Imantodes guane, Missassi, Alexandre F. R. & Prudente, Ana L. C., 2015
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3980.4.6 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C13F5A20-2E38-44BC-BC3E-4FDB6ECBB806 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5661756 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/C01087BF-5248-BE24-F397-F8E4AE718B0F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Imantodes guane |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Imantodes guane sp. nov.
( Figs. 2–3 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 )
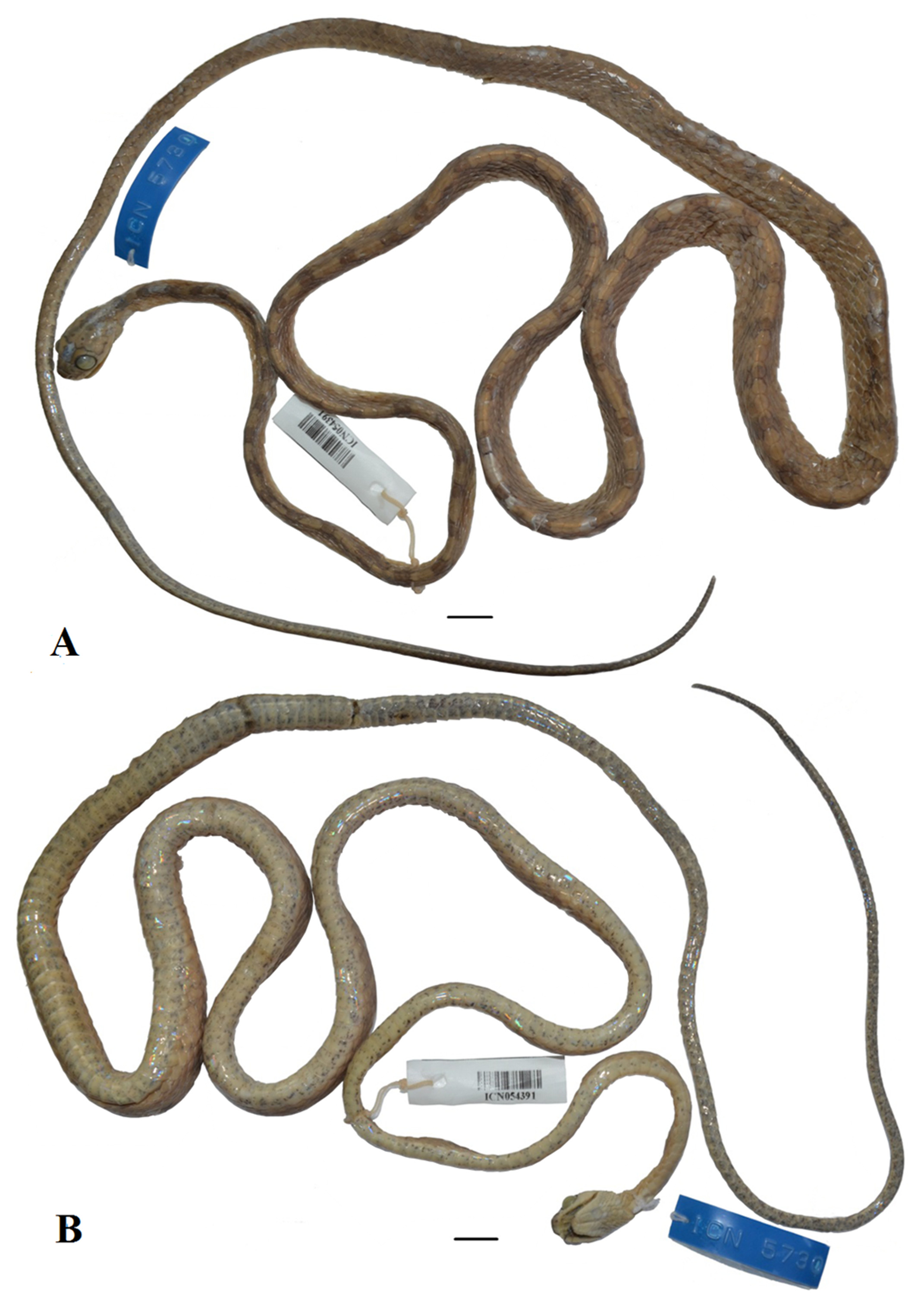
Holotype. Adult male, ICN 5730, collected by R. Hernández in 1981 at headwater of the Luisito River, Virolín ( 6º18’18”N, 73º10’25”W; 1750 m asl), municipality of Charalá, department of Santander, Colombia.
Paratype. Juvenile female, UIS-R 1705, Cerro de La Paz ( 6º58’20”N, 73º26’ 18”W; 2324 m asl) collected by E. Brisceño at municipality of Zapatoca, department of Santander, Colombia ( Figs. 4 View FIGURE 4 , 5 View FIGURE 5 B).
Diagnosis. Imantodes guane is distinguish from all congeners by the combination of the following characters: smooth dorsal scale rows 17/17/15; apical pits absent; infralabials 12–13; ventrals 227–236; subcaudals 147–148; loreal scale present; cloacal plate divided; dark brown temporal stripe between the lower edge of temporal scales and upper region of supralabials; dorsum of body light brown with dark brown transversal streaks, weakly evident in lateral view; hemipenis in situ extending to the level of 11th subcaudal and reaches the 10th subcaudal when everted; hemipenis with sulcus spermaticus laterally expanded inside capitulum.
Comparisons. Imantodes guane differs from I. lentiferus by having 17 dorsal scale rows anteriorly and at the midbody (vs. 15); from I. cenchoa , I. gemmistratus , and I. tenuissimus by having color pattern light brown with dark brown transversal streaks, weakly evident in lateral view (vs. well defined body blotches with shape of wide saddles); differs from I. cenchoa , I. gemmistratus , and I. inornatus by having 12–13 infralabials (vs. 8–11, 9 –10 and 8–11, respectively); differs from I. inornatus by having 227–236 ventrals and 147–148 subcaudals scales (vs. 196–218 ventrals and <140 subcaudals); differs from I. phantasma by the presence of a dark brown temporal stripe (vs. absence of a dark pigmentation on temporal region), dorsum of the head light brown with dark brown blotches (vs. dorsum of the head orangish brown mottled with grayish brown), and 147–148 subcaudals (vs.> 150 subcaudals); differs from I. chocoensis by presence of loreal (vs. absence of loreal), presence of dark brown temporal stripe (vs. absence of a dark brown temporal stripe), dorsal scale rows with posterior reduction to 15 rows (vs. dorsal scales without reduction), and cloacal plate divided (vs. cloacal plate entire). Refers to Table 1 View TABLE 1 for additional morphological characters differing Imantodes guane from remaining species in the genus.
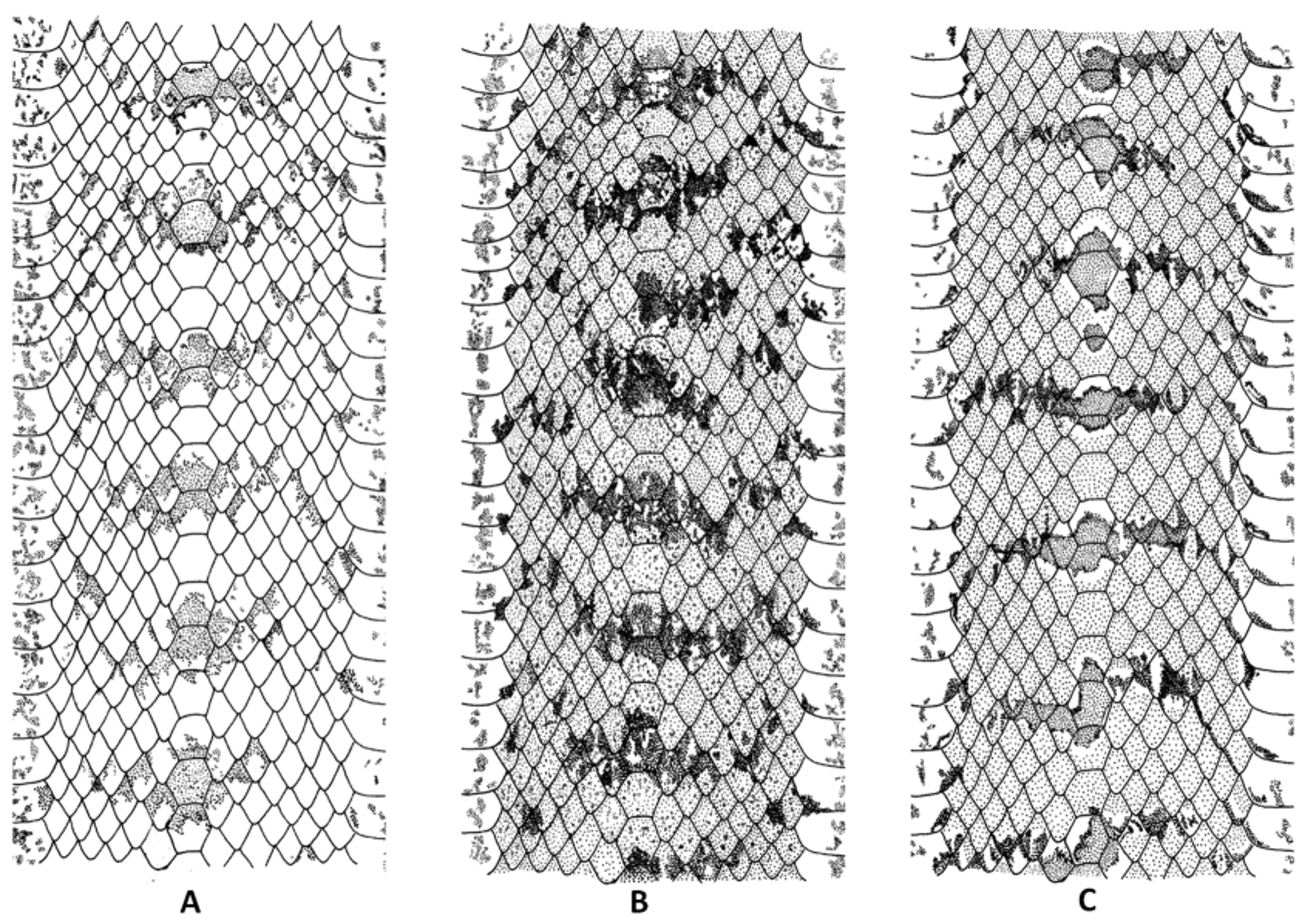
Description of the holotype ( Figs. 2–3 View FIGURE 2 View FIGURE 3 , 5 View FIGURE 5 A). Adult male; SVL 748 mm; CL 348 mm (46.5% SVL); head sharply distinct from the neck, head length 15.3 mm (2% SVL) and width 9.8 mm (64% head length); distance between the nostrils 3.3 mm (34% head width); snout short and truncated, 4.5 mm length (29.5% head length); eyes large, rounded, and protuberant; eyes diameter 4.2 mm (27% head length); canthus rostralis conspicuous; rostral scale trapezoidal, 2.1 mm wide, 3.1 mm high; internasal and prefrontal scales slightly wider than long; frontal pentagonal, anterior region 1.3 times wider than posterior; supraocular and parietal scales wider than long; nine supralabial scales with fourth to sixth contacting eye; six anterior supralabial shorter than seventh and eighth; ninth supralabial wider and similar in height to first six supralabials; nasal entire, contacting rostral, internasal, prefrontal, loreal, and first two supralabials; loreal 0.7 mm wide, 1.4 mm high, contacting nasal, prefrontal, preocular, second and third supralabials; preocular single; postoculars three on both sides; upper postocular taller than the two lower postoculars; ventral apex of lower postocular inserted between dorsal portion of sixth and seventh supralabials; temporals 2+2+2/2+2+3; symphysial triangular, 2.3 mm wide, 1.3 mm high; infralabials 12/ 12, first six contacting anterior chinshield, sixth and seventh contacting posterior chinshields; seventh infralabial wider and taller than other infralabials; first pair of infralabial scales in contact after symphysial, preventing contact between symphysial and anterior chinshields; anterior chinshield longer and wider than posterior; presence of tubercles on symphysial, first to tenth infralabial, chinshields, and gular scales; smooth dorsal scale rows 17/17/15, reduction at the level of 196th (right) and 199th (left) ventrals; conspicuous dorsal vertebral scale row, 2.3 times wider than adjacent paravertebral scales; preventral one, ventrals 227, subcaudals 147 (terminal spine absent). Maxillary with 18/19 prediastemal teeth and single postdiastemal tooth.
Dorsum of head light brown, except for grey frontal scale. Head dorsally with small brown spots at snout region; brown blotches covering the suture region of supraoculars, frontal, and parietals; parietals with two small brown blotches on the anterior region of each scale and two dark brown stripes posteriorly, extending to occipital region. Supralabials light brown, clearest at labial border; region around the orbit blackish; dark brown temporal stripe on the suture between inferior edge of temporals and superior region of seventh, eighth, and ninth supralabials. Ventral surface of head creamish yellow with brownish red spots on the anterior border of symphysial, first and second infralabials; remain infralabials, chinshields, gulars, and preventral immaculate creamish yellow. Background of body light brown with sixty-nine dark brown diffused dorsal blotches, almost restricted to vertebral region; lateral portion of body with dark brown transversal streaks, weakly evident in lateral view; belly creamish yellow scattered with small dark spots concentrated in the lateral edges of ventral scales, forming two irregular lateral stripes more conspicuous on the posterior region of the body; dorsal surface of tail with six evident dorsal blotches and posteriorly small irregular spots; ventral surface of tail creamish yellow with brown spots (dark base and light distal border of scales).
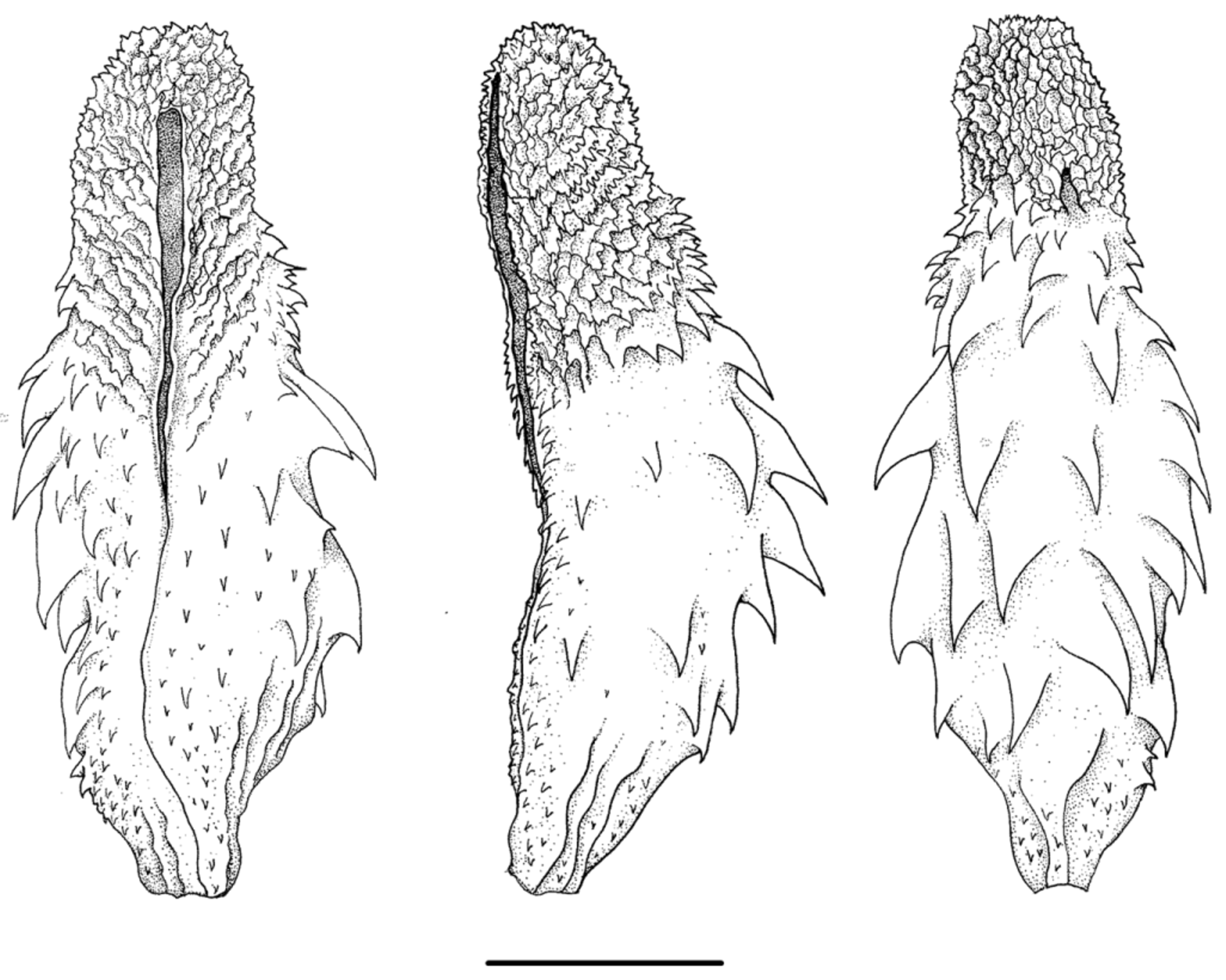
Hemipenis of the holotype ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 ). Right organ in situ extending to the level of 11th subcaudal ( 22 mm length) and reaches the 10th subcaudal when everted. Hemipenis unilobated, capitate, and calyculate; calyces in transverse rows, conspicuous in sulcate, lateral, and asulcate sides of capitulum; asulcate side with small naked pocket located at the base of capitulum; asulcate side with two rows of small spines separating capitulum from the hemipenial body; capitular portion of sulcus spermaticus laterally expanded; lateral expansion of sulcus spermaticus begin at the base and extending the mid-distal region of capitulum; sulcus spermaticus margins narrow and bordered with spinules from the base of hemipenial body until beginning of capitulum; hemipenial body with four rows of large spines disposed transversally and dispersed spinules concentrated on the basal region of organ.
Variation of the paratype. Two postocular scales on both sides; 2+2+3/2+2+3 temporal scales; infralabial scales 12/13; vertebral scale row 1.9 times wider than paravertebral scales; ventrals 236 and subcaudals 148. Dorsum of the head with dark brown blotches bordering internasals and two small rounded blotches at the suture of prefrontals; blotches covering region of suture among supraoculars and frontal connected to small circular blotches on the parietals; suture of parietals with dark brown blotch followed by two small blotches at posterior region of each scale; posterior region of parietals with two dark brown stripes transversally connected on the neck. Sides of head with dark brown spots on first to third supralabials; dark brown spots also covering postoculars and temporals. Dorsum of body with eighty dark brown blotches; tail with twenty-eight blotches.
Etymology. The specific epithet “ guane ” alludes to the name given to indigenous people that lived in the northeast region of the Colombia, where the new specimens were collected. This native Indians occupied the margin of the Fonce and Suárez Rivers, to the left margin Sogamoso river, in Cañon of Chicamocha ( Gómez 2005; Corona & Moreno 2010). The men of the tribe would have their skulls deformed from the birth to the first year of life by using splints in the frontal and posterior surface of the skull ( Correal & Flórez 1992; Corona & Moreno 2010). The resulting cranial shape denominated “tabular oblique deformation” (sensu Correal & Flórez 1992) reminded us the elongated head typical of the genus Imantodes .
Geographic distribution ( Fig. 7 View FIGURE 7 ). Imantodes guane is known from the municipalities of Charalá and Zapatoca in the eastern Cordillera of Colombia.
TABLE 1. Selected qualitative and quantitative morphological characters for the genus Imantodes. Numbers in parenthesis represent the number of specimens examined and additional data was obtained or augmented from the following literature: for I. chocoensis data from Torres-Carvajal et al. (2012) and Jaramillo-Martinéz et al. (2013); for I. cenchoa, I. inornatus, I. lentiferus, and I. phantasma data from Myers (1982); for I. gemmistratus data from Zweifel (1959) and Myers (1982); and for I. tenuissimus data from Cope (1866). The abbreviations are as following: GeA = Anterior chinshield; GeP = Posterior chinshield.
| Character Imantodes guane Loreal Present | I. chocoensis Absent | I. cenchoa Present | I. gemmistratus Present | I. inornatus I. lentiferus Present Present | I.phantasma Present | I.tenuissimus Present |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supralabials 8–9 (2) | 9 (11) | 7–10 (263) | 6–9 (8) | 7–9 (18) 7–9 (27) | 9 (2) | 8 (1) |
| Infralabials 12–13 (2) | 12–15 (11) | 8–11 (263) | 9–10 (8) | 8–11 (18) 10–12 (26) | 11–12 (2) | — |
| Infralabials 6 (2) contacting GeA Infralabials 6–7 (2) contacting GeP Temporal stripe Present | 6 (4) 6–8 (4) Absent | 4–6 (263) 5–7 (263) Absent | 4–5 (8) 5–6 (8) Absent | 5 (2) 5–6 (26) 5–6 (2) 6–7 (26) Absent Absent | 6 (2) 6–7 (2) Absent | — — — |
| Anterior dorsal 17 (2) scale rows Midbody dorsal 17 (2) scale rows Posterior Dorsal 15 (2) scale rows Ventrals 227–236 (2) | 17 (11) 17 (11) 17 (11) 232–251 (11) | 19 or 17 (263) 17 (263) 17 or 15 (263) 235–282 (263) | 19 or 17 (8) 17 (8) 17 (8) 217–253 (48) | 17 or 15 (18) 15 (27) 19 or 17 (18) 15 (27) 17, 15 or 13 (18) 15 (27) 196–218 (18) 222–240 (27) | 17 (2) 17 (2) 17 or 15 (2) 235–236 (2) | — 17 (1) — 250 (1) |
| Subcaudals 147–148 (2) | 140–161 (9) | 137–192 (223) | 109–170 (32) | 108–132 (16) 138–163 (22) | 156–161 (2) | 157 (1) |
| Cloacal plate Divided | Entire | Divided | Divided | Divided/entire Divided/entire | Entire/divided | Divided |
| Expanded area Present on the distal portion of the sulcus spermaticus Hemipenis 10 (1) length of everted organs in relation to the number of subcaudals | Absent 6 (2) | Absent 4–6 (18) | Absent 5 (2) | Absent Absent 6–8 (6) 6–7 (4) | Absent 6 (1) | — — |
| ICN |
Instituto de Ciencias Naturales, Museo de Historia Natural |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.