Rosapha brevispinosa, Kovac, Damir & Rozkošný, Rudolf, 2012
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.3333.1.1 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5911613 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/AA699C29-8F2B-FFF2-5AA4-FCAAFC450E16 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Rosapha brevispinosa |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Rosapha brevispinosa View in CoL sp. nov.
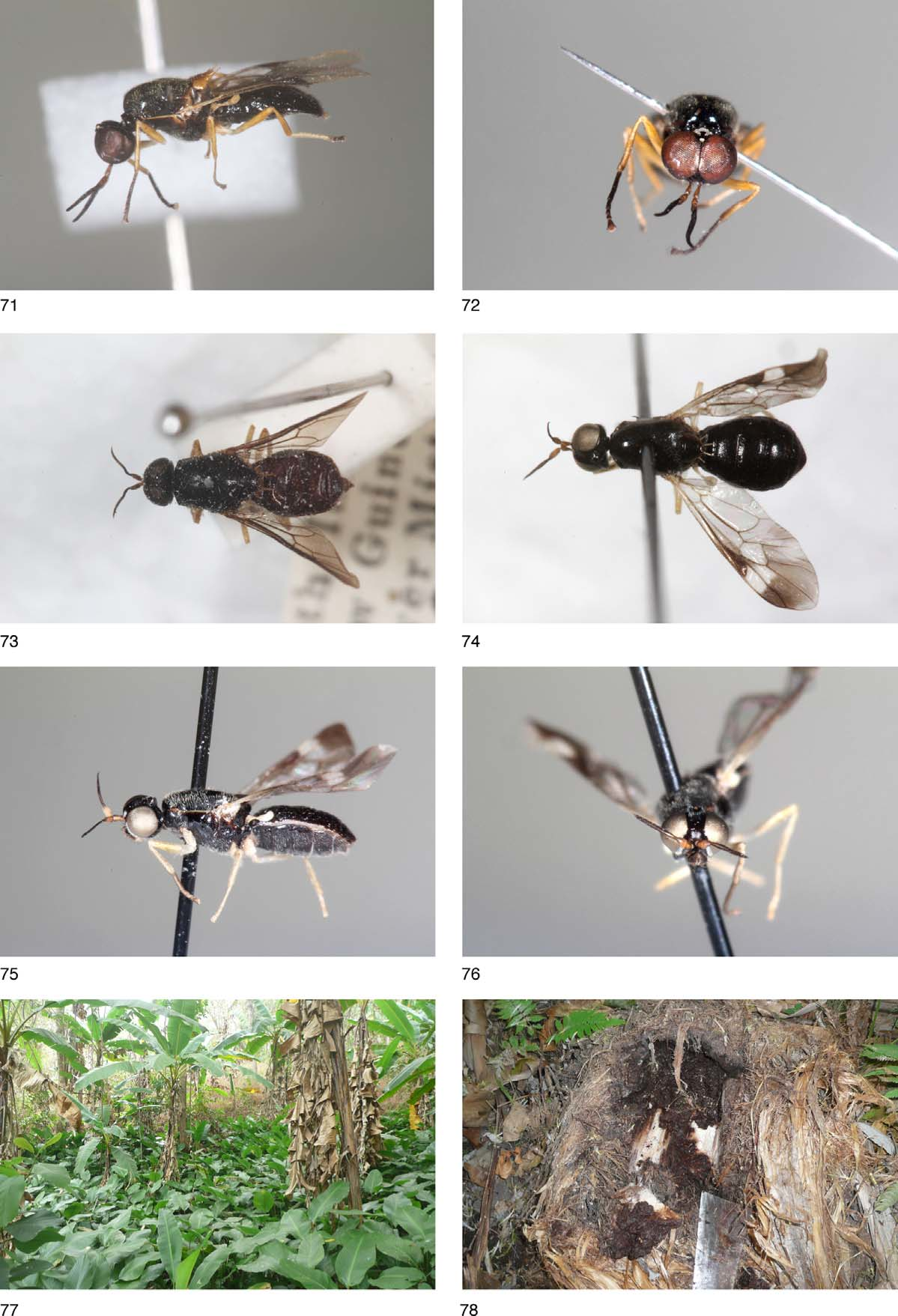
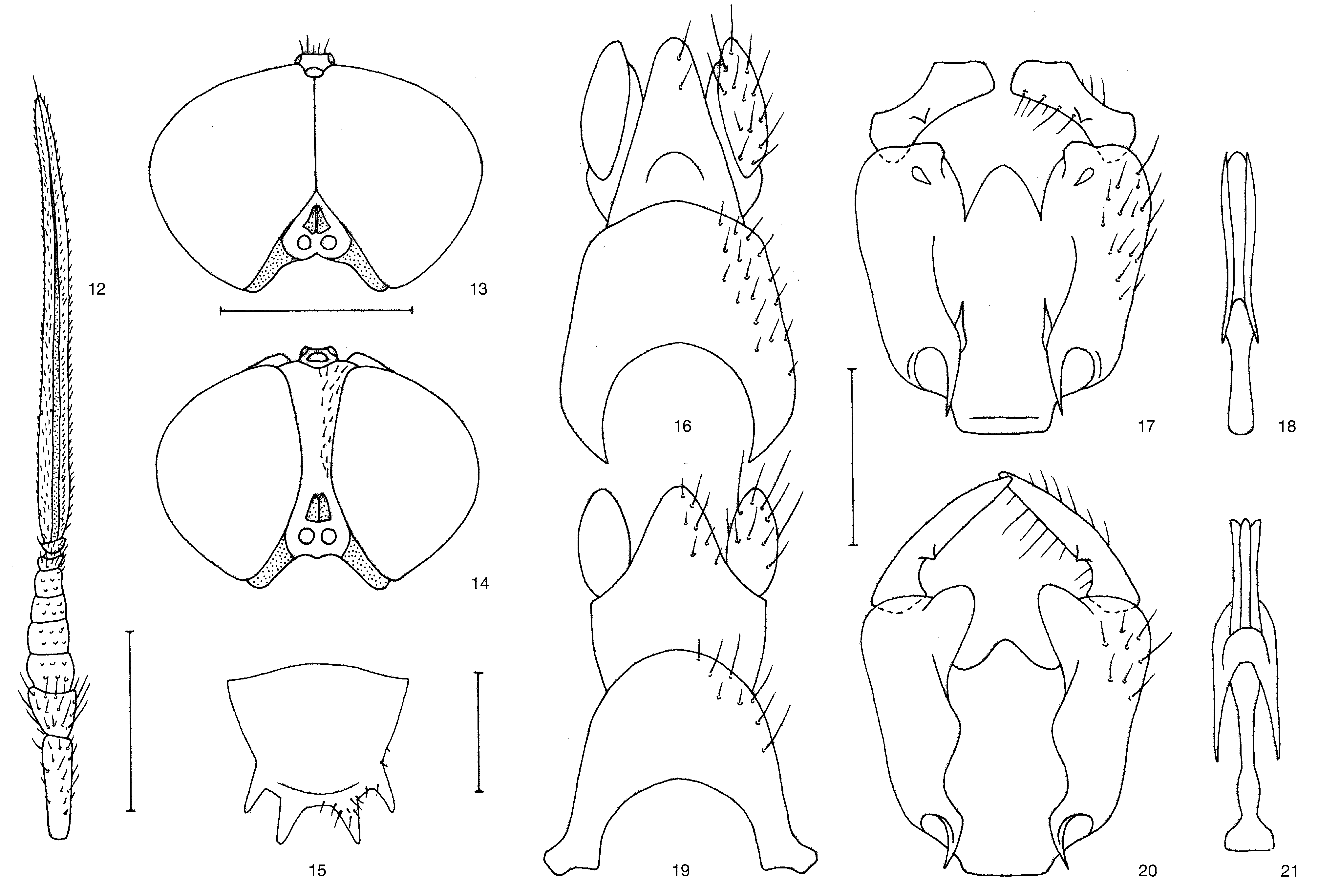
( Figs 8–15 View FIGURES 1 – 11 View FIGURES 12 – 21 , 57–59 View FIGURES 55 – 62 , 80 View FIGURE 80 )
Diagnosis. Last flagellomere flattened, band-shaped, frontal tomentose spot well developed, in the form of a narrow, high triangle with fine dark midline. This spot well separated from eye margins and not fused with whitish facial stripes. Scutellar spines about as long as half length of scutellum. Wing completely and intensively brown infuscated, halter blackish. Legs yellow, only 1–4 apical tarsomeres darkened, abdomen black.
