Glypta extincta Ratzeberg 1852
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3755.1.1 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:EDD12B94-69A6-440A-80ED-31AFE0D45D2F |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5663034 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/AD5187FA-A01F-F729-FF35-FF6BFD377978 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Glypta extincta Ratzeberg 1852 |
| status |
|
Glypta extincta Ratzeberg 1852 View in CoL
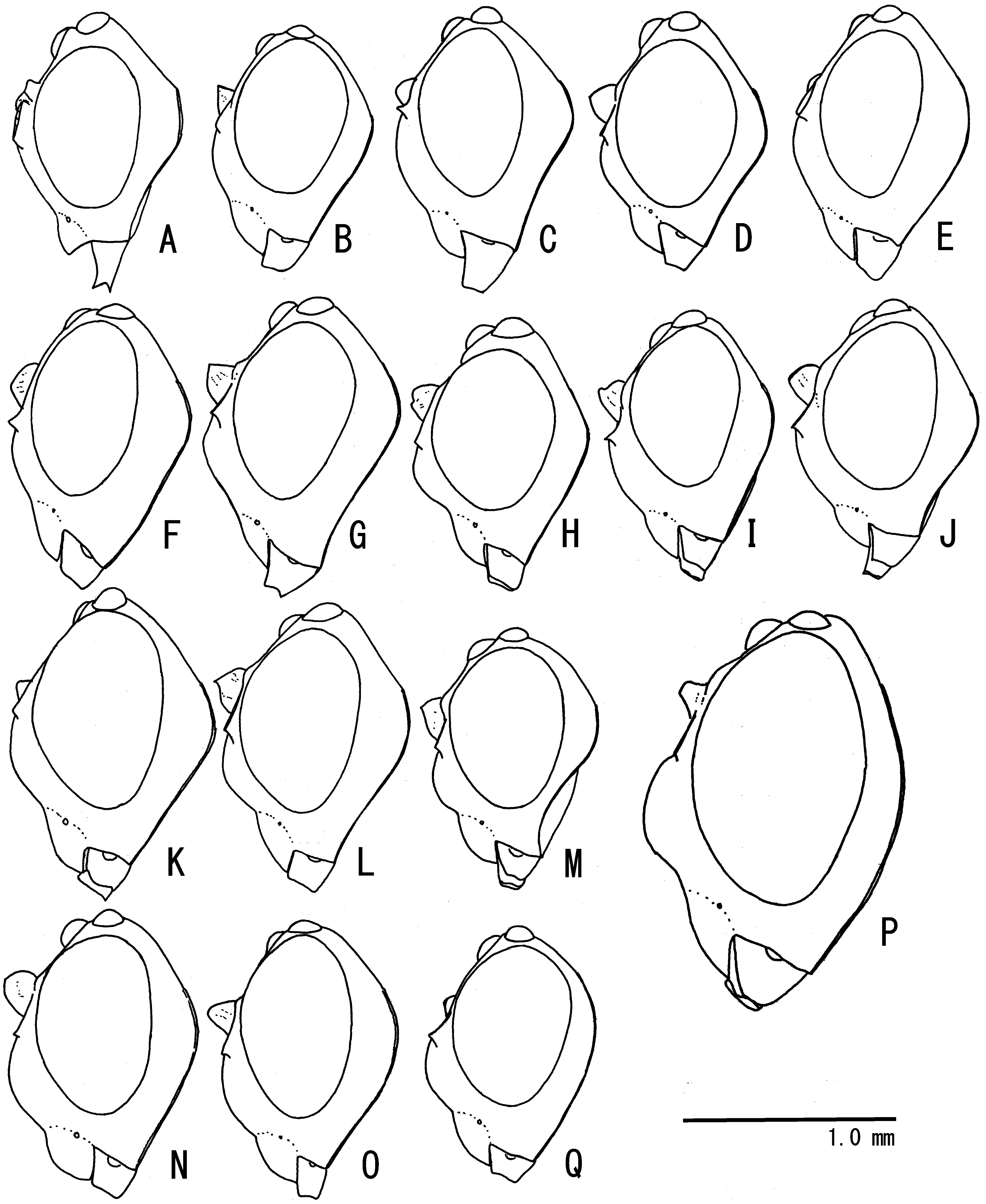
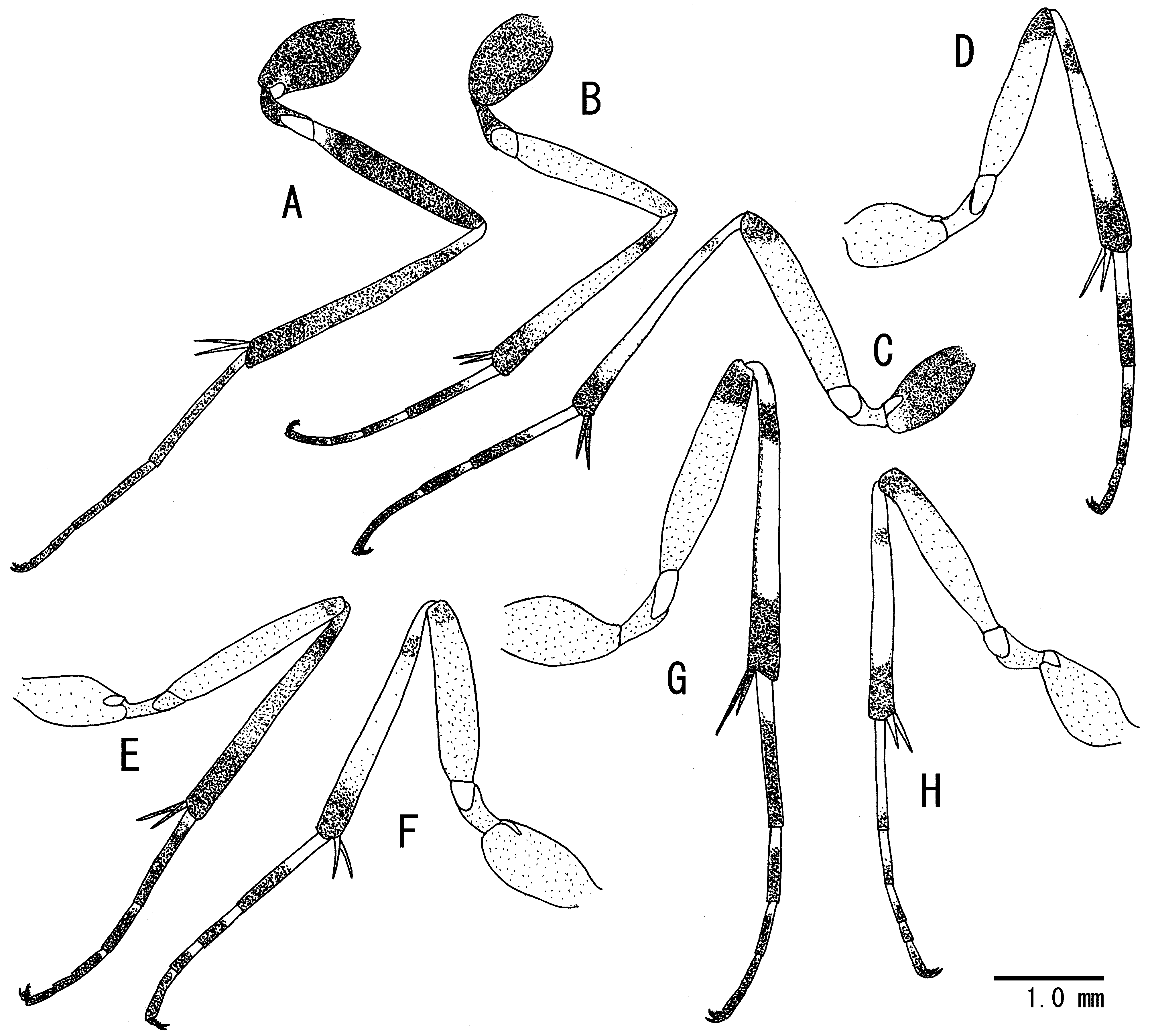
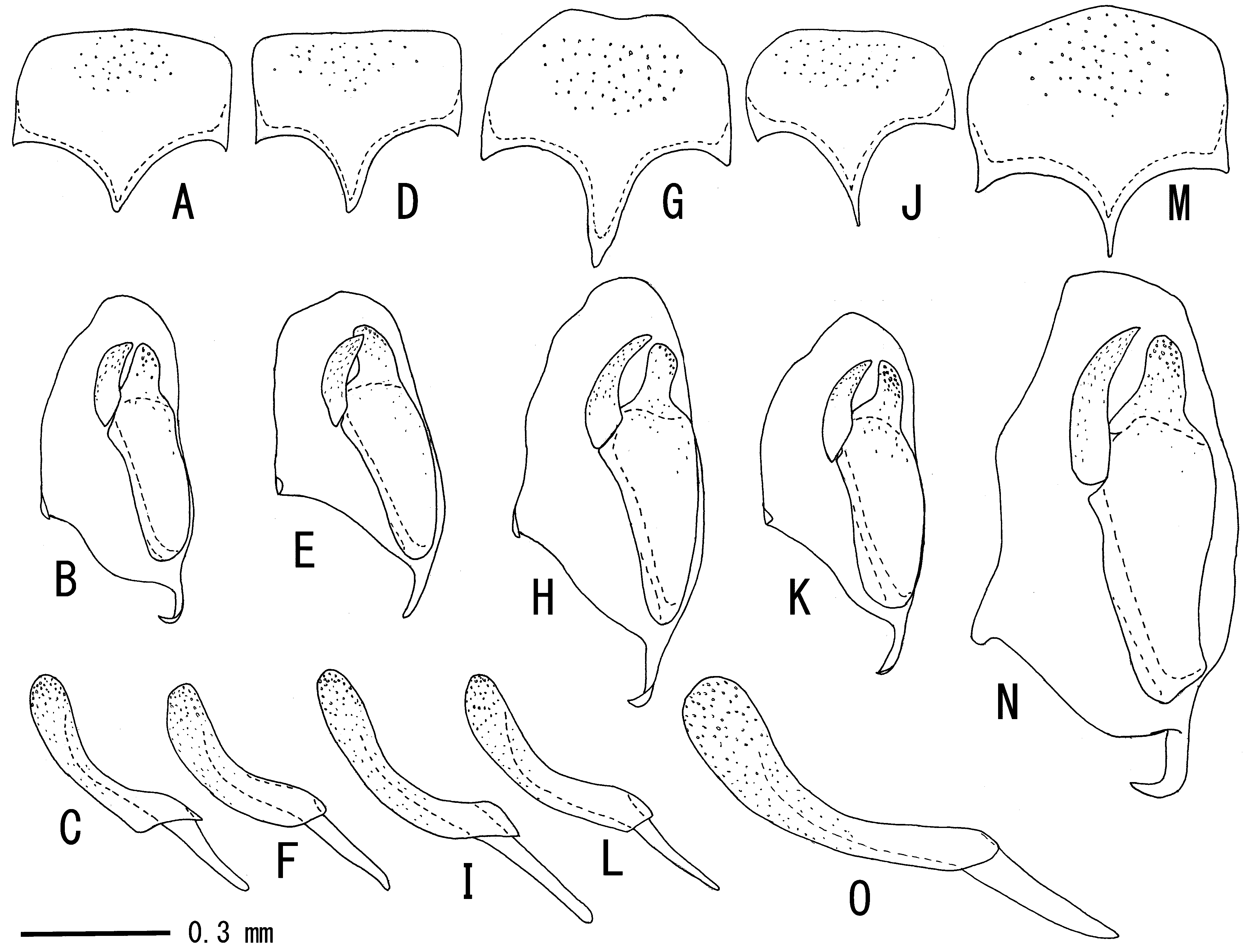
( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 G, 2 G, 3 F, 4 G, 6 G, 7 G, R, 8 G–I, 9 E, F)
Glypta extincta Ratzeberg 1852: 112 View in CoL .
Glypta nigriventris Thomson 1889: 1325 View in CoL .
Description based on Japanese specimens: Female (n=5). Body length 8.5–10.0 mm.
Head. Ca. 0.6 times as long as wide. Clypeus 0.7 times as long as wide, roundly convex in lateral view ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 G). Face strongly convex medially ( Fig. 2 View FIGURE 2 G), 0.5 times as long as wide. Frons with a large median horn between each antennal socket, its apex relateively pointed ( Figs. 1 View FIGURE 1 G, 3 F). OOL 1.6–1.8 times as long as OD; POL 1.8–2.0 times as long as OD. Mandible with narrow ventral flange by basal 0.6, its base flat. MSL 1.0–1.1 times as long as BWM. Antenna with 39–40 flagellomeres. F1 1.5–1.6 times as long as F2.
Mesosoma. Densely punctate, punctures on lateral lobes of mesoscutum (excluding near notaulus) separated by 0.3–1.8 (usually ca. 1.0) times their diameter. Epomia weak and short. Lateral area of pronotum entirely punctate. Both sides of mesoscutum near tegula weakly and obtusely produced posteriorly. Propodeum entirely densely punctate. Posterior transverse carina and pleural carina of propodeum complete. Other carinae of propodeum absent. Fore wing length 6.0– 7.5 mm. Fore coxa with weak ridge antero-dorsally. Hind femur 6.0 times as long as maximum depth in lateral view. Hind TS1 2.0–2.1 times as long as TS2.
Metasoma. T1–T4 densely punctate ( Figs. 6 View FIGURE 6. T 1 G, 7 G, R). T1 1.3–1.4 times as long as maximum width, its median dorsal carina present on ca. basal 0.5 of tergite ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6. T 1 G). T2 1.0 times as long as maximum width. T2–T4 each with moderate a pair of oblique groove ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7. T 2 G, R). Ovipositor sheath ca. 0.8 times as long as fore wing, 1.7– 1.9 times as long as hind tibia.
Colouration. Body (excluding wings and legs) black, except for: apical half of clypeus, small spot of mandible, palpi, posterodorsal corner of pronotum, tegula, membranous parts of sternites and posterior part of subgenital plate yellow to yellowish-brown; posterior margin of each metasomal tergite tinged with reddish-brown; flagellum blackish-brown, its ventral surface more or less paler than dorsal surface; ovipositor reddish-brown to yellowishbrown. Wings hyaline; veins and pterostigma brown except for yellow wing base. Legs (hind leg: Fig. 4 View FIGURE 4 G) reddish-brown, except for: all trochanters, all trochanters and base of all tibiae pale yellow; hind femur darkened apically; subbasal band, ventral surface and apical part of hind tibia black; hind tibia excluding yellow and black areas whitish-yellow; middle and hind tarsus blackish-brown to black with basal yellow areas on TS1–TS3 and slightly on TS4. Basal yellow area of TS1–TS3 shorter than black areas of each segment.
Male (n=2). Similar to female. OOL 1.4–1.8 times as long as OD; POL 1.6–2.0 times as long as OD. MSL 0.9 times as long as BWM. Antenna with 42 flagellomeres. F1 1.4–1.5 times as long as F2. Lateral section of anterior transverse carina and basal section of lateromedian longitudinal carina present. Hind femur 6.0–6.1 times as long as maximum depth in lateral view. Hind TS1 1.8–2.0 times as long as TS2. Posterior margin of subgenital plate convex with median weak concavity ( Fig. 8 View FIGURE 8 G). Apical margin of paramere roundly produced ( Figs. 8 View FIGURE 8 H, 9 E, F). Dorsal margin of paramere with convexity apically ( Figs. 8 View FIGURE 8 H, 9 E). Clypeus entirely yellow.
Material examined. JAPAN: 1F, Yamagata Pref., Shirafutakayu, 29. vi. 1967, H. Higuchi leg. (KU); 1M, Yamanashi Pref., Mt. Daibosatsu, Sagashio-kosen, Hikawa-rindo, 16. vi. 2007, K. Watanabe leg. ( KPMNH: KPM- NK5001180); 2F, same data excluding T. Ban leg. ( KPMNH: KPM-NK5001181); 2F, Nagano Pref., Utsukushigahara, 5. viii. 1970, H. Takizawa leg. (KU); 1M, Fukui Pref., Oono city, Koike, 8. vi. 1980, H. Kurokawa leg. ( KPMNH: KPM-NK5001182). MOLDOVA: 1F (det. by Kuslitzky), “Оницканы Криулянский” (Onitskany, Criuleni), 16. v. 1978, Kuslitzky leg. ( ZIS).
Distribution ( Fig. 12 View FIGURE 12 ). Japan (Honshu*); widely recorded from Eurasia.
Biology. Unknown in Japan. A host, Acleris rosana ( Lepidoptera : Tortricidae ), was recorded in Europe (e.g. Ratzeburg 1852; Constantineanu & Pisica 1977).
Remarks. This is the first record of this species from Japan. By the result of comparison, no differences were found between Japanese and Moldvanese females. This species can be distinguished from other Japanese species by the combination of characters of above key.
| ZIS |
Universitaet Saarbruecken |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Banchinae |
|
Genus |
Glypta extincta Ratzeberg 1852
| Watanabe, Kyohei & Maeto, Kaoru 2014 |
Glypta nigriventris
| Thomson 1889: 1325 |