Rivulus berovidesi, Silva, Rodet Rodriguez, 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3949.2.9 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:6EE53509-2ED0-4466-986B-A9DA84413CB3 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5662820 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/AC2787EC-F334-B064-FF7C-5CF61DE1A07B |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Rivulus berovidesi |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Rivulus berovidesi View in CoL , new species
( Figs. 2–6 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 View FIGURE 4 View FIGURE 5 View FIGURE 6 )
Holotype. CZACC-9.83, adult male, 37.3 mm SL, Sierra de Cajalbana, Pinar del Rio province, Cuba, 220 46’ 31.7’’N, -830 26’ 37.7’’W, 26 February, 2014. R. Rodriguez Silva.
Paratypes. All from Sierra de Cajalbana, Pinar del Rio province, Cuba. Same date and collector as holotype. CZACC-9.84, three males, 31.1–34.7 mm SL; CZACC-9.85, three females, 36.3–37.9 mm SL; MFP 18.00570, two males 32.2–32.8 mm SL and two females 33.7–34.3 mm SL; MNHN 1457 one male 31.3 mm SL and two females 31–35.6 mm SL; MZC 171656 and 171657 two males 32.7–37.9 mm SL respectively and MZC 171658 and 171659 two females 31.4–33.5 mm SL respectively.
Diagnosis. Both males and females of Rivulus berovidesi sp.n. are readily distinguished from Rivulus cylindraceus by the presence of a dark lateral band situated longitudinally along the lateral line, extended from the posterior margin of the eye to the base of the caudal fin (versus a lack of this dark lateral band in Rivulus cylindraceus ). Dorsal fin slightly shifted to the caudal peduncle in relation to the origin of anal fin ( 1–3 mm) when compared to Rivulus cylindraceus . Frontal scalation pattern in Rivulus berovidesi sp. n. is d - type versus e - type pattern in Rivulus cylindraceus ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 )
Description. Morphometric and meristic data for holotype and 22 paratypes are presented in Tables 1 View TABLE 1 and 2. Largest examined male 37.9 mm SL; largest examined female 38.0 mm SL. Body subcylindrical anteriorly and compressed posteriorly. Dorsal profile slightly convex from the snout to the posterior base of dorsal fin. Ventral profile slightly convex from the lower jaw to the anal fin origin. Both paired and impaired fins rounded and without filaments. Dorsal fin origin above base of the 5th or 6th anal fin ray. Pectoral fins inserted behind to the posterior margin of opercles. Pelvic fins are the smallest, reaching anus. Dorsal fin rays 6–9, caudal fin rays 15–19, anal fin rays 8–11, pelvic fin rays 4–6 and pectoral fin rays 11–14.
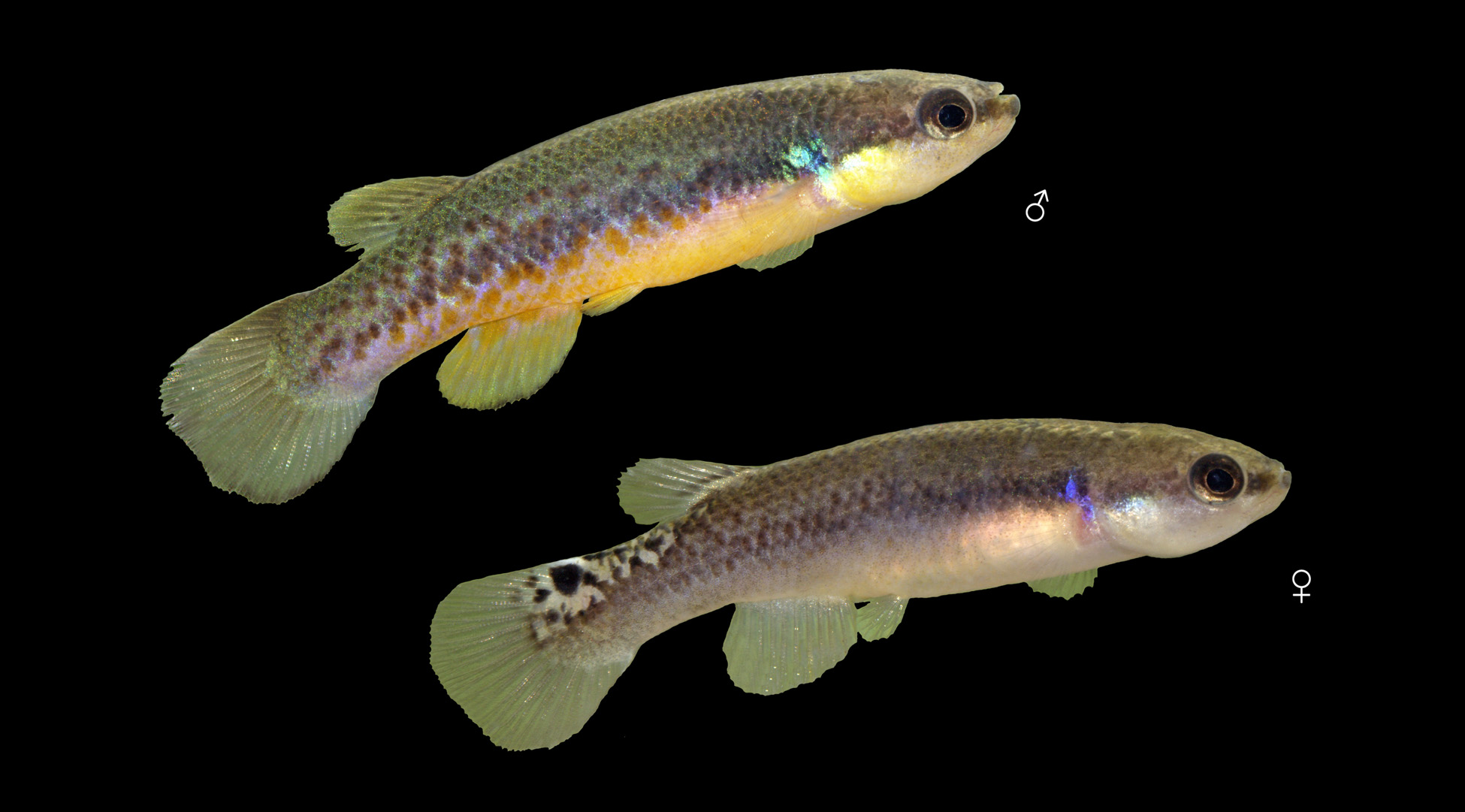
Body and head entirely scaled with cycloid scales. Longitudinal series of scales 34–37, transverse series of scales 9, pre-dorsal scales 21–25. Frontal scalation is d - type pattern. Males of Rivulus berovidesi sp.n. are yellow and orange ventrally, whereas females are less colored. Figure 3 View FIGURE 3 shows sexual dimorphism in this species, which includes differences in color of body and fins as well as females characterized by a distinctive ocellated caudal spot. Females have a diffuse ocellated caudal spot which can extend from the posterior base of the dorsal fin to the upper margin of the caudal fin.
Counts Holotype Paratypes (N=23)
Pre-dorsal scales 23 21 (4) 22 (4) 23 (6) 24 (6) 25 (3) Lateral scales 37 34 (4) 35 (7) 36 (7) 37 (5) Dorsal rays 7 6 (4) 7 (9) 8 (8) 9 (2) Caudal rays 19 15 (1) 16 (2) 17 (9) 18 (7) 19 (4) Anal rays 10 8 (2) 9 (12) 10 (8) 11 (1) Pelvic rays 5 4 (4) 5 (10) 6 (9)
Pectoral rays 11 11 (10) 12 (9) 13 (2) 14 (2)
Color in life. Males ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ): Body coloration is greenish or olive-green dorsally. There is a wide dark lateral band extended from the posterior margin of the eye to the base of the caudal fin. Ventral ground coloration is yellowish with orange spots reaching the anal fin base. An iridescent blue spot is present behind the margin of opercle in both sexes. Males have an iridescent olive- green spot on the opercle too. Dorsal fin is greenish, caudal fin is slightly greenish on its base and more transparent to the edges. Anal fin is spotted in orange in their base and yellow or yellow- green to the ends. Pelvic fins are yellow and pectoral fins are transparent.
Females ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 ): Body coloration less striking when compared to males. General body coloration brown, darker dorsally than ventrally. Ventral coloration is paler with some small yellowish spots. There is a narrow dark lateral band extended from the posterior margin of the eye to the base of the caudal. Diffuse ocellated caudal spot present which can extends from the posterior base of dorsal fin to the superior margin of caudal fin and sometimes along the caudal fin base too ( Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 and 5 View FIGURE 5 ). All fins slightly greenish or transparent.
Color in preserved specimens. Preserved specimens with the typical dark lateral band from the posterior margin of the eye to the base of caudal fin in both sexes, although slightly paler than living specimens. Ventral region of the body with a yellowish homogeneous coloration while dorsal region is brownish-gray. Males with a reticulated pattern on scales above lateral dark band ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 ) while females with the diffuse ocellated caudal spot extended from the end of dorsal fin to the superior margin of caudal fin ( Fig. 5 View FIGURE 5 ). All fins with a whitish coloration.
Etymology. The specific name of this new species is given in honor to the Professor Vicente Berovides Alvarez, professor at the Faculty of Biology, Universidad de la Habana, Cuba in recognition of his life-long dedication and contribution to train several generations of new researchers in biological sciences.
Distribution and habitat. Rivulus berovidesi sp. n. is known only from northwest mountain system in Pinar del Rio province. Particularly, in Sierra de Cajalbana ( type locality) and Rio Camarones. Both localities are situated in northwestern Cuba ( Fig. 1 View FIGURE 1 ). This species inhabits small mountain streams with a depth of 30–70 cm approximately and bottom substrate basically composed by stones, sand and dead leaves ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ). There is not aquatic vegetation in the area. The streams are clear with pH 7.5 and water temperature 24°C. Other freshwater fish collected together with Rivulus berovidesi sp. n. were: Gambusia punctata , Girardinus uninotatus , Girardinus creolus , Girardinus microdactylus , Nandopsis tetracanthus , Agonostomus monticola and Gobiomorus dormitor .
TABLE 1. Morphometric data for holotype and paratypes of Rivulus berovidesi sp. n. Standard length (SL) and head length (HL) are expressed in millimeters; all other measurements are expressed as percentage of SL except for eye diameter and snout length, which are given as percentage of HL.
| Holotype | N | Paratypes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morphometric variables | Mean | Min Max | SD | ||
| Standard length (mm) | 37.3 | 23 | 33.8 | 28.9 37.9 | 2.5 |
| Pre-dorsal length | 68.0 | 23 | 70.1 | 67.3 71.5 | 1.6 |
| Pre-anal length | 60.9 | 23 | 61.9 | 59.5 65.3 | 1.2 |
| Interdorsal-anal length | 7.1 | 23 | 8.2 | 6.8 10.6 | 1.1 |
| Caudal peduncle depth | 13.7 | 23 | 12.7 | 11.1 14.4 | 0.9 |
| Head length (mm) | 10.4 | 23 | 9.0 | 8.1 10.4 | 0.6 |
| Snout length | 28.1 | 23 | 30.1 | 25.9 33.5 | 2.0 |
| Eye diameter | 23.7 | 23 | 26.6 | 23.7 30.0 | 1.8 |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |