Ceratina ( Zadontomerus ) kopili Flórez-Gómez, Ayala & Hinojosa-Díaz, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5214.2.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D982762A-A869-4375-9803-13A74D71335D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7386267 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/B7057956-C421-1F7F-7BCF-03BD6E5AF8CA |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Ceratina ( Zadontomerus ) kopili Flórez-Gómez, Ayala & Hinojosa-Díaz |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Ceratina ( Zadontomerus) kopili Flórez-Gómez, Ayala & Hinojosa-Díaz new species
( Figures 7 View FIGURE 7 , 8 View FIGURE 8 , 21B View FIGURE 21 , 22D View FIGURE 22 , 23E View FIGURE 23 , 24D View FIGURE 24 , 27 View FIGURE 27 )
Diagnosis. S mall to medium-sized bees: females from 4.8–6.0 mm, males from 4.0– 5.5 mm in length. Pronotal lobe with yellow mark, highly conspicuous preoccipital foveate carina, beginning in the upper third of the occiput, forming a strong depression, being more developed in males ( Fig. 7E View FIGURE 7 ),; body dark green with metallic tones; female frons with punctures separated by a distance 0.5-2.0 times puncture diameter; disc of scutum with punctures along the anteromedial line and punctures densely distributed around the parapsidal lines; males with hind femur strongly dilated medially, forming an angle ( Fig. 22D View FIGURE 22 ); and T7, posterior margin concave, forming a medial, narrowly rounded projection ( Fig. 23E View FIGURE 23 ). Females similar in appearance to those of C. nautlana ; however, C. kopili can be easily recognized by the presence of a well-developed preoccipital carina, the absence of a longitudinal yellow mark on the foretibia (present in C. nautlana ), as well as punctuation in the scutum disc (almost entirely impunctate in C. nautlana ).
Description. Holotype female. Length 5.68 mm. Body dark green with metallic tones, metasoma olive green.
Head. Round. Mandibles with three teeth, black and middle area brownish; outer margin with scattered short whitish hairs. Hypostomal carina rounded. Clypeus with yellow medial oval mark; area around the mark with dense punctures separated by a distance less than 0.5 times a puncture diameter. Supraclypeal area with dense and fine punctation between antennal sockets, medial area with punctures irregularly distributed, separated by more than a puncture diameter. Lower and upper paraocular area densely punctate, distance equal to or less than a puncture diameter. Antennocular area (area between antennal bases and inner margins of compound eyes) with punctures separated by a distance equal or less than 0.5 times a puncture diameter. Frons with impunctate swellings, surrounding area with punctures separated by a distance 0.5–1.5 times puncture diameter. Vertex densely punctate, with whitish pubescence, short and scattered. Gena with upper and medial area densely punctate, becoming sparse below; with whitish and short hairs. Preoccipital margin with well-developed carina, beginning in the upper third of the occiput, forming a strong depression. Antennae dark brown. Head length 1.46 mm; head width 1.36 mm; lower interocular distance 0.76 mm; upper interocular distance 0.90 mm; ocellocular distance 0.33 mm.
Mesosoma. Pronotum with lateral carina; dorsolateral angle with transverse carina; pronotal lobe with yellow mark. Mesepisternum densely punctate, punctures separated by less than a puncture diameter; hypoepimeral area with dense punctures covering almost all the area, lower area impunctate. Metepisternum with fine, closely spaced punctures, puncture size less than those on mesepisternum. Scutum anterior area between notauli and anteromedial line, with close punctures; disc with punctures along anteromedial line, punctures reaching posterior margin; area around parapsidal lines densely punctate; posterior area with close punctures. Scutellum similar in punctation to scutum, medial area with sparser punctures. Propodeum, basal area with striae, one in the middle longer than the lateral striae; the rest of propodeum finely and densely punctate, with whitish plumose hairs. Length of forewing 3.52 mm. Tegula brown and impunctate. Wings subhyaline, pterostigma dark brown, venation light brown. Scutum length 0.8 mm; scutum width 1.15 mm. Legs. Dark brown with greenish metallic tones. Base of tibia with yellow spot. Tibial spurs whitish. Tarsi light brown. Metasoma. T1 polished, disc with small area with fine and close punctures. T2 and T3 with dense punctation laterally, separated by a distance less than equal to a puncture diameter, becoming more separated on the disc. T4 densely punctate, as T2 and T3; posterior margin of T4with short and yellowish hairs, densely distributed. T5 and T6 rugose, with short and scattered yellowish hairs.
Paratype male. Length 4.66 mm. Same color as female.
Head. Mandibles with two teeth, color and pubescence as in female. Labrum with yellow rounded mark in the middle area. Clypeus, with inverted T-shaped yellow mark. Supraclypeal and paraocular area densely punctate, separated by a distance of less than one puncture diameter. Frons as in female. Vertex densely punctated, with long and scattered whitish hairs. Gena with dense punctation and short, whitish hairs. Preoccipital carina well developed, more so than in females, beginning in the upper third of the occiput, forming a strong depression. Antennae as in female. Head length 1.27 mm; head width 1.37 mm; lower interocular distance 0.65 mm; upper interocular distance 0.89 mm; ocellocular distance 0.27 mm.
Mesosoma. Generally, as in female, but with longer and more conspicuous whitish hairs. Length of forewing 3.27 mm. Scutum length 0.72 mm; scutum width 0.97 mm. Legs. Hind trochanter ventral margin forming a right angle, with short whitish hairs. Hind femur strongly dilated forming an acute angle in the middle area; ventral margin almost hairless ( Fig. 22D View FIGURE 22 ).
Metasoma. Punctures as in the female. T6, middle area with tuft of whitish pubescence. T7, apex with concave lateral margins, forming a medial acute projection; posterior margin with long sparse hairs ( Fig. 23E View FIGURE 23 ). S6, as shown in Fig. 24D View FIGURE 24 . Genital capsule as shown in Figure 8 View FIGURE 8 .
Type material: Holotype ( ♀ MZFC: 03274 ): MEXICO: Morelos: Tepoztlán, Km 12,Autopista México-Cuautla , 1650 m, 18.973, - 99.0825, 11-V-1997, J. Salinas. GoogleMaps Described paratype ( 1♂: 2196): same locality as holotype. Other GoogleMaps paratypes: same locality as holotype ( MZFC: 2♀: 2942, 2197). Mexico City: Ciudad Universitaria , 2328 m, 19.31449, -99.19178, 18 -VII- 2015, C. Martínez ( CNIN: 1♂). GoogleMaps 19.31418, -99.19189, 5-IX-2015 ( CNIN: 1♂). GoogleMaps 19.31457, -99.1919, 28-VI-2016 ( CNIN: 2♀). GoogleMaps 19.31402, -99.19172, 1-VIII-2015 ( CNIN: 3♂). GoogleMaps Jalisco: Mazamitla, 20 km SW, 5 km S, 18 km SE, 18-29-III-1990, C. M. Estrada (EBCh: 6♀, 2♂). Morelos: Cuernavaca, 20-XI-1987, F. Parker ( BBSL: 2♀, 4♂). Tepoztlán, km 4.5, Autopista México-Cuautla, 1940 m, 19.00416, -99.12944, 9-VI-1996, I. Hinojosa, O. Yáñez ( MZFC: 2♀: 4229, 3962. 5♂: 3961, 3981, 3983, 3984, 3982). GoogleMaps Oaxaca: Cuyotepeji, 3-10-III-1972, F. Parker ( BBSL: 5♀, 29♂). Puebla: Tehuacán, 1-III-1972, F. Parker ( BBSL: 1♂). Cholula, UDLA, 13-IX-1998, T. Griswold ( BBSL: 3♀, 7♂). Acatepec, 5 km N, 18.212778, -97.62833, 15-IX-1998, T. Griswold ( BBSL: 1♂). GoogleMaps
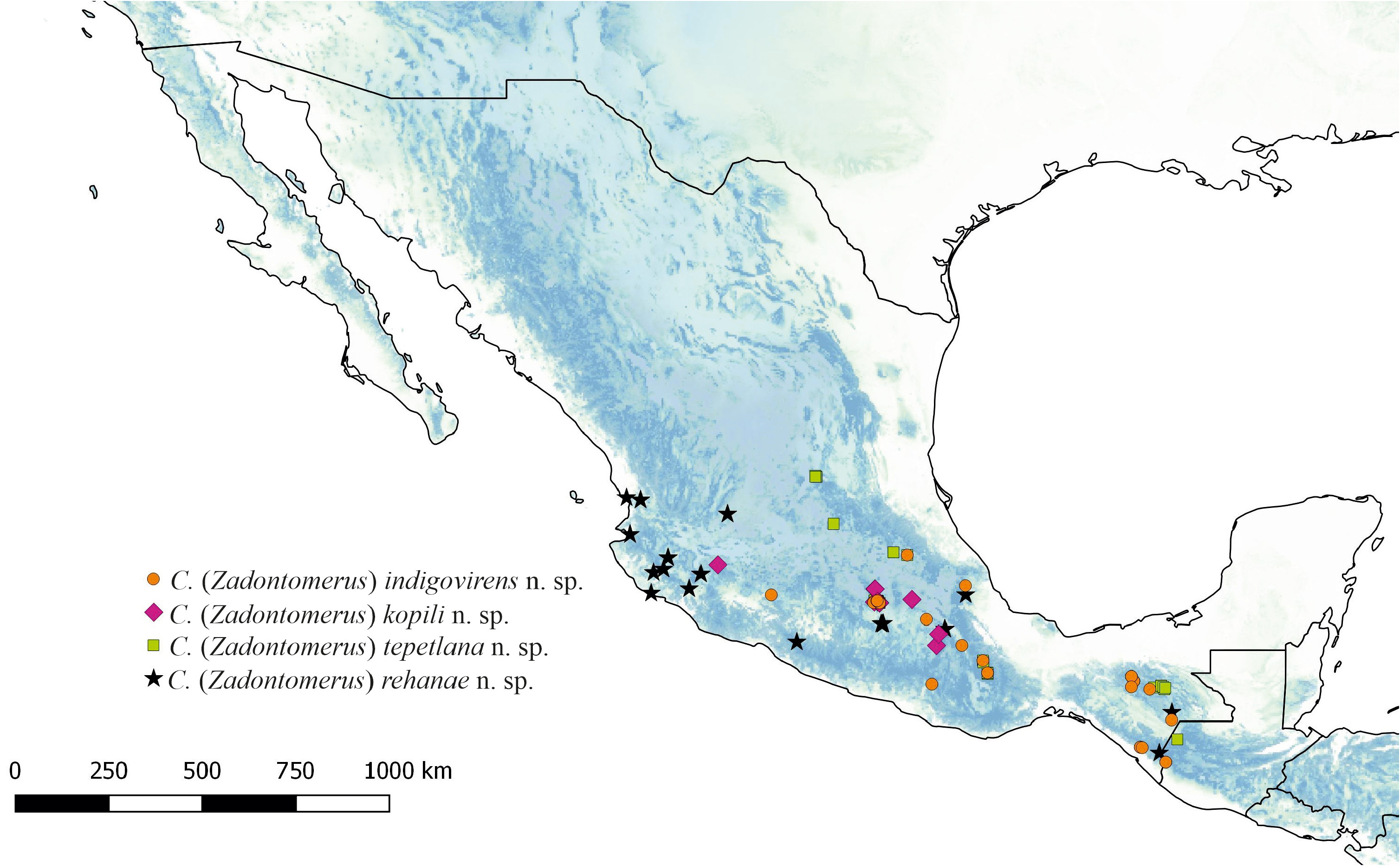
Distribution: Cerataina ( Z.) kopili is endemic to Mexico. It is known for the Transmexican Volcanic Belt, in Morelos, Jalisco, Oaxaca, Puebla and Mexico City. It ranges from 1500 m to 2400 m elevation.
Etymology: Kopili in Náhuatl means crown, referring to the conspicuous preoccipital carina which resembles a crown. It is a noun in apposition.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |
|
|
SubGenus |
Zadontomerus |