Description. Male ( Figs 8–15 View FIGURES 1 – 11 View FIGURES 12 – 21 ). Length: body 6.8–7.4 mm, wing 7.2–7.4 mm. Head ( Fig. 13 View FIGURES 12 – 21 ) almost hemispherical in lateral view, about 1.4 times higher than long and transversely broadened, about 1.4 times as broad as long. Ocellar triangle at posterior margin of head, upper frons subtriangular, as broad as anterior ocellus and slightly shorter than ocellar triangle. Lower frons subtriangular, with narrow and medially finely divided whitish tomentose spot being well separated from eye margins. Antenna ( Fig. 12 View FIGURES 12 – 21 ) reddish yellow with three apical flagellomeres black, thickened basal complex of flagellomeres slender, subconical, last flagellomere flattened, band-shaped, 1.5 times longer than rest of antenna and slightly narrower than scape, short and densely black pilose on entire surface, pointed apically, with short apical seta. Facial whitish tomentose stripes along eyes margin confluent with pile covering entire concave face below antennae but well separated from supra-antennal frontal spot. Black erect hairs distinct on central area of face. Labellum blackish in distal half, oval apical segment of palpus velvety black. Narrow gena below eyes with short black hairs, long and erect hairs on ventral part of head and hairs of postgena mixed black and white.
Thorax shining black including scutellum, only tops of postpronotal and postalar callus more brownish and narrow subnotopleural stripe whitish. Scutellar spines ( Fig. 15 View FIGURES 12 – 21 ) rather short, yellowish toward apices. Thoracic pile black, erect and dense on scutum, scutellum and basal halves of spines. Hairs on pleura mixed black and white, especially long white hairs present on propleura and posterior margins of anepisternum and katepisternum, anterior half of anepisternum extensively bare. Wing membrane entirely infuscated, especially darkened from stigma to wing apex, virtually all veins blackish. Halter black with yellowish base. Legs pale yellow including coxae, only tarsus of fore leg, and 2 apical tarsomeres of mid and hind legs darkened.
Abdomen distinctly longer than broad, with dense semi-appressed hairs. Pubescence black dorsally and whitish ventrally, also longer hairs at lateral margins in basal half black. Male terminalia ( Figs 8–11 View FIGURES 1 – 11 ) yellowish brown and black haired, proctiger not widened in basal half, cercus relatively long ( Fig. 8 View FIGURES 1 – 11 ); genital capsule ( Fig. 9 View FIGURES 1 – 11 ) with proximal transverse prominence and distal conical medial process, gonostylus with small but sharp inner spine and subapical dilation visible in posterolateral view ( Fig. 10 View FIGURES 1 – 11 ), gonocoxite with rectangular inner process distally. Aedeagal complex ( Fig. 11 View FIGURES 1 – 11 ) relatively slender and long, with proximally dilated aedeagal apodeme.
Female ( Figs 14 View FIGURES 12 – 21 , 57–59 View FIGURES 55 – 62 ). Length: body 7.0– 7.5 mm, wing 6.4–7.1 mm. Head ( Fig. 14 View FIGURES 12 – 21 ) about 1.2 times higher than long in profile and 1.5 times broader than long in dorsal view. Frons at narrowest point as broad as or narrower than ocellar triangle, frontal whitish tomentose spot above antennae finely divided in middle, in the form of a slen- der triangle being broadly separated from eye margins ( Fig. 59 View FIGURES 55 – 62 ). Upper frons above narrowest point covered with yellow hairs but lower third bare. Postocular area in dorsal view about as broad as pedicel is long. Basal antennal segments and swollen basal part of flagellum reddish yellow, two apical flagellomeres black and black haired. Length of last flagellomere (without apical seta) about 1.2 times as long as rest of antenna. Gena more whitish tomentose than in male. Thorax, wing, halter and legs as in male, only darkening of tarsomeres less extensive. Abdomen broadly oval, 1.5 times as long as broad ( Fig. 57 View FIGURES 55 – 62 ).
Etymology. The name indicates the relatively short scutellar spines (brevis = short, spinosus = spinulate).
Variation. Variation was noticed in the female frons: the minimum width varies between 0.5–0.8 times the width of the ocellar triangle, and the whitish tomentose frontal spot is always narrow, but variably high.
Material examined. Type material: Holotype: Male, North Thailand, Mae Hong Son Province , Pangmapha , near Ban Nam Rin, Rudi valley (left stream), larva in rotting banana stump, 29. iii.2010, 1 3, emerged on 24.vi.2010, D. Kovac, in SMF.
Paratypes: North Thailand, Mae Hong Son, Pangmapha , near Ban Nam Rin, Rudi valley (left stream), larvae found in banana stump, 29. iii.2010, 1 ♀, emerged on 16.vi.2010, D. Kovac, in SMF, 1 ♀, emerged on 3.vi.2010, D. Kovac, in FSMU; 1 ♀, emerged on 24.vi.2010; near Ban Nam Rin, 2 3 sweeping along small stream, 19.v.2011, D. Kovac in SMF; Mae Hong Son, Pangmapha, Pai Viewpoint [=Kiew Lom] area, larvae collected in rotting banana stump, 12. iv.2010, 1 ♀, emerged on 7.vi.2010, in SMF, 1 m, emerged on 7.vi.2010, in FSMU, 1 ♀, emerged on 10.vi.2010, D. Kovac, in SMF ; Mae Hong Son Province, Pangmapha, Viewpoint [=Kiew Lom] (left), larva from rotting banana stump, 12. iv.2010, 1 3, emerged on 7.vi.2010, D. Kovac, in FSMU ; Mae Hong Son, district Pangmapha, near Pai Viewpoint [=Kiew Lom] (left), along small stream, ca. 1500 m, 30. iv.2010, 1 3, D. Kovac, in SMF . Laos, Bolikhamsai Province, Ban Nape env., 18°20´N, 105°08´E, 400+- 100 m, 7.–16. v.2004 1 ♀, E. Jendek & O. Šauša, in ZIB.
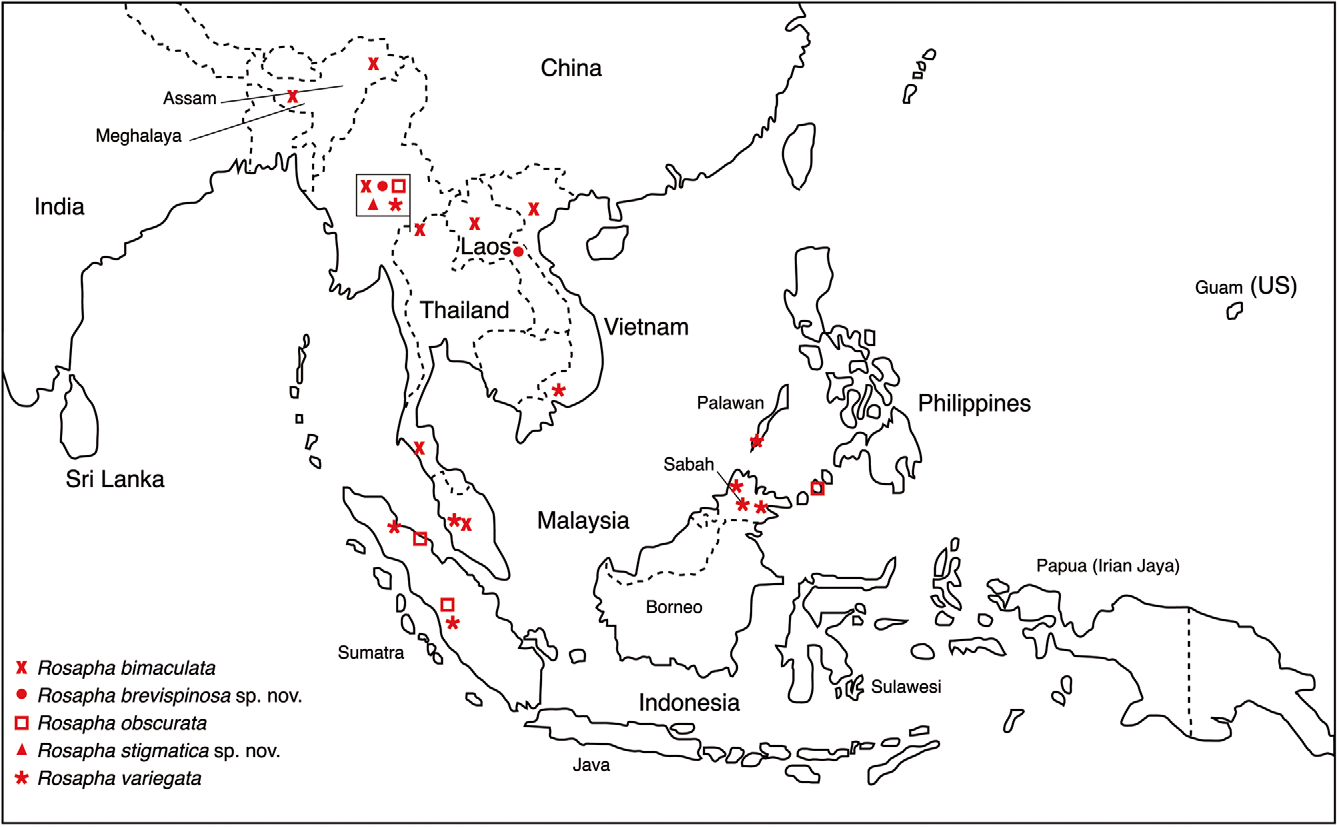
Distribution. Rosapha brevispinosa sp. nov. is known from three localities in the district pangmapha in North Thailand and one locality in Laos ( Fig. 80 View FIGURE 80 ).
Habitat. Larvae of R. brevispinosa were found twice in stumps of felled banana stems. They fed in rotting parts of the underground stem (personal observation, Figs 77 and 78 View FIGURES 71 – 78 ).
| SMF |
Forschungsinstitut und Natur-Museum Senckenberg |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |