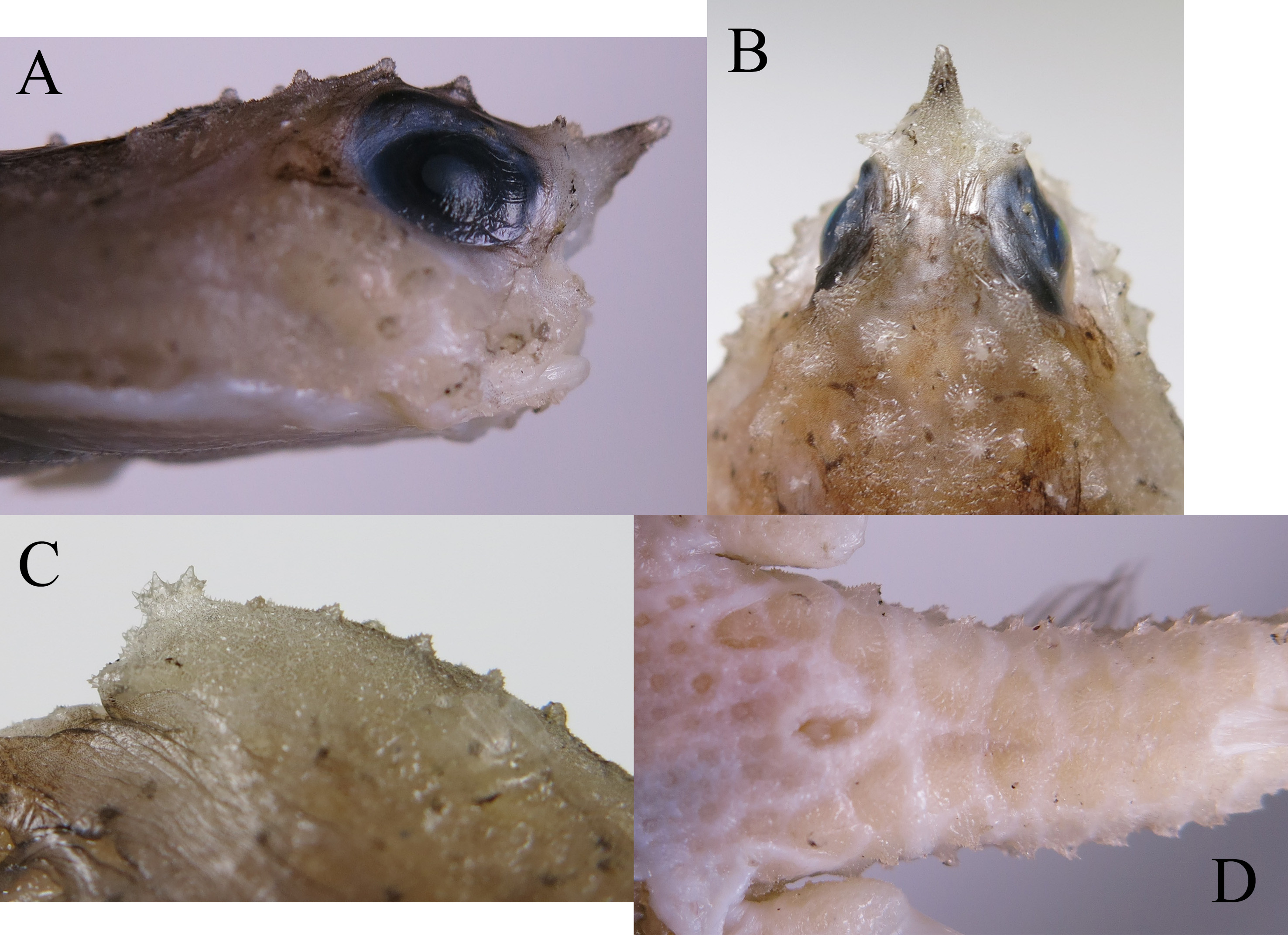
Body depressed, disk markedly triangular in dorsal view, cranium elevated above general surface of other parts of disk; caudal peduncle cylindrical, tapering posteriorly; rostrum small, its base moderately wide of genus, terminal spine conical, directed forward horizontally ( Fig. 4A View FIGURE 4 ), distinctly overhanging illicial cavity and beyond the mouth; rostrum relatively short, eye diameter/rostral length 1.9 ( 1.4–1.7 in paratypes); eye relatively small, its diameter 12.6% SL (12.7%–14.0% SL), directed dorsolaterally; no pupillary operculum; interorbital space moderately wide, its width 6.8% (5.9–8.1% SL), shallowly concave ( Fig. 4B View FIGURE 4 ); illicial cavity a small rounded cave, relatively broad in outline, about as wide as high; esca a single oval bulb, bearing 2 small cirri on dorsal margin; mouth small, terminal; small villiform teeth on jaws forming narrow bands, those on fifth ceratobranchial forming 2 large and elongated patches close together, and teeth on vomer and palatines in quadrangular patch.
Scales on body surface in the form of bucklers, moderately low and pointed ( Fig. 3 View FIGURE 3 ), mostly associated with lateral line, skeleton and body edge; small prickle-like bucklers densely covered on body surface among principal bucklers, except for eyes and fins. Each side of frontal ridge with 5 (5–6) bucklers, the first two situated at antero- lateral corner of orbit; the second pair direct outward, and with the rostral spine forming a trident; last two bucklers relatively large in size. A pair of bucklers on dorsal surface of base of rostrum. Skin above eye with many small bucklers ( Fig. 4A View FIGURE 4 ).
Dorsal surface of skull with four or five moderately large pointed bucklers, not arranged in regular rows ( Fig. 4B View FIGURE 4 ); followed by a median widely-spaced, irregular row of smaller bucklers at postcephalic region; numerous small prickle-like bucklers densely cover dorsal surface of disk, except for small naked areas around pectoral-fin base. Ventral surface of disk with several relatively large bucklers (mainly in front of inter-pelvic space) and elsewhere densely covered by numerous small prickle-like bucklers, except for narrow naked areas on outer portion of gill chamber; buckler of subopercular dull, bearing few spinelets, none especially enlarged; two flat, triangular bucklers with several spinelets on post-subopercular margin ( Figs. 4C, D View FIGURE 4 ); caudal peduncle covered by moderately large bucklers, those on dorsal surface forming 5 irregular, scattered rows, 1 median row behind dorsal fin, 2 rows on each side of dorsal fin, 2 rows on each lateral side associated with lateral line; bucklers on ventral surface of caudal peduncle forming 2 regular rows between anus and anal fin, relatively flattened; 1 buckler (some paratypes with 2) on each side of posterior portion of anus, these not larger than neighboring ones ( Fig. 4E View FIGURE 4 ).
All fins naked, without bucklers, except for some small ones running out along base of caudal fin rays; interradials of pectoral fins thin, transparent; dermal cirri flap-like, present on disk margin and lateral sides of tail associated with lateral line scales.
Coloration. When fresh ( Figs. 1–2 View FIGURE 1 View FIGURE 2 ), body background uniformly grayish; ventral surface of disk pale, that of caudal peduncle grayish; dorsal surface with irregular blackish stain marks or spots on central region; irregular black patches on dorsal surface of head in some paratypes; anterior portion of rostral spine surrounded by a blackish ring; indistinct broad dark band across dorsal-fin base in holotype and a few paratypes, absent in the others; base and posterior third of caudal fin blackish; outer third of pectoral fin with a narrow band; dorsal fin blackish; anal-fin base blackish (uniformly pale in some paratypes). When preserved, the blackish marks become darker. Peritoneal membrane white with tiny black dots.
Size. Apparently a small species with adult size slightly over 50 mm SL.
Etymology. The specific name is derived from Formosa, meaning beautiful in Portuguese, and an old name for Taiwan.
Distribution. Known only from the type series collected from off southwestern Taiwan; rarely seen in bycatch of bottom trawlers.
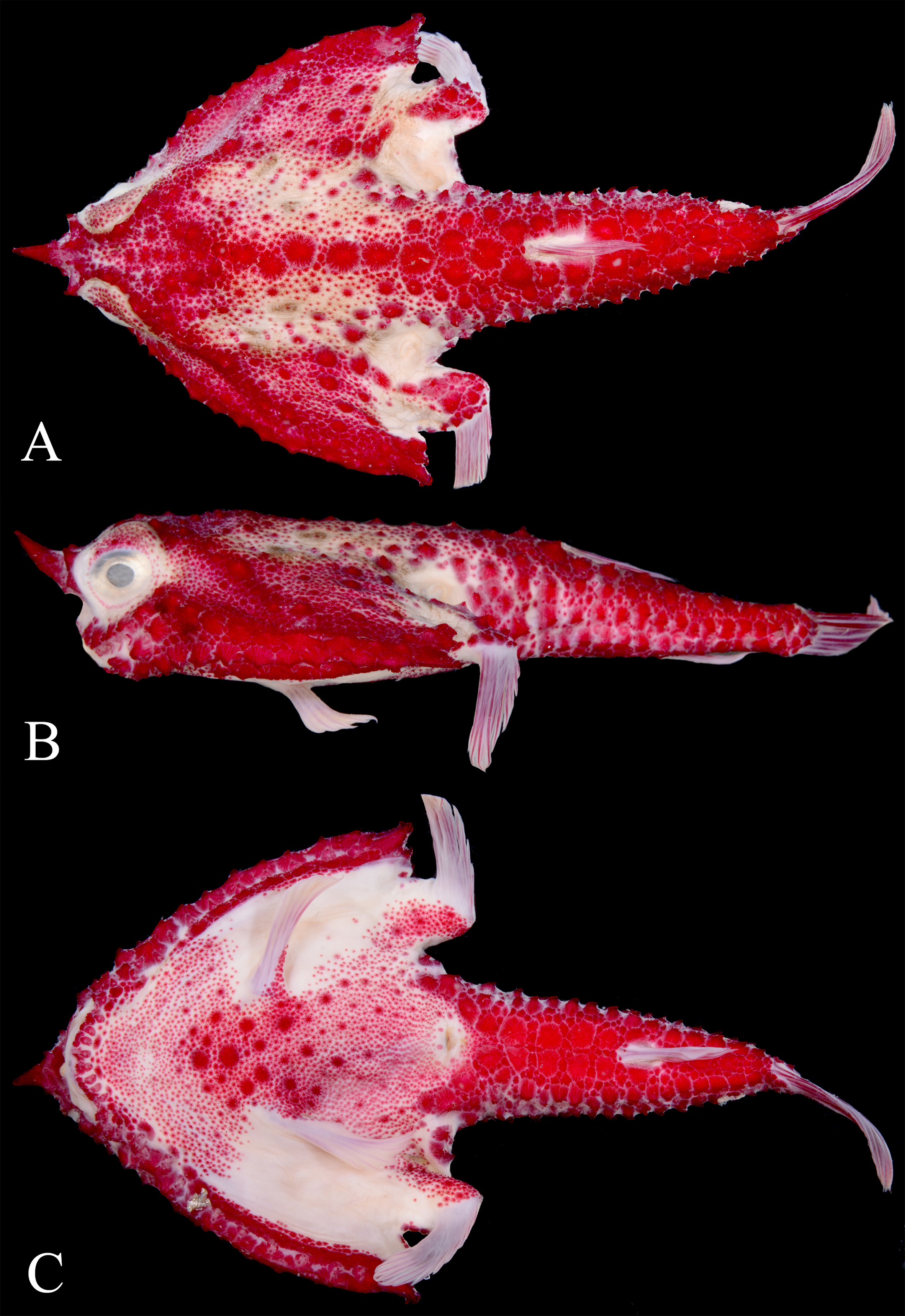
Comparison. Malthopsis formosa is similar to Malthopsis tiarella ( Figs. 5–7 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 View FIGURE 7 ) and M. kobayashii ( Figs. 8–9 View FIGURE 8 View FIGURE 9 ) in squamation and coloration. However, these three species differ from each other in several ways. Malthopsis tiarella has a naked interorbital space, membrane above eye with a single row of a few bucklers (naked elsewhere), large naked areas on throat and outer surface of gill chamber, compared with more numerous small prickle-like bucklers in these areas in two other species. Moreover, the relatively more fin rays (6 or 7 in dorsal fin and 13 or 14 in pectoral fin) can also separate it from two other species.
Both M. formosa and M. kobayashii have 5 dorsal-fin rays (rarely 4 or 6 in M. kobayashii ), 11 or 12 pectoral-fin rays, and uniformly grayish dorsal surface with some irregular blackish spots at central portion of disk. Malthopsis formosa differs from M. kobayashii in having the rostral spine directed forward horizontally (vs. rather upward; Figs. 8B View FIGURE 8 , 9A View FIGURE 9 ); body loosely covered with principal bucklers (vs. densely and heavily covered with bucklers; Figs. 8A, B View FIGURE 8 ); most of ventral surface densely covered with small prickle-like bucklers, except for narrow naked areas on outer gill chamber (vs. large naked areas on outer region of gill chamber; Fig. 8C View FIGURE 8 ); 1 (sometimes 2) buckler on each side of posterior portion of anus (vs. 3 or 4 bucklers on same region; Fig. 8C View FIGURE 8 ).
TABLE 1. Morphometrics and meristics data of three species of genus Malthopsis recognized from Taiwan. Pectoral-fin rays are counted on both sides.
| M. formosa sp. nov. | M. tiarella | M. kobayashii | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Holotype | All types | NMMB- P28508 | NMMB- P03366 | Non-types | |
| SL | 50.8 | 39.1–50.8 (n=9) | 50.9 | 33.3 | 53.0–63.0 (n=5) |
| (% SL) | Mean (Range) | ||||
| Skull length | 27.8 | 28.1 (27.1–29.1) | 29.5 | 32.0 | 27.0 (25.9–27.8) |
| Head width | 22.8 | 22.9 (21.3–23.5) | 23.0 | 25.0 | 22.4 (21.1–24.3) |
| Head depth | 22.6 | 22.0 (20.3–23.4) | 23.6 | 21.9 | 23.7 (21.1–26.9) |
| Eye diameter (ED) | 12.6 | 13.2 (12.6–14.0) | 13.4 | 15.7 | 13.5 (11.6–14.3) |
| Interorbital width (IO) | 6.8 | 7.0 (5.9–8.1) | 6.5 | 6.7 | 6.7 (6.3–7.0) |
| Rostal length (RL) | 6.7 | 8.4 (6.7–9.6) | 6.9 | 7.5 | 8.5 (7.3–9.7) |
| Illicial cavity width | 5.1 | 5.0 (3.7–5.7) | 13.7 | 4.5 | 5.5 (5.1–6.2) |
| Mouth width | 14.1 | 13.6 (12.9–14.2) | 12.1 | 14.5 | 13.7 (12.1–15.5) |
| Predosal length | 66.9 | 66.2 (64.1–68.2) | 66.0 | 69.8 | 64.7 (63.3–67.2) |
| Postanus length | 56.7 | 54.6 (52.2–57.1) | 58.0 | 59.6 | 54.1 (52.6–54.8) |
| Preanal length | 79.9 | 80.3 (78.4–84.3) | 81.1 | 84.9 | 78.5 (76.8–79.4) |
| Disk margin length | 43.6 | 43.3 (42.2–44.9) | 43.0 | 44.9 | 42.7 (40.1–46.8) |
| Pectoral fin length | 23.8 | 23.2 (19.3–25.7) | 22.8 | 28.8 | 22.3 (21.2–22.9) |
| Anal fin length | 21.1 | 17.9 (14.7–21.1) | 18.1 | 21.9 | 17.1 (16.4–17.7) |
| Dorsal fin length | 17.6 | 17.3 (14.9–19.0) | 20.0 | 23.7 | 17.0 (16.4–17.9) |
| Caudal fin length | 25.2 | 26.8 (24.1–28.9) | 25.3 | 31.5 | 24.0 (18.1–26.4) |
| ED/RL ration | 1.9 | 1.6 (1.4–1.9) | 1.9 | 2.1 | 1.6 (1.2–2.0) |
| ED/IO ration | 1.9 | 1.9 (1.7–2.3) | 2.1 | 2.4 | 2.0 (1.7–2.2) |
| Meristics | Frequency | ||||
| Dorsal-fin rays | 5 | 4 (1), 5 (8) | 7 | 6 | 5 |
| Pectoral-fin rays | 11;11 | 11 (6), 12 (12) | 13;13 | 13;14 | 12 |
| Anal-fin rays | 4 | 3 (2), 4 (7) | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Caudal-fin rays | 9 | 9 (9) | 9 | 9 | 9 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |