Pseudocalolampra inexpectata Roth & Princis, 1971
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1196003 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5589342 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/BC2887A2-FFAC-9922-5EB2-F1304DD6FBD2 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Pseudocalolampra inexpectata Roth & Princis, 1971 |
| status |
|
Pseudocalolampra inexpectata Roth & Princis, 1971 View in CoL
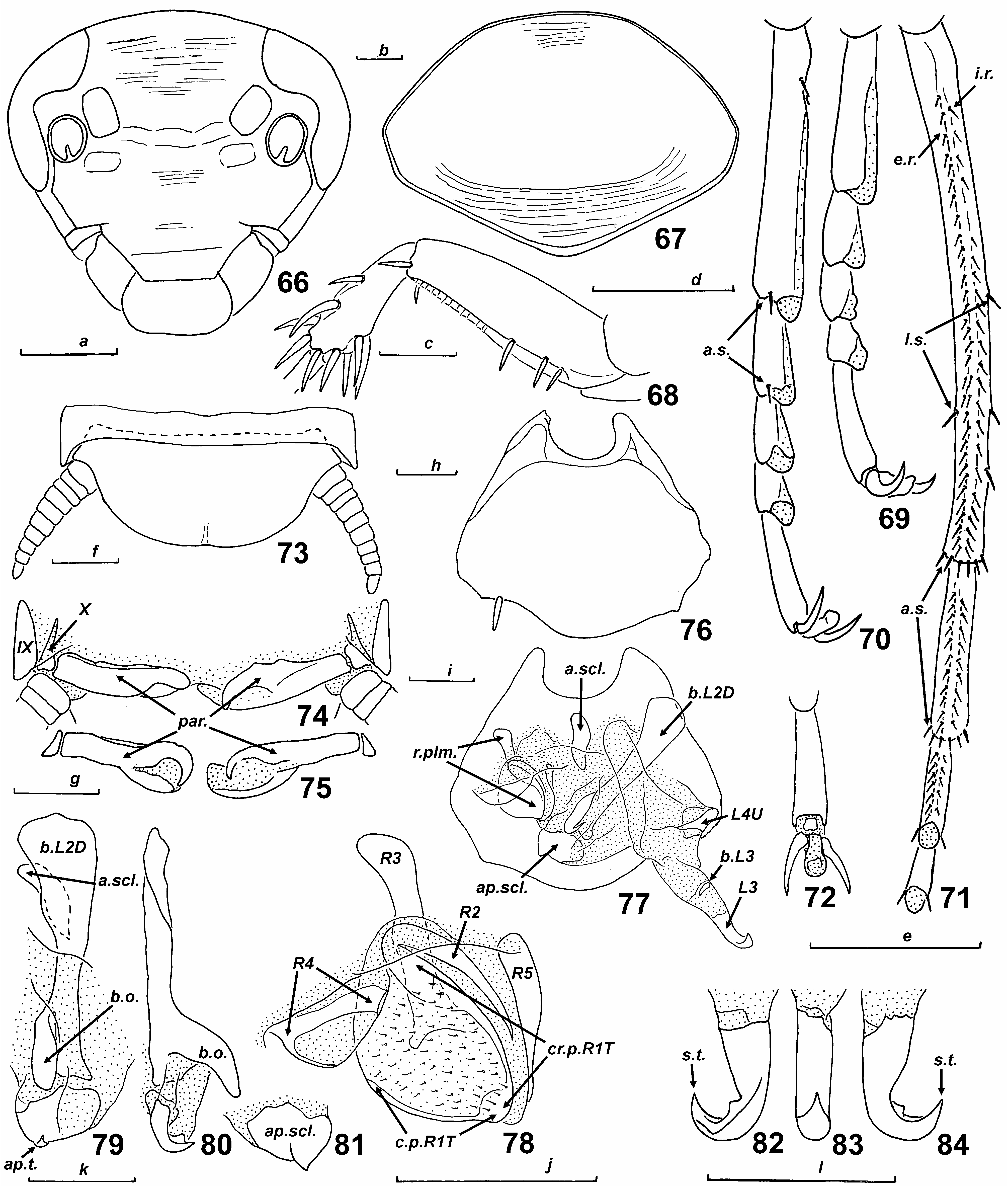
Figs 7 View Figs 1-9 , 66-84 View Figs 66-84
Material examined: MHNG; 2 males (genital complex of one male in prep. 250317/01); Kenya, Mombasa, Leisure Lodge ; 6.- 10.06.1980; coll. C. Schomo. – MHNG; 1 male; Kenya, “ Leisure L. Jioni Gerch ” (handwritten illegible text); 4.06.1981; coll. C. Schomo. Remarks : The original description ( Roth & Princis, 1971) can be supplemented with the following details, based on specimens listed above. The holotype (not examined) of this species is kept in Natural History Museum of London .
Somatic characters of male: General colour yellowish brown, with scattered black dots. Colouration of head as in Fig. 7 View Figs 1-9 , eyes black, facial part of head with large black or dark brown spot between eyes. Scapi and about 8-10 proximal segments of antennae yellowish, distal part greyish. Rest of head, mouthparts, legs, thorax and abdomen seen from below dirty yellow. Surfaces smooth and lustrous, head and pronotum with distinct transverse wrinkles ( Figs 7 View Figs 1-9 , 66-67 View Figs 66-84 ), weak punctuation present on pronotum. Head wider than long, with large impression between eyes and antennal sockets ( Figs 7 View Figs 1-9 , 66 View Figs 66-84 ); ocellar spots large; distance between eyes about as long as eye length; distance between antennal sockets about 2.3-2.7 times scape length (~ 0.6-0.7 mm); approximate length ratio of 3rd-5th segments of maxillary palps 1.1-1.2: 1.0: 1.0. Pronotum as in Fig. 67 View Figs 66-84 . Tegmina and wings completely developed, surpassing abdominal apex. Tegmina with rounded apex, sclerotized in costal field; venation slightly reticulate; costal field long, about one third of tegmen length, and narrow; Sc thickened (well visible on ventral side of tegmen); R, M and CuP basally fused; CuP long, about one half of tegmen length. Wings membranous, only with weakly sclerotized area of Sc and anterior rami of R. Fore tibiae distinctly thickened distally ( Fig. 68 View Figs 66-84 ). Anterior margin of fore femora of armed type B, with 4 spines, including 1 apical one ( Fig. 68 View Figs 66-84 ). Tibial spines well developed. Structure of hind tarsus ( Figs 69-72 View Figs 66-84 ): metatarsus a little longer than other tarsal segments combined, with 2 unequal rows of spines along lower margin: exterior row ( Fig. 71 View Figs 66-84 , e.r.) consisting of 31-37, interior row ( Fig. 71 View Figs 66-84 , i.r.) of 16-23 spines; 2nd and 3rd segments with 10-13/5-8 and 6-9/3- 5 spines in exterior and interior rows, respectively; other segments without spines along lower margin; very small euplantulae present on 3rd-4th segments; distal ends of 1st-4th segments bordered with 6, 5 and 3 “additional spines, respectively ( Figs 70-71 View Figs 66-84 , a.s.); 1-3 large spines located on lateral sides of metatarsus ( Fig. 71 View Figs 66-84 , l.s.); interior rows of spines displaced laterally on all segments; claws symmetrical, simple; arolium distinct, about half as long as claw ( Figs 69-72 View Figs 66-84 ). Fore ( Fig. 69 View Figs 66-84 ) and mid ( Fig. 70 View Figs 66-84 ) tarsi dissimilar to hind tarsi: metatarsal euplantulae large, spines along lower margin absent; one pair of “additional spines” present only on 1st-2nd segments of mid tarsi. Abdomen without visible glandular specializations; spiracle-bearing outgrowths of tergite VIII weakly expressed, without attenuate posterolateral angles. Anal plate (tergite X) wider than long, with nearly straight hind margin ( Fig. 73 View Figs 66-84 ). Cerci robust, with distinct segments ( Fig. 73 View Figs 66-84 ). Left and right paraprocts with hook-shaped caudomedial process ( Figs 74-75 View Figs 66-84 , par.). Hypandrium asymmetrical, hind margin between styli projected and rounded ( Figs 76-77 View Figs 66-84 ); right stylus slender and cylindrical, left one vestigial or absent.
Male genitalia ( Figs 77-84 View Figs 66-84 ): Right phallomere ( R +N): caudal part of sclerite R 1 T thin and weakly sclerotized ( Fig. 78 View Figs 66-84 , c.p. R 1T View Figs 1-9 ), cranial part widely rounded ( Fig. 78 View Figs 66-84 , cr.p. R 1 T); R 1 T densely covered with bristles; R 2 rounded; R 3 long, with cranial part rodlike and caudally forked; R 4 only partly sclerotized; R 5 elongated. Sclerite L2D (L1) divided into basal and apical parts ( Figs 77, 79-80 View Figs 66-84 ); basal part robust, distinctly widened cranially ( Figs 77, 79-80 View Figs 66-84 , b.L 2D View Figs 1-9 ), with large “bent outgrowth” at caudal end ( Figs 79-80 View Figs 66-84 , b.o.), “additional sclerite” under basal part of L2D large ( Figs 77, 79 View Figs 66-84 , a.scl.); apical part in shape of flattened, plate-like sclerite ( Figs 77, 79-81 View Figs 66-84 , ap.scl.), with upwardcurved “apical tooth” ( Figs 79-81 View Figs 66-84 , ap.t.); bristles absent. Sclerite L3 (L2d) with basal subsclerite ( Fig. 77 View Figs 66-84 , b.L 3 View Figs 1-9 ); “folded structure” and bristles absent; apex of L3 with “small tooth” ( Figs 82-84 View Figs 66-84 , s.t.); groove hge absent. Sclerite L4U (L3d) large ( Fig. 77 View Figs 66-84 ).
Dimensions (in mm): Head length 2.8-3.1, head width 3.0-3.2; pronotum length 4.5-5.0, pronotum width 6.5- 7.2; tegmen length 17.2-18.0, tegmen width 5.5-6.1.
| MHNG |
Museum d'Histoire Naturelle |
| R |
Departamento de Geologia, Universidad de Chile |
| T |
Tavera, Department of Geology and Geophysics |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
SubFamily |
Epilamprinae |
|
Genus |