Polystichum napoense C.Xiong & R.H.Jiang, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.601.1.2 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8129428 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/AB4D8171-FFAB-1263-D7BA-FDD3FD5628D3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Polystichum napoense C.Xiong & R.H.Jiang |
| status |
sp. nov. |
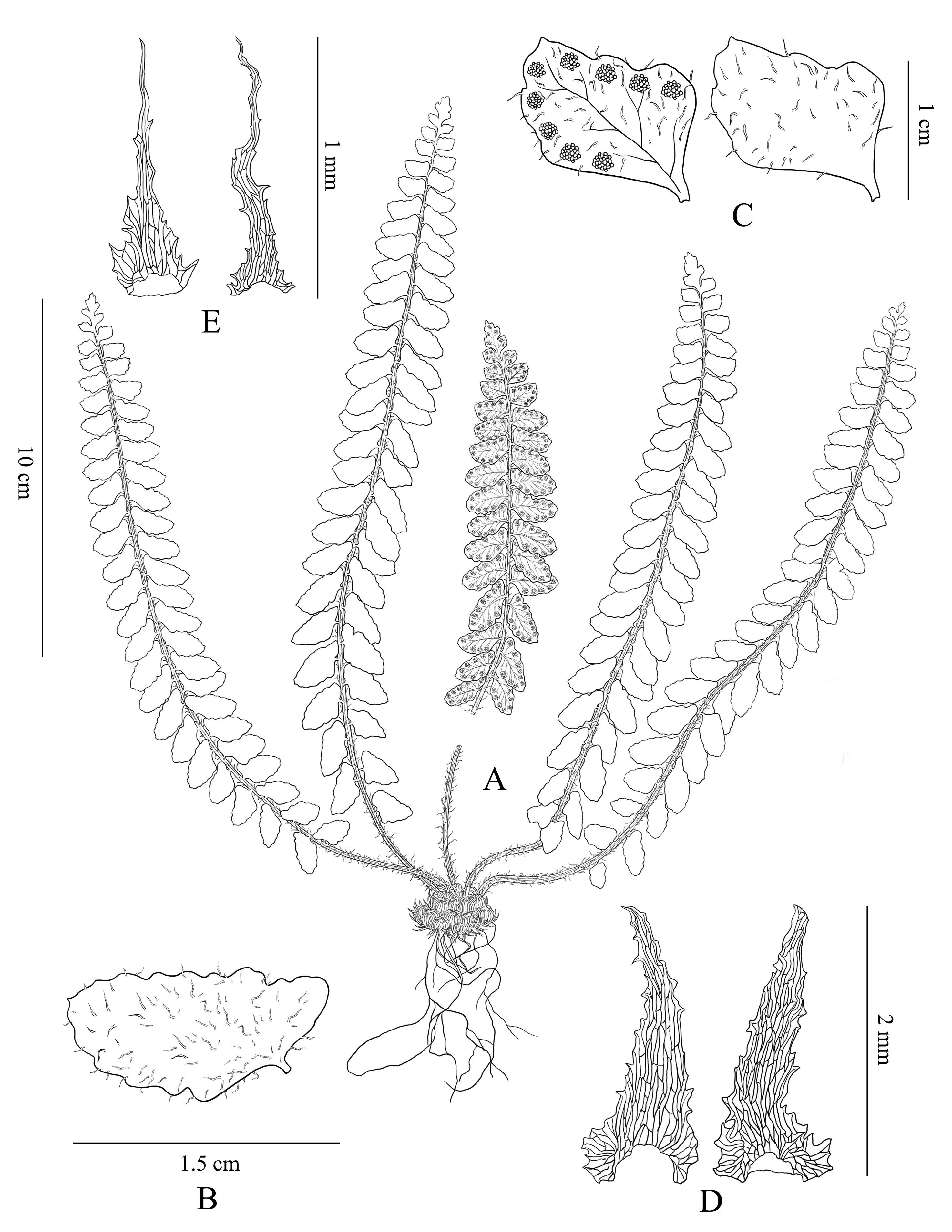
Polystichum napoense C.Xiong & R.H.Jiang View in CoL sp. nov. ( Figs 1 View FIGURE 1 & 2 View FIGURE 2 )
Type: — CHINA. Guangxi Zhuangzu Autonomous Region: Baise City , Napo County, Longhe Town , Yuantuo village , 23.3897°N, 105.9864°E, elev. ca. 1080 m, 18 October 2022, Chi Xiong & Zheng-long Li DXGJ20221018-06 ( holotype IBK!) GoogleMaps
Diagnosis: — Polystichum napoense is characterized by its rhomboidal or deltoidovate pinnae, deflexed basal pinnae, and a large number of scales present on both surfaces of the pinnae.
Description:—Plants perennial, evergreen, 12–26 cm tall. Rhizome erect, short, ca. 2.5 cm in diam., covered with scales; scales broad ovate-lanceolate, brown, c. 3–4× 1–1.5 mm, margin erose, apex caudate. Fronds cespitose, 6– 15 per rhizome, 12–28 cm long; stipes green, 1.5–3.5 cm long, 0.4–0.6 mm in diam., stramineous, adaxially shallowly canaliculate; densely scaly; scales on base of stipe long-triangular to lanceolate, membranous, dark brown, 1.5–3 × 0.5–1 mm, margin sparsely toothed, apex acuminate to caudate; scales on distal petiole similar but narrower. Lamina lanceolate, 9–25 × 2–2.5 cm, base slightly contracted, apex acuminate, 1-pinnate; rachis stramineous, covered with scales; scales lanceolate, narrowly lanceolate to sublinear, membranous, dark brown, 0.5–1.5 × 0.1–0.3 mm, with 1–3 teeth on margin, apex fibriform. Pinnae 10–25 pairs, chartaceous, greyish green, alternate, slightly imbricate, subexplanate, attached at 80–150° to rachis, short petiolate, rhomboidal or deltoidovate, 0.8–1.8 × 0.5–0.7 cm at middle, base asymmetric, acroscopic base auriculate, margin repand, basiscopic base truncate and forming a 15–40(–60)° angle with rachis, margin dentate, apex obtuse, both surfaces scaly; scales linear, filiform, ca. 0.5 mm long; veins pinnate, abaxially slightly distinct, adaxially indistinct. Sori terminal on veins of distal pinnae, close to pinna margin, 8–13 (3–5 below midrib, 5–8 above midrib) per fertile pinna; indusia absent. Sporangia almost round, 0.3–0.4 mm diam., ca. 0.1 mm thick, dark brown when mature; annuli with 15–17 thickened cells. Spores circular in the polar view and elliptic in the equatorial view, 43.8–47.5 (–50.3) × 50.8–59.4 (–63.8) µm (polar axis × equatorial axis); the ratio of the length of the polar axis to that of the equatorial axis is 0.74–0.87; perispore sculpturing is alveolate or forming large folds on it.
Distribution and ecology: — Polystichum napoense is currently found only from the type locality at an elevation of ca. 1080 m. This species grows on rocks in a karst cave, spanning from the entrance zone to the twilight zone.
Etymology: —Derived from the type locality, Napo County ( Guangxi, China).
Vernacular name:—Ďāff̎ (nà pô ěr jué).
Conservation status: — Polystichum napoense is currently known only to exist in one population at the type locality. The population size is estimated to be around 100–150 mature individuals. Following the IUCN ( The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) guidelines ( IUCN, 2023), the species is temporarily assessed as Critically Endangered (CR).
| IBK |
Guangxi Institute of Botany |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |