Homogryllacris foveolis, Zhang & Pang & Bian, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.5353.1.3 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:8F93674B-7ABB-4C9A-B1A2-0EB1DE9426F3 |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10563525 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/CB551A2F-B46B-3D5F-FF34-FC10FD58FF59 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Homogryllacris foveolis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Homogryllacris foveolis View in CoL sp. nov.
ufiñșŝ
Figure 2 View FIGURE 2
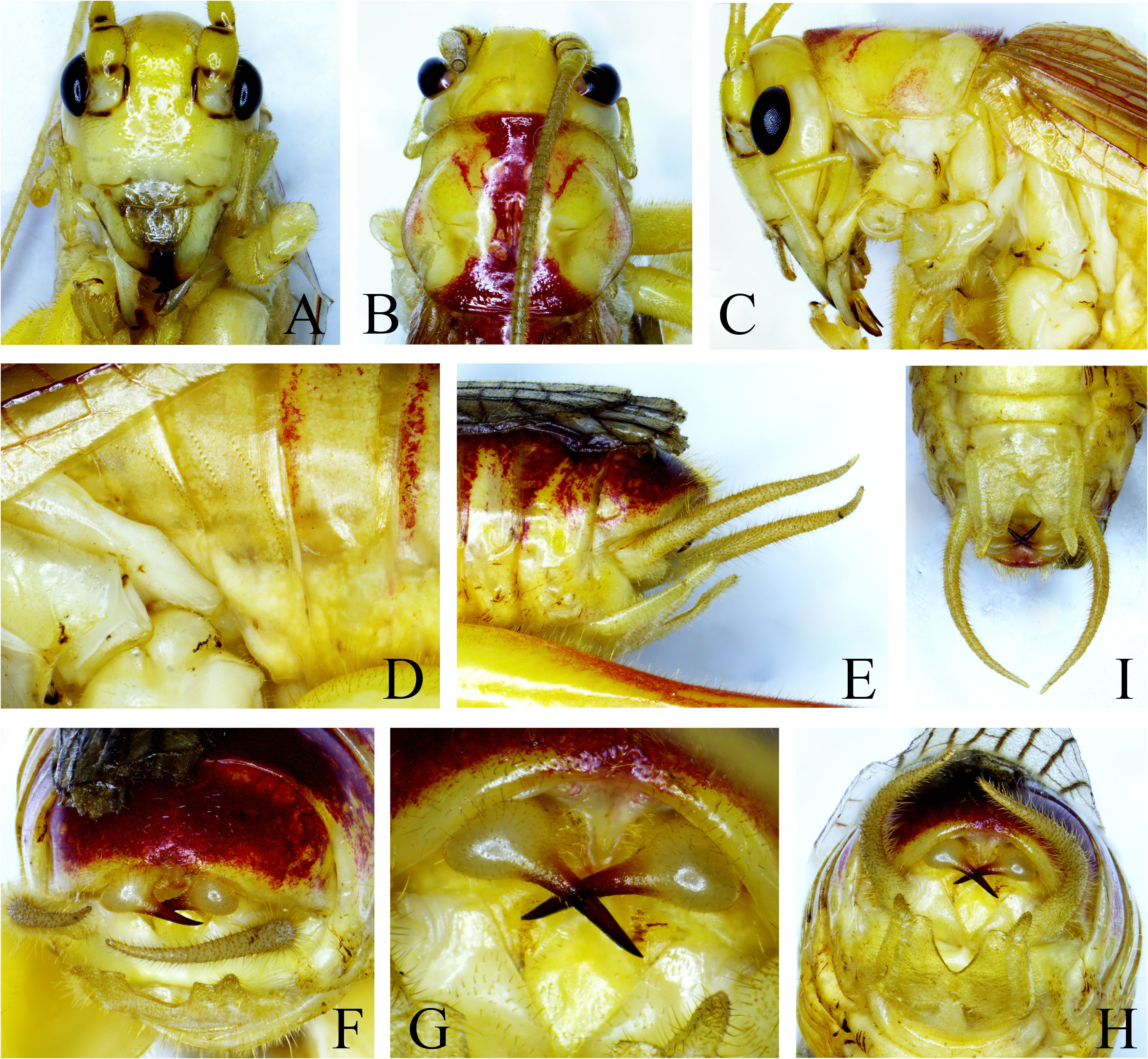
Description. Male. Body medium. Face with impressed dots; fastigium verticis about 2 times as wide as scape; fastigium frontis separated from fastigium verticis by a very fine suture ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ). Ocelli distinct, median ocellus slightly larger than lateral ocelli ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ).
Anterior margin of pronotum projected in middle, posterior margin nearly straight ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ); lateral lobes longer than high, anterior angle widely rounded, posterior angle rounded angular, humeral sinus indistinct ( Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ).
Wings slightly surpassing the hind femora. Fore and middle femora unarmed on ventral surfaces; hind femora with 7–10 internal and 4–7 external spines. Fore and middle tibiae with 4 pairs of spurs and 1 pair of apical spurs on ventral surfaces; middle tibiae with 1 internal apical spine on dorsal surface. Hind tibiae with 6 pairs of dorsal spines and 1 pair of apical spurs on dorsal surface, ventral surface with 1 pair of subapical spurs and 2 pairs of apical spurs.
Abdominal tergites two and three each with two rows of stridulatory pegs ( Fig. 2D View FIGURE 2 ). Eighth and ninth abdominal tergites prolonged and down-curved. Tenth abdominal tergite short with 1 pair of hooks, its basal half stout, apical half right-angularly incurved and terminating into a sharp spine, its apex pointing inward ( Fig. 2F–H View FIGURE 2 ). Subgenital plate longer than wide, lateral margins subparallel, posterior margin widely concave in middle ( Fig. 2I View FIGURE 2 ). Styli slender located on both sides of the subapical area of subgenital plate ( Fig. 2I View FIGURE 2 ).
Female. Unknown.
Coloration. Body yellow with purplish red spots. Margins of antennal cavities black; bases and apices of scape and bases of pedicel with black spots ( Fig. 2A View FIGURE 2 ). Pronotum with purplish red median band which widened at anterior and posterior margins ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ). All legs with purplish red spots. Tegmina semitransparent yellow; veins purplish red. Dorsal surface of abdomen purplish red. Apical half of processes of male tenth abdominal tergite black ( Fig. 2F View FIGURE 2 ).
Measurements (mm). Male: BL 23.44–24.16, PL 5.41–5.93, TL 17.99–19.19, HFL 12.96–13.52.
Material examined. Holotype: male, Kengdi, Shouning , Fujian, July 17, 2023, coll. by Fanduo Cai . Paratype: 1 male, the other information as holotype.
Discussion. The new species differs from Homogryllacris rufovaria Liu, 2007 (Chinese name: ÷äñșŝ) by the spines of male tenth abdominal tergite directing inwards ( Fig. 2G View FIGURE 2 ) instead of directing interno-ventrad ( Fig. 3G View FIGURE 3 ); posterior margin of male subgenital plate with shallow concavity in middle ( Fig. 2I View FIGURE 2 ), while the latter species has deeper concavity ( Fig. 3I View FIGURE 3 ).
Etymology. The name of the new species is derived from Latin fove referring to the posterior margin of male subgenital plate shallowly concave in the middle.
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